Adafruit Trinket M0
CircuitPython or Arduino IDE on this tiny little microcontroller board
- Overview
- Guided Tour
- Pinouts
- Windows Driver Installation
- What is CircuitPython?
- CircuitPython
- CircuitPython Essentials
- CircuitPython Pins and Modules
- CircuitPython Built-Ins
- CircuitPython Digital In & Out
- CircuitPython Analog In
- CircuitPython Analog Out
- CircuitPython PWM
- CircuitPython Servo
- CircuitPython Cap Touch
- CircuitPython Internal RGB LED
- CircuitPython NeoPixel
- CircuitPython DotStar
- CircuitPython UART Serial
- CircuitPython I2C
- CircuitPython HID Keyboard and Mouse
- CircuitPython CPU Temp
- CircuitPython Storage
- CircuitPython Expectations
- MakeCode
- Arduino IDE Setup
- UF2 Bootloader Details
- Downloads
CircuitPython Servo
In order to use servos, we take advantage ofpwmio. Now, in theory, you could just use the rawpwmio calls to set the frequency to 50 Hz and then set the pulse widths. But we would rather make it a little more elegant and easy!
So, instead we will useadafruit_motor which manages servos for you quite nicely!adafruit_motor is a library so be sure tograb it from the library bundle if you have not yet! If you need help installing the library, check out theCircuitPython Libraries page.
Servos come in two types:
- Astandard hobby servo - the horn moves 180 degrees (90 degrees in each direction from zero degrees).
- Acontinuous servo - the horn moves in full rotation like a DC motor. Instead of an angle specified, you set a throttle value with 1.0 being full forward, 0.5 being half forward, 0 being stopped, and -1 being full reverse, with other values between.
The connections for a servo are the same for standard servos and continuous rotation servos.
Connect the servo'sbrownor blackground wire to ground on the CircuitPython board.
Connect the servo'sred power wire to 5V power. USB power can in some cases good for a servo or two. But some USB ports supply limited current, and operating a servo from the USB 5V line may cause a power brownout and board crash.
For more servos, you'll need an external battery pack or external power supply. Do not use 3.3V for powering a servo!
Connect the servo'syellow orwhite signal wire to the control/data pin, in this caseA1 orA2 but you can use any PWM-capable pin.
For example, to wire a servo toTrinket, connect the ground wire toGND, the power wire toUSB, and the signal wire to0.
Remember,A2 on Trinket is labeled "0".
ForGemma, use jumper wire alligator clips to connect the ground wire toGND, the power wire toVOUT, and the signal wire toA2.
ForCircuit Playground Express and Circuit Playground Bluefruit, use jumper wire alligator clips to connect the ground wire toGND, the power wire toVOUT, and the signal wire toA2.
For boards likeFeather M0 Express,ItsyBitsy M0 Express andMetro M0 Express, connect the ground wire to anyGND, the power wire toUSB or 5V, and the signal wire toA2.
For theMetro M4 Express,ItsyBitsy M4 Express and theFeather M4 Express, connect the ground wire to anyG orGND, the power wire toUSB or5V, and the signal wire toA2.
Standard Servo Code
Here's an example that will sweep a servo connected to pinA2 from 0 degrees to 180 degrees (-90 to 90 degrees) and back.
To use with CircuitPython, you need to first install a few libraries, into the lib folder on yourCIRCUITPY drive. Then you need to updatecode.py with the example script.
Thankfully, we can do this in one go.In the example below, click theDownload Project Bundle button below to download the necessary libraries and thecode.py file in a zip file. Extract the contents of the zip file, open the directoryCircuitPython_Essentials/CircuitPython_Servo/ and then click on the directory that matches the version of CircuitPython you're using and copy the contents of that directory to yourCIRCUITPY drive.
