- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork0
xluo11/Rmst
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Rmst allows uers to use the bottom-up or the top-down approach toassemble computerized adaptive multistage tests (MSTs). See more detailsregarding automated test assembly (ATA) and mixed integer programming(MIP) inRata. After assembling MSTpanels, users can simulate the administration of those MST panels, whichis a useful means of evaluating the psychometric and contentcharacteristics of those panels.
Install the stable version from CRAN:
install.packages("Rmst")Install the most recent version fromgithub:
devtools::install_github("xluo11/Rmst")
Users would use the following functions to build an ATA model forassembling MST panels:
mst: initiate an ATA model for assembling MST panels.mst_route: add or remove routes from the MST panel designmst_objective: add an absolute or relative objective to the modelmst_constraint: add categorical and continuous constraints to themodelmst_stage_length: set the limits on the module length in a stagemst_rdp: anchor the TIF intersections between two adjacent modulesmst_module_info: set the minimum and/or maximum values of themodule information functionmst_assemble: assemble MST panels using MIPmst_get_items: retrieve items from the solved ATA modelplot: plot the TIF of assembled modules or routes
Usemst(..., method=) to choose between thetop-down and thebottomp-upapproach. In the top-down appraoch, objectives and constraints are addeddirectly on routes, and thus theindices refers to the route index inthe top-down approach and the module index in the bottom-up approach. Ifneeded, usemst_objective(..., method=) andmst_constraint(..., method=) to override the default method in order to implement a hybridassembly approach.
First, let’s load some packages and write a helper function forgenerating item pools. By default, the pool includes 400 3PL items, 20GPCM items, and 20 GRM items. Each item has a categorical item attribute(content area) and a continuous attribute (response time).
library(Rirt)library(dplyr,warn.conflicts=FALSE)library(ggplot2,warn.conflicts=FALSE)item_pool<-function(types=c('3pl','gpcm','grm'),n_3pl=400,n_gpcm=20,n_grm=20,seed=987653) { set.seed(seed)items<- model_mixed_gendata(1,n_3pl,n_gpcm,n_grm,n_c=3)$itemsif(n_3pl>0)items$'3pl'<- cbind(items$'3pl',id=1:n_3pl,type='3PL',content=sample(4,n_3pl,replace=TRUE),time=round(rlnorm(n_3pl,4.0,.28)),group=sort(sample(n_3pl/2,n_3pl,replace=TRUE)))if(n_gpcm>0)items$'gpcm'<- cbind(items$'gpcm',id=1:n_gpcm,type='GPCM',content=sample(4,n_gpcm,replace=TRUE),time=round(rlnorm(n_gpcm,4.0,.28)),group=sort(sample(n_gpcm/2,n_gpcm,replace=TRUE)))if(n_grm>0)items$'grm'<- cbind(items$'grm',id=1:n_grm,type='GRM',content=sample(4,n_grm,replace=TRUE),time=round(rlnorm(n_grm,4.0,.28)),group=sort(sample(n_grm/2,n_grm,replace=TRUE)))items[names(items)%in%types]}
Assemble 2 panels of 1-2 MST using the top-down design approach. Eachroute includes 40 items, and no item reuse is allowed. Maximize TIF overthe [-1.64, 0] for the route 1M-2E and over [0, 1.64] for the route1M-2H in hopes of covering the regioin [-1.64, 1.64] (90% of thepopulation) jointly with adequate test information.
As for non-statistical constraints, each route is required to have 363PL items, 2 GPCM items, and 2 GRM items. Also, each route includes 9 to11 items in each of the four content domains and has an average responsetime of 60 +/- 4 seconds per item.
Solve the model usinglp_solveunder a time limit of 5minutes.
x<- mst(item_pool(),design='1-2',n_panels=2,method='topdown',test_len=40,max_use=1)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-1.64,0,length.out=3),'max',indices=1)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(0,1.64,length.out=3),'max',indices=2)x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=36,max=36,level='3PL')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=2,max=2,level='GPCM')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=2,max=2,level='GRM')for(iin1:4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'content',min=9,max=11,level=i)x<- mst_constraint(x,'time',min=56*40,max=64*40)x<- mst_assemble(x,'lpsolve',time_limit=60*5)
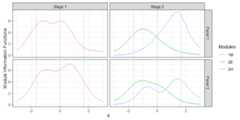
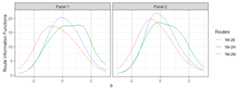
## the model is sub-optimal, optimum: 9.791 (12.613, 2.822)# Plot the route information functionsplot(x,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
# Plot the module information functionsplot(x,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
To achieve a more balanced routing distribution, anchor the TIFintersection of Module 2E and 2M at 0 and solve the model again.
x<- mst_rdp(x,0,2:3,tol=.1)x<- mst_assemble(x,'lpsolve',time_limit=60*5)
## the model is sub-optimal, optimum: 9.24 (12.57, 3.33)# Plot the route information functionsplot(x,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
# Plot the module information functionsplot(x,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
Alternatively, the model can be solved by usingGLPK.
