numpy.bartlett#
- numpy.bartlett(M)[source]#
Return the Bartlett window.
The Bartlett window is very similar to a triangular window, exceptthat the end points are at zero. It is often used in signalprocessing for tapering a signal, without generating too muchripple in the frequency domain.
- Parameters:
- Mint
Number of points in the output window. If zero or less, anempty array is returned.
- Returns:
- outarray
The triangular window, with the maximum value normalized to one(the value one appears only if the number of samples is odd), withthe first and last samples equal to zero.
Notes
The Bartlett window is defined as
\[w(n) = \frac{2}{M-1} \left(\frac{M-1}{2} - \left|n - \frac{M-1}{2}\right|\right)\]Most references to the Bartlett window come from the signal processingliterature, where it is used as one of many windowing functions forsmoothing values. Note that convolution with this window produces linearinterpolation. It is also known as an apodization (which means “removingthe foot”, i.e. smoothing discontinuities at the beginning and end of thesampled signal) or tapering function. The Fourier transform of theBartlett window is the product of two sinc functions. Note the excellentdiscussion in Kanasewich[2].
References
[1]M.S. Bartlett, “Periodogram Analysis and Continuous Spectra”,Biometrika 37, 1-16, 1950.
[2]E.R. Kanasewich, “Time Sequence Analysis in Geophysics”,The University of Alberta Press, 1975, pp. 109-110.
[3]A.V. Oppenheim and R.W. Schafer, “Discrete-Time SignalProcessing”, Prentice-Hall, 1999, pp. 468-471.
[4]Wikipedia, “Window function”,https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function
[5]W.H. Press, B.P. Flannery, S.A. Teukolsky, and W.T. Vetterling,“Numerical Recipes”, Cambridge University Press, 1986, page 429.
Examples
>>>importnumpyasnp>>>importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt>>>np.bartlett(12)array([ 0. , 0.18181818, 0.36363636, 0.54545455, 0.72727273, # may vary 0.90909091, 0.90909091, 0.72727273, 0.54545455, 0.36363636, 0.18181818, 0. ])
Plot the window and its frequency response (requires SciPy and matplotlib).
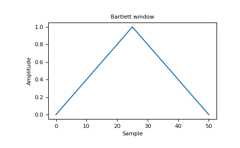
importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltfromnumpy.fftimportfft,fftshiftwindow=np.bartlett(51)plt.plot(window)plt.title("Bartlett window")plt.ylabel("Amplitude")plt.xlabel("Sample")plt.show()
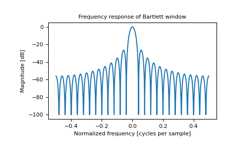
plt.figure()A=fft(window,2048)/25.5mag=np.abs(fftshift(A))freq=np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,len(A))withnp.errstate(divide='ignore',invalid='ignore'):response=20*np.log10(mag)response=np.clip(response,-100,100)plt.plot(freq,response)plt.title("Frequency response of Bartlett window")plt.ylabel("Magnitude [dB]")plt.xlabel("Normalized frequency [cycles per sample]")plt.axis('tight')plt.show()