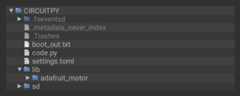
YourCIRCUITPY drive should now look similar to the following image:
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2018 Kattni Rembor for Adafruit Industries## SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT"""CircuitPython Essentials Servo standard servo example"""import timeimport boardimport pwmiofrom adafruit_motor import servo# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.A2, duty_cycle=2 ** 15, frequency=50)# Create a servo object, my_servo.my_servo = servo.Servo(pwm)while True: for angle in range(0, 180, 5): # 0 - 180 degrees, 5 degrees at a time. my_servo.angle = angle time.sleep(0.05) for angle in range(180, 0, -5): # 180 - 0 degrees, 5 degrees at a time. my_servo.angle = angle time.sleep(0.05)
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2018 Kattni Rembor for Adafruit Industries## SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT"""CircuitPython Essentials Servo standard servo example"""import timeimport boardimport pwmiofrom adafruit_motor import servo# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.A2, duty_cycle=2 ** 15, frequency=50)# Create a servo object, my_servo.my_servo = servo.Servo(pwm)while True: for angle in range(0, 180, 5): # 0 - 180 degrees, 5 degrees at a time. my_servo.angle = angle time.sleep(0.05) for angle in range(180, 0, -5): # 180 - 0 degrees, 5 degrees at a time. my_servo.angle = angle time.sleep(0.05)
Continuous Servo Code
There are two differences with Continuous Servos vs. Standard Servos:
- The
servoobject is created likemy_servo = servo.ContinuousServo(pwm)instead ofmy_servo = servo.Servo(pwm) - Instead of using
myservo.angle, you usemy_servo.throttleusing a throttle value from 1.0 (full on) to 0.0 (stopped) to -1.0 (full reverse). Any number between would be a partial speed forward (positive) or reverse (negative). This is very similar to standard DC motor control with theadafruit_motor library.
This example runs full forward for 2 seconds, stops for 2 seconds, runs full reverse for 2 seconds, then stops for 4 seconds.
To use with CircuitPython, you need to first install a few libraries, into the lib folder on yourCIRCUITPY drive. Then you need to updatecode.py with the example script.
Thankfully, we can do this in one go.In the example below, click theDownload Project Bundle button below to download the necessary libraries and thecode.py file in a zip file. Extract the contents of the zip file, open the directoryCircuitPython_Essentials/CircuitPython_Continuous_Servo/ and then click on the directory that matches the version of CircuitPython you're using and copy the contents of that directory to yourCIRCUITPY drive.
YourCIRCUITPY drive should now look similar to the following image:

# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2019 Anne Barela for Adafruit Industries## SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT"""CircuitPython Essentials Servo continuous rotation servo example"""import timeimport boardimport pwmiofrom adafruit_motor import servo# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.A2, frequency=50)# Create a servo object, my_servo.my_servo = servo.ContinuousServo(pwm)while True: print("forward") my_servo.throttle = 1.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("stop") my_servo.throttle = 0.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("reverse") my_servo.throttle = -1.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("stop") my_servo.throttle = 0.0 time.sleep(4.0)# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2019 Anne Barela for Adafruit Industries## SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT"""CircuitPython Essentials Servo continuous rotation servo example"""import timeimport boardimport pwmiofrom adafruit_motor import servo# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.A2, frequency=50)# Create a servo object, my_servo.my_servo = servo.ContinuousServo(pwm)while True: print("forward") my_servo.throttle = 1.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("stop") my_servo.throttle = 0.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("reverse") my_servo.throttle = -1.0 time.sleep(2.0) print("stop") my_servo.throttle = 0.0 time.sleep(4.0)Pretty simple!
Note that we assume that 0 degrees is 0.5ms and 180 degrees is a pulse width of 2.5ms. That's a bit wider than the official 1-2ms pulse widths. If you have a servo that has a different range you can initialize theservo object with a differentmin_pulse andmax_pulse. For example:
my_servo = servo.Servo(pwm,min_pulse=500,max_pulse=2500)
For more detailed information on using servos with CircuitPython, check out theCircuitPython section of the servo guide!
Page last edited January 22, 2025
Text editor powered bytinymce.
