x_glpk<- mst_assemble(x,'glpk',time_limit=60*5)
## time limit exceeded, optimum: 9.227 (13.079, 3.852)# Plot the route information functionsplot(x_glpk,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
# Plot the module information functionsplot(x_glpk,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.64,1.64,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
Examine the distribution of item type, content domain and averageresponse time in each panel and route in the lp_solve solution.
rs<-NULLfor(pin1:x$n_panels)for(iin1:x$n_routes) {items<- mst_get_items(x,panel_ix=p,route_ix=i)item_content<- rowSums(sapply(items,function(x) freq(x$content,1:4)$freq)) names(item_content)<- paste('content',1:4,sep='')item_type<- unlist(Map(nrow,items))item_time<- mean(unlist(sapply(items,function(x)x$time)))rs<- rbind(rs, c(panel=p,route=i,item_content,item_type,time=item_time)) }rs
## panel route content1 content2 content3 content4 3pl gpcm grm time## [1,] 1 1 11 10 9 10 36 2 2 56.075## [2,] 1 2 11 9 9 11 36 2 2 57.875## [3,] 2 1 10 10 9 11 36 2 2 56.300## [4,] 2 2 9 10 10 11 36 2 2 56.075Examine the number of items in each module.
Map(function(x) mutate(x,module=paste(stage,label,sep='')) %>% select(id,panel,module,type),x$items) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>% group_by(panel,module) %>% summarise(n=n(),n_3pl=sum(type=='3PL'),n_gpcm=sum(type=='GPCM'),n_grm=sum(type=='GRM')) %>% as.data.frame()
## panel module n n_3pl n_gpcm n_grm## 1 1 1M 35 33 1 1## 2 1 2E 5 3 1 1## 3 1 2H 5 3 1 1## 4 2 1M 16 14 0 2## 5 2 2E 24 22 2 0## 6 2 2H 24 22 2 0Let’s simulate the administration of these assembled two MST panels to3,000 students drawn from the standard normal distribution. Afterfinishing Stage 1, students are routed to Stage 2 using a fixed pointtheta=0.
true_t<- rnorm(3000,0,1)sims<- Map(function(t) mst_sim(x,t,rdp=list('stage2'=0)),true_t)rs<- Map(function(xx) { cbind(true=xx$true,est=xx$theta,panel=xx$admin$'3pl'$panel[1],se=xx$stats$se[x$n_stages],info=xx$stats$info[x$n_stages],route=x$module[xx$stats$route, c('stage','label')] %>% apply(.,1,paste,collapse='') %>% paste(.,collapse='-'),n_items=sum(xx$stats$n_items))},sims) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>%data.frame(.,stringsAsFactors=FALSE)rs$true<- as.numeric(rs$true) %>% round(.,4)rs$est<- as.numeric(rs$est) %>% round(.,4)rs$info<- as.numeric(rs$info) %>% round(.,4)rs$se<- as.numeric(rs$se) %>% round(.,4)rs$n_items<- as.integer(rs$n_items)rs$panel<- paste('Panel',rs$panel)# Panel usagefreq(rs$panel) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 Panel 1 1463 0.49 1463 0.49## 2 Panel 2 1537 0.51 3000 1.00# Route usagefreq(rs$route) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
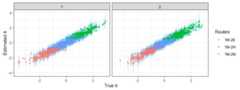
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 1M-2E 1915 0.64 1915 0.64## 2 1M-2H 1085 0.36 3000 1.00# Compare true and estimated thetaswith(rs, c(corr=cor(true,est),rmse=rmse(true,est))) %>% round(.,2)
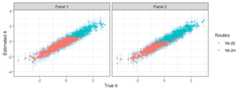
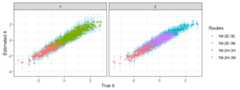
## corr rmse ## 0.96 0.27mutate(rs,lb=est-1.96*se,ub=est+1.96*se) %>% ggplot(aes(true,est,ymin=lb,ymax=ub,color=route))+ geom_linerange(color='skyblue',alpha=.5)+ geom_point(alpha=.5)+ facet_wrap(~panel)+ xlab(expression(paste('True',theta)))+ ylab(expression(paste('Estimated',theta)))+ theme_bw()+ scale_color_discrete(guide=guide_legend('Routes'))
Assemble 2 panels of 1-3 MST using the bottom-up design approach. Eachmodule includes 20 items so that each route has 40 items, and no itemreuse is allowed. Maximize TIF over the [-1.96, -0.65] for the easyroute (1M-2E), over [-0.65, 0.65] for the moderate route (1M-2M), andover [0.65, 1.96] for the hard route (1M-2H). Together, the centralregion of the scale from -1.96 to 1.96 which includes 95% of thepopulatoin is supplied with high test information.
