Esophageal candidiasis
| Esophageal candidiasis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Candidal esophagitis, monilial esophagitis | |
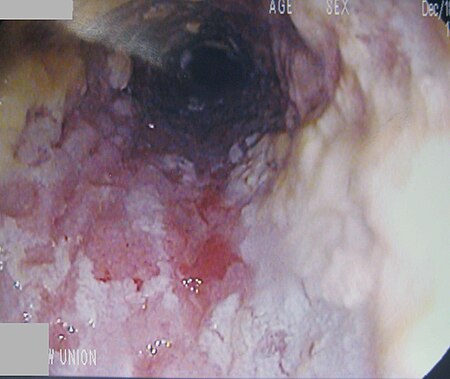 | |
| A severe case of esophageal candidiasis | |
 | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Esophageal candidiasis is anopportunistic infection of theesophagus byCandida albicans.
The disease usually occurs in people inimmunocompromised states, including post-chemotherapy and inAIDS. However, it can also occur in those with no predisposing risk factors, and is more likely to be asymptomatic in this case.[1]
Signs and symptoms
People with esophageal candidiasis typically present withdifficult orpainful swallowing. Longstanding esophageal candidiasis can result inweight loss. There is often concomitantthrush in the mouth.
Some patients present with esophageal candidiasis as a first presentation of systemiccandidiasis.
Risk factor
The risk factors of Esophageal candidiasis which is an opportunistic infection in immunosuppressed individuals are:[2]
- HIV positive and AIDS
- Chemotherapy
- Antibiotic therapy
- Topical inhaledcorticosteroids
Diagnosis
In most cases, the diagnosis is established based on response to therapy. Patients in whom esophageal candidiasis is suspected should receive a brief course of antifungal therapy withfluconazole. If the infection resolves after treatment withfluconazole, then the diagnosis of esophageal candidiasis is made and no further investigation is needed. However, if the infection persists or if there are other factors involved which may warrant further investigation, then patient will undergo anesophagogastroduodenoscopy if it is safe to do so. Endoscopy often reveals classic diffuse raised plaques that characteristically can be removed from themucosa by the endoscope. Brushing orbiopsy of the plaques showsyeast andpseudohyphae byhistology that are characteristic ofCandida species.
Esophageal candidiasis stained by periodic acid-Schiff procedure
Esophageal candidiasis stained by periodic acid-Schiff procedure
Treatment

The first-line treatment isfluconazole, 200 mg on the first day, followed by daily dosing of 100 mg. for at least 21 days total. Treatment should continue for 14 days after relief of symptoms.Other therapy options include:
- Nystatin is an effective treatment for mild esophageal candidiasis.[3] It can be used as (swish, do not swallow) treatment for oral candidiasis that occurs with the use of asthma pumps.
- Suspected cases of esophageal candidiasis should be treated with short-term fluconazole antifungal therapy. When symptoms recover after therapy, we can diagnosis esophageal candidiasis and do not need more investigations.[4] Oral fluconazole is most commonly used medication for esophageal candididasis. For patients who cannot tolerate oral medication, IV fluconazole can be used alternatively.[4]
- Other oraltriazoles, such asitraconazole andvoriconazole can be other options.[4]
- Amphotericin B can be used in nonresponsive cases, but should not be used routinely due to its serious side effects.[4]
- Posaconazole is effective in severe and refractory esophageal candidiasis.[4]
References
- ↑Mimidis, K; Papadopoulos, V; Margaritis, V; Thomopoulos, K; Gatopoulou, A; Nikolopoulou, V; Kartalis, G (February 2005). "Predisposing factors and clinical symptoms in HIV-negative patients with Candida oesophagitis: are they always present?".International Journal of Clinical Practice.59 (2): 210–3.doi:10.1111/j.1742-1241.2004.00249.x.PMID 15854199.
- ↑Robertson, Kyle D.; Nagra, Navroop; Mehta, Dhruv (2022). "Esophageal Candidiasis".StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.Archived from the original on 28 November 2022. Retrieved3 January 2023.
- ↑ Gary W. Falk, David A. Katzka, in Goldman's Cecil Medicine (Twenty Fourth Edition), 2012,Diseases of the Esophagus
- ↑4.04.14.24.34.4Mohamed, Abdimajid Ahmed; Lu, Xin-liang; Mounmin, Faycal Awaleh (2019)."Diagnosis and Treatment of Esophageal Candidiasis: Current Updates".Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2019.doi:10.1155/2019/3585136.PMID 31772927.Archived from the original on 2023-01-03. Retrieved2023-01-03.
External links
| Classification |
|---|

