Note
Go to the endto download the full example code.
Boxplots#
Visualizing boxplots with matplotlib.
The following examples show off how to visualize boxplots withMatplotlib. There are many options to control their appearance andthe statistics that they use to summarize the data.
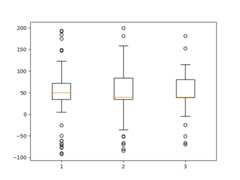
importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportnumpyasnpfrommatplotlib.patchesimportPolygon# Fixing random state for reproducibilitynp.random.seed(19680801)# fake up some dataspread=np.random.rand(50)*100center=np.ones(25)*50flier_high=np.random.rand(10)*100+100flier_low=np.random.rand(10)*-100data=np.concatenate((spread,center,flier_high,flier_low))fig,axs=plt.subplots(2,3)# basic plotaxs[0,0].boxplot(data)axs[0,0].set_title('basic plot')# notched plotaxs[0,1].boxplot(data,notch=True)axs[0,1].set_title('notched plot')# change outlier point symbolsaxs[0,2].boxplot(data,sym='gD')axs[0,2].set_title('change outlier\npoint symbols')# don't show outlier pointsaxs[1,0].boxplot(data,sym='')axs[1,0].set_title("don't show\noutlier points")# horizontal boxesaxs[1,1].boxplot(data,sym='rs',orientation='horizontal')axs[1,1].set_title('horizontal boxes')# change whisker lengthaxs[1,2].boxplot(data,sym='rs',orientation='horizontal',whis=0.75)axs[1,2].set_title('change whisker length')fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.08,right=0.98,bottom=0.05,top=0.9,hspace=0.4,wspace=0.3)# fake up some more dataspread=np.random.rand(50)*100center=np.ones(25)*40flier_high=np.random.rand(10)*100+100flier_low=np.random.rand(10)*-100d2=np.concatenate((spread,center,flier_high,flier_low))# Making a 2-D array only works if all the columns are the# same length. If they are not, then use a list instead.# This is actually more efficient because boxplot converts# a 2-D array into a list of vectors internally anyway.data=[data,d2,d2[::2]]# Multiple box plots on one Axesfig,ax=plt.subplots()ax.boxplot(data)plt.show()
Below we'll generate data from five different probability distributions,each with different characteristics. We want to play with how an IIDbootstrap resample of the data preserves the distributionalproperties of the original sample, and a boxplot is one visual toolto make this assessment
random_dists=['Normal(1, 1)','Lognormal(1, 1)','Exp(1)','Gumbel(6, 4)','Triangular(2, 9, 11)']N=500norm=np.random.normal(1,1,N)logn=np.random.lognormal(1,1,N)expo=np.random.exponential(1,N)gumb=np.random.gumbel(6,4,N)tria=np.random.triangular(2,9,11,N)# Generate some random indices that we'll use to resample the original data# arrays. For code brevity, just use the same random indices for each arraybootstrap_indices=np.random.randint(0,N,N)data=[norm,norm[bootstrap_indices],logn,logn[bootstrap_indices],expo,expo[bootstrap_indices],gumb,gumb[bootstrap_indices],tria,tria[bootstrap_indices],]fig,ax1=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,6))fig.canvas.manager.set_window_title('A Boxplot Example')fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.075,right=0.95,top=0.9,bottom=0.25)bp=ax1.boxplot(data,notch=False,sym='+',orientation='vertical',whis=1.5)plt.setp(bp['boxes'],color='black')plt.setp(bp['whiskers'],color='black')plt.setp(bp['fliers'],color='red',marker='+')# Add a horizontal grid to the plot, but make it very light in color# so we can use it for reading data values but not be distractingax1.yaxis.grid(True,linestyle='-',which='major',color='lightgrey',alpha=0.5)ax1.set(axisbelow=True,# Hide the grid behind plot objectstitle='Comparison of IID Bootstrap Resampling Across Five