Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can trysigning in orchanging directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can trychanging directories.
Get started with Storage Explorer
In this article
Overview
Microsoft Azure Storage Explorer is a standalone app that makes it easy to work with Azure Storage data on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
In this article, we demonstrate several ways of connecting to and managing your Azure storage accounts.
Prerequisites
The following versions of Windows support the latest versions of Storage Explorer:
- Windows 11
- Windows 10
Other requirements include:
- Your Windows installation must support 64-bit applications (starting with Storage Explorer 1.30.0).
- You must have a .NET 8 runtime installed (starting with Storage Explorer 1.34.0) which matches the architecture of your Storage Explorer install. The Storage Explorer installer installs a .NET 8 runtime if you don't already have one installed, but it might not be the latest version available. It is your responsibility to keep your .NET install up to date. You can download the latest .NET 8 runtime fromhere.
Download and install
To download and install Storage Explorer, seeAzure Storage Explorer.
Connect to a storage account or service
Storage Explorer provides several ways to connect to Azure resources:
- Sign in to Azure to access your subscriptions and their resources
- Attach to an individual Azure Storage resource
Sign in to Azure
Note
To fully access resources after you sign in, Storage Explorer requires both management (Azure Resource Manager) and data layer permissions. This means that you need Microsoft Entra permissions to access your storage account, the containers in the account, and the data in the containers. If you have permissions only at the data layer, consider choosing theSign in using Microsoft Entra ID option when attaching to a resource. For more information about the specific permissions Storage Explorer requires, see theAzure Storage Explorer troubleshooting guide.
In Storage Explorer, selectView >Account Management or select theManage Accounts button.

ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT now displays all the Azure accounts you're signed in to. To connect to another account, selectAdd an account....
TheConnect to Azure Storage dialog opens. In theSelect Resource panel, selectSubscription.

In theSelect Azure Environment panel, select an Azure environment to sign in to. You can sign in to global Azure, a national cloud or an Azure Stack instance. Then selectNext.

Tip
For more information about Azure Stack, seeConnect Storage Explorer to an Azure Stack subscription or storage account.
Storage Explorer opens a webpage for you to sign in.
After you successfully sign in with an Azure account, the account and the Azure subscriptions associated with that account appear underACCOUNT MANAGEMENT. Select the Azure subscriptions that you want to work with, and then selectApply.

EXPLORER displays the storage accounts associated with the selected Azure subscriptions.

Attach to an individual resource
Storage Explorer lets you connect to individual resources, such as an Azure Data Lake Storage container, using various authentication methods. Some authentication methods are only supported for certain resource types.
| Resource type | Microsoft Entra ID | Account Name and Key | Shared Access Signature (SAS) | Public (anonymous) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage accounts | Yes | Yes | Yes (connection string or URL) | No |
| Blob containers | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| Data Lake Storage containers | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| Data Lake Storage directories | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | Yes |
| File shares | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | No |
| Queues | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | No |
| Tables | Yes | No | Yes (URL) | No |
Storage Explorer can also connect to alocal storage emulator using the emulator's configured ports.
To connect to an individual resource, select theConnect button in the left-hand toolbar. Then follow the instructions for the resource type you want to connect to.

