Note
Go to the endto download the full example code.
Asinh scale#
Illustration of theasinh axis scaling,which uses the transformation
For coordinate values close to zero (i.e. much smaller thanthe "linear width"\(a_0\)), this leaves values essentially unchanged:
but for larger values (i.e.\(|a| \gg a_0\), this is asymptotically
As with thesymlog scaling,this allows one to plot quantitiesthat cover a very wide dynamic range that includes both positiveand negative values. However,symlog involves a transformationthat has discontinuities in its gradient because it is builtfromseparate linear and logarithmic transformations.Theasinh scaling uses a transformation that is smoothfor all (finite) values, which is both mathematically cleanerand reduces visual artifacts associated with an abrupttransition between linear and logarithmic regions of the plot.
Note
scale.AsinhScale is experimental, and the API may change.
SeeAsinhScale,SymmetricalLogScale.
importmatplotlib.pyplotaspltimportnumpyasnp# Prepare sample values for variations on y=x graph:x=np.linspace(-3,6,500)
Compare "symlog" and "asinh" behaviour on sample y=x graph,where there is a discontinuous gradient in "symlog" near y=2:
fig1=plt.figure()ax0,ax1=fig1.subplots(1,2,sharex=True)ax0.plot(x,x)ax0.set_yscale('symlog')ax0.grid()ax0.set_title('symlog')ax1.plot(x,x)ax1.set_yscale('asinh')ax1.grid()ax1.set_title('asinh')

Compare "asinh" graphs with different scale parameter "linear_width":
fig2=plt.figure(layout='constrained')axs=fig2.subplots(1,3,sharex=True)forax,(a0,base)inzip(axs,((0.2,2),(1.0,0),(5.0,10))):ax.set_title(f'linear_width={a0:.3g}')ax.plot(x,x,label='y=x')ax.plot(x,10*x,label='y=10x')ax.plot(x,100*x,label='y=100x')ax.set_yscale('asinh',linear_width=a0,base=base)ax.grid()ax.legend(loc='best',fontsize='small')

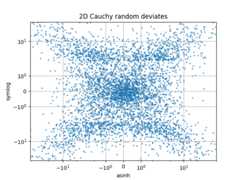
Compare "symlog" and "asinh" scalingson 2D Cauchy-distributed random numbers,where one may be able to see more subtle artifacts near y=2due to the gradient-discontinuity in "symlog":
fig3=plt.figure()ax=fig3.subplots(1,1)r=3*np.tan(np.random.uniform(-np.pi/2.02,np.pi/2.02,size=(5000,)))th=np.random.uniform(0,2*np.pi,size=r.shape)ax.scatter(r*np.cos(th),r*np.sin(th),s=4,alpha=0.5)ax.set_xscale('asinh')ax.set_yscale('symlog')ax.set_xlabel('asinh')ax.set_ylabel('symlog')ax.set_title('2D Cauchy random deviates')ax.set_xlim(-50,50)ax.set_ylim(-50,50)ax.grid()plt.show()
References
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.597 seconds)