numpy.linspace#
- numpy.linspace(start,stop,num=50,endpoint=True,retstep=False,dtype=None,axis=0,*,device=None)[source]#
Return evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval.
Returnsnum evenly spaced samples, calculated over theinterval [start,stop].
The endpoint of the interval can optionally be excluded.
Changed in version 1.20.0:Values are rounded towards
-infinstead of0when anintegerdtypeis specified. The old behavior canstill be obtained withnp.linspace(start,stop,num).astype(int)- Parameters:
- startarray_like
The starting value of the sequence.
- stoparray_like
The end value of the sequence, unlessendpoint is set to False.In that case, the sequence consists of all but the last of
num+1evenly spaced samples, so thatstop is excluded. Note that the stepsize changes whenendpoint is False.- numint, optional
Number of samples to generate. Default is 50. Must be non-negative.
- endpointbool, optional
If True,stop is the last sample. Otherwise, it is not included.Default is True.
- retstepbool, optional
If True, return (samples,step), wherestep is the spacingbetween samples.
- dtypedtype, optional
The type of the output array. If
dtypeis not given, the data typeis inferred fromstart andstop. The inferred dtype will never bean integer;float is chosen even if the arguments would produce anarray of integers.- axisint, optional
The axis in the result to store the samples. Relevant only if startor stop are array-like. By default (0), the samples will be along anew axis inserted at the beginning. Use -1 to get an axis at the end.
- devicestr, optional
The device on which to place the created array. Default: None.For Array-API interoperability only, so must be
"cpu"if passed.New in version 2.0.0.
- Returns:
- samplesndarray
There arenum equally spaced samples in the closed interval
[start,stop]or the half-open interval[start,stop)(depending on whetherendpoint is True or False).- stepfloat, optional
Only returned ifretstep is True
Size of spacing between samples.
See also
arangeSimilar to
linspace, but uses a step size (instead of the number of samples).geomspaceSimilar to
linspace, but with numbers spaced evenly on a log scale (a geometric progression).logspaceSimilar to
geomspace, but with the end points specified as logarithms.- How to create arrays with regularly-spaced values
Examples
>>>importnumpyasnp>>>np.linspace(2.0,3.0,num=5)array([2. , 2.25, 2.5 , 2.75, 3. ])>>>np.linspace(2.0,3.0,num=5,endpoint=False)array([2. , 2.2, 2.4, 2.6, 2.8])>>>np.linspace(2.0,3.0,num=5,retstep=True)(array([2. , 2.25, 2.5 , 2.75, 3. ]), 0.25)
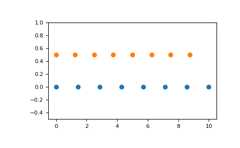
Graphical illustration:
>>>importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt>>>N=8>>>y=np.zeros(N)>>>x1=np.linspace(0,10,N,endpoint=True)>>>x2=np.linspace(0,10,N,endpoint=False)>>>plt.plot(x1,y,'o')[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>]>>>plt.plot(x2,y+0.5,'o')[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>]>>>plt.ylim([-0.5,1])(-0.5, 1)>>>plt.show()