When a connection to a storage account is successfully added, a new tree node appears underLocal & Attached >Storage Accounts.
For other resource types, a new node is added underLocal & Attached >Storage Accounts >(Attached Containers). The node appears under a group node matching its type. For example, a new connection to an Azure Data Lake Storage container appears underBlob Containers.
If Storage Explorer couldn't add your connection, or if you can't access your data after successfully adding the connection, see theAzure Storage Explorer troubleshooting guide.
The following sections describe the different authentication methods you can use to connect to individual resources.
Microsoft Entra ID
Storage Explorer can use your Azure account to connect to the following resource types:
- Blob containers
- Azure Data Lake Storage containers
- Azure Data Lake Storage directories
- Queues
Microsoft Entra ID is the preferred option if you have data layer access to your resource but no management layer access.
- Sign in to at least one Azure account using thesign-in steps.
- In theSelect Resource panel of theConnect to Azure Storage dialog, selectBlob container,ADLS Gen2 container, orQueue.
- SelectSign in using Microsoft Entra ID and selectNext.
- Select an Azure account and tenant. The account and tenant must have access to the Storage resource you want to attach to. SelectNext.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the URL of the resource. SelectNext.
- Review your connection information in theSummary panel. If the connection information is correct, selectConnect.
Account name and key
Storage Explorer can connect to a storage account using the storage account's name and key.
You can find your account keys in theAzure portal. Open your storage account page and selectSettings >Access keys.
- In theSelect Resource panel of theConnect to Azure Storage dialog, selectStorage account.
- SelectAccount name and key and selectNext.
- Enter a display name for your connection, the name of the account, and one of the account keys. Select the appropriate Azure environment. SelectNext.
- Review your connection information in theSummary panel. If the connection information is correct, selectConnect.
Shared access signature (SAS) connection string
Storage Explorer can connect to a storage account using a connection string with a Shared Access Signature (SAS). A SAS connection string looks like this:
SharedAccessSignature=sv=2020-04-08&ss=btqf&srt=sco&st=2021-03-02T00%3A22%3A19Z&se=2020-03-03T00%3A22%3A19Z&sp=rl&sig=fFFpX%2F5tzqmmFFaL0wRffHlhfFFLn6zJuylT6yhOo%2FY%3F;BlobEndpoint=https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/;FileEndpoint=https://contoso.file.core.windows.net/;QueueEndpoint=https://contoso.queue.core.windows.net/;TableEndpoint=https://contoso.table.core.windows.net/;- In theSelect Resource panel of theConnect to Azure Storage dialog, selectStorage account.
- SelectShared access signature (SAS) and selectNext.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the SAS connection string for the storage account. SelectNext.
- Review your connection information in theSummary panel. If the connection information is correct, selectConnect.
Shared access signature (SAS) URL
Storage Explorer can connect to the following resource types using a SAS URI:
- Blob container
- Azure Data Lake Storage container or directory
- File share
- Queue
- Table
A SAS URI looks like this:
https://contoso.blob.core.windows.net/container01?sv=2020-04-08&st=2021-03-02T00%3A30%3A33Z&se=2020-03-03T00%3A30%3A33Z&sr=c&sp=rl&sig=z9VFdWffrV6FXU51T8b8HVfipZPOpYOFLXuQw6wfkFY%3F- In theSelect Resource panel of theConnect to Azure Storage dialog, select the resource you want to connect to.
- SelectShared access signature (SAS) and selectNext.
- Enter a display name for your connection and the SAS URI for the resource. SelectNext.
- Review your connection information in theSummary panel. If the connection information is correct, selectConnect.
Local storage emulator
Storage Explorer can connect to an Azure Storage emulator. Currently, there are two supported emulators:
- Azure Storage Emulator (Windows only)
- Azurite (Windows, macOS, or Linux)
If your emulator is listening on the default ports, you can use theLocal & Attached >Storage Accounts >Emulator - Default Ports node to access your emulator.
If you want to use a different name for your connection, or if your emulator isn't running on the default ports:
Start your emulator.
Important
Storage Explorer doesn't automatically start your emulator. You must start it manually.
In theSelect Resource panel of theConnect to Azure Storage dialog, selectLocal storage emulator.
Enter a display name for your connection and the port number for each emulated service you want to use. If you don't want to use to a service, leave the corresponding port blank. SelectNext.
Review your connection information in theSummary panel. If the connection information is correct, selectConnect.
Generate a shared access signature in Storage Explorer
Account level shared access signature
Right-click the storage account you want share, and then selectGet Shared Access Signature.

InShared Access Signature, specify the time frame and permissions you want for the account, and then selectCreate.
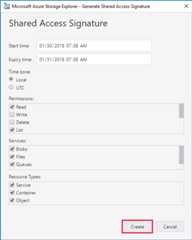
Copy either theConnection string or the rawQuery string to your clipboard.
Service level shared access signature
You can get a shared access signature at the service level. For more information, seeGet the SAS for a blob container.
Search for storage accounts
To find a storage resource, you can search in theEXPLORER pane.
As you enter text in the search box, Storage Explorer displays all resources that match the search value you entered up to that point. This example shows a search forendpoints:

Note
To speed up your search, useAccount Management to deselect any subscriptions that don't contain the item you're searching for. You can also right-click a node and selectSearch From Here to start searching from a specific node.
Next steps
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Need help with this topic?
Want to try using Ask Learn to clarify or guide you through this topic?
Additional resources
- Last updated on
2025-04-14
In this article
Was this page helpful?
Want to try using Ask Learn to clarify or guide you through this topic?
[8]ページ先頭