Distributions',xlabel='Distribution',ylabel='Value',)# Now fill the boxes with desired colorsbox_colors=['darkkhaki','royalblue']num_boxes=len(data)medians=np.empty(num_boxes)foriinrange(num_boxes):box=bp['boxes'][i]box_x=[]box_y=[]forjinrange(5):box_x.append(box.get_xdata()[j])box_y.append(box.get_ydata()[j])box_coords=np.column_stack([box_x,box_y])# Alternate between Dark Khaki and Royal Blueax1.add_patch(Polygon(box_coords,facecolor=box_colors[i%2]))# Now draw the median lines back over what we just filled inmed=bp['medians'][i]median_x=[]median_y=[]forjinrange(2):median_x.append(med.get_xdata()[j])median_y.append(med.get_ydata()[j])ax1.plot(median_x,median_y,'k')medians[i]=median_y[0]# Finally, overplot the sample averages, with horizontal alignment# in the center of each boxax1.plot(np.average(med.get_xdata()),np.average(data[i]),color='w',marker='*',markeredgecolor='k')# Set the axes ranges and axes labelsax1.set_xlim(0.5,num_boxes+0.5)top=40bottom=-5ax1.set_ylim(bottom,top)ax1.set_xticklabels(np.repeat(random_dists,2),rotation=45,fontsize=8)# Due to the Y-axis scale being different across samples, it can be# hard to compare differences in medians across the samples. Add upper# X-axis tick labels with the sample medians to aid in comparison# (just use two decimal places of precision)pos=np.arange(num_boxes)+1upper_labels=[str(round(s,2))forsinmedians]weights=['bold','semibold']fortick,labelinzip(range(num_boxes),ax1.get_xticklabels()):k=tick%2ax1.text(pos[tick],.95,upper_labels[tick],transform=ax1.get_xaxis_transform(),horizontalalignment='center',size='x-small',weight=weights[k],color=box_colors[k])# Finally, add a basic legendfig.text(0.80,0.08,f'{N} Random Numbers',backgroundcolor=box_colors[0],color='black',weight='roman',size='x-small')fig.text(0.80,0.045,'IID Bootstrap Resample',backgroundcolor=box_colors[1],color='white',weight='roman',size='x-small')fig.text(0.80,0.015,'*',color='white',backgroundcolor='silver',weight='roman',size='medium')fig.text(0.815,0.013,' Average Value',color='black',weight='roman',size='x-small')plt.show()

Here we write a custom function to bootstrap confidence intervals.We can then use the boxplot along with this function to show these intervals.
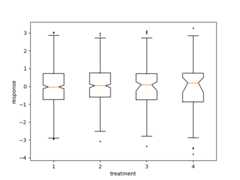
deffake_bootstrapper(n):""" This is just a placeholder for the user's method of bootstrapping the median and its confidence intervals. Returns an arbitrary median and confidence interval packed into a tuple. """ifn==1:med=0.1ci=(-0.25,0.25)else:med=0.2ci=(-0.35,0.50)returnmed,ciinc=0.1e1=np.random.normal(0,1,size=500)e2=np.random.normal(0,1,size=500)e3=np.random.normal(0,1+inc,size=500)e4=np.random.normal(0,1+2*inc,size=500)treatments=[e1,e2,e3,e4]med1,ci1=fake_bootstrapper(1)med2,ci2=fake_bootstrapper(2)medians=[None,None,med1,med2]conf_intervals=[None,None,ci1,ci2]fig,ax=plt.subplots()pos=np.arange(len(treatments))+1bp=ax.boxplot(treatments,sym='k+',positions=pos,notch=True,bootstrap=5000,usermedians=medians,conf_intervals=conf_intervals)ax.set_xlabel('treatment')ax.set_ylabel('response')plt.setp(bp['whiskers'],color='k',linestyle='-')plt.setp(bp['fliers'],markersize=3.0)plt.show()
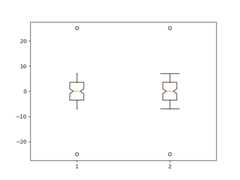
Here we customize the widths of the caps .
x=np.linspace(-7,7,140)x=np.hstack([-25,x,25])fig,ax=plt.subplots()ax.boxplot([x,x],notch=True,capwidths=[0.01,0.2])plt.show()
Tags:domain: statisticsplot-type: boxplot
References
The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shownin this example:
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.523 seconds)