In addition, each module is required to comply with the followingconstraints:
- 15 3PL items, 2 to 3 GPCM items, and 2 to 3 GRM items
- 4 to 6 items in each of the four content domains
- 56 to 64 seconds of response time per item
The model is solved using lp_solve under a time limit of 5minutes.
x<- mst(item_pool(),design='1-3',n_panels=2,method='bottomup',test_len=20,max_use=1)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-.65,.65,length.out=3),'max',indices=c(1,3))x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-1.96,-0.65,length.out=3),'max',indices=2)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(0.65,1.96,length.out=3),'max',indices=4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=15,max=15,level='3PL')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=2,max=3,level='GPCM')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=2,max=3,level='GRM')for(iin1:4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'content',min=4,max=6,level=i)x<- mst_constraint(x,'time',min=56*20,max=64*20)x<- mst_assemble(x,'lpsolve',time_limit=60*5)
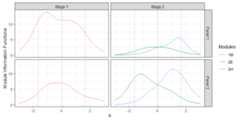
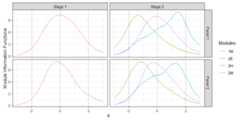
## the model is sub-optimal, optimum: 4.012 (7.436, 3.424)# Plot the route functionsplot(x,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.96,1.96,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
# Plot the module information functionsplot(x,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.96,1.96,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
Examine the compliance of the solution with the content constraints.
Map(function(x) mutate(x,module=paste(stage,label,sep='')) %>% select(id,panel,module,type,content,time),x$items) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>% group_by(panel,module) %>% summarise(n=n(),n_3pl=sum(type=='3PL'),n_gpcm=sum(type=='GPCM'),n_grm=sum(type=='GRM'),time=round(mean(time),2),content1=sum(content==1),content2=sum(content==2),content3=sum(content==3),content4=sum(content==4)) %>% as.data.frame()
## panel module n n_3pl n_gpcm n_grm time content1 content2 content3## 1 1 1M 20 15 3 2 58.80 6 6 4## 2 1 2E 20 15 3 2 56.65 5 4 6## 3 1 2H 20 15 3 2 59.60 5 4 6## 4 1 2M 20 15 2 3 58.70 6 4 6## 5 2 1M 20 15 2 3 56.15 6 4 4## 6 2 2E 20 15 3 2 56.55 4 6 4## 7 2 2H 20 15 2 3 57.90 6 4 4## 8 2 2M 20 15 2 3 57.50 5 4 6## content4## 1 4## 2 5## 3 5## 4 4## 5 6## 6 6## 7 6## 8 5After test assembly, administer the panels to 3,000 students drawn fromthe standard normal distribution using the maximum information routingrule.
true_t<- rnorm(3000,0,1)sims<- Map(function(t) mst_sim(x,t),true_t)rs<- Map(function(xx) { cbind(true=xx$true,est=xx$theta,panel=xx$admin$'3pl'$panel[1],se=xx$stats$se[x$n_stages],info=xx$stats$info[x$n_stages],route=x$module[xx$stats$route, c('stage','label')] %>% apply(.,1,paste,collapse='') %>% paste(.,collapse='-'),n_items=sum(xx$stats$n_items))},sims) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>%data.frame(.,stringsAsFactors=FALSE)rs$true<- as.numeric(rs$true) %>% round(.,4)rs$est<- as.numeric(rs$est) %>% round(.,4)rs$info<- as.numeric(rs$info) %>% round(.,4)rs$se<- as.numeric(rs$se) %>% round(.,4)rs$panel<- as.integer(rs$panel)rs$n_items<- as.integer(rs$n_items)# Panel usagefreq(rs$panel) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 1 1517 0.51 1517 0.51## 2 2 1483 0.49 3000 1.00# Route usagefreq(rs$route) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 1M-2E 730 0.24 730 0.24## 2 1M-2H 756 0.25 1486 0.50## 3 1M-2M 1514 0.50 3000 1.00# Compare true and estimated thetaswith(rs, c(corr=cor(true,est),rmse=rmse(true,est))) %>% round(.,2)
## corr rmse ## 0.97 0.25mutate(rs,lb=est-1.96*se,ub=est+1.96*se) %>% ggplot(aes(true,est,ymin=lb,ymax=ub,color=route))+ geom_linerange(color='skyblue',alpha=.5)+ geom_point(alpha=.5)+ facet_wrap(~panel)+ xlab(expression(paste('True',theta)))+ ylab(expression(paste('Estimated',theta)))+ theme_bw()+ scale_color_discrete(guide=guide_legend('Routes'))
Assemble 2 panels of 1-2-3 MST using the top-down approach. Two routeswith capricious ability change (1M-2E-3H & 1M-2H-3E) are blocked. Itemsare allowed to be used up to four times. Each route needs to meet thefollowing criteria:
- Maximize TIF over [-1.96, -0.64] for the easy route (1M-2E-3E),over [-0.64, 0.64] for the moderate routes (1M-2E-3M & 1M-2H-3M),and over [0.64, 1.96] for the hard route (1M-2H-3H)
- Include a total of 40 items
- 34 to 38 3PL items, 1 to 3 GPCM items, and 1 to 3 GRM items
- 8 to 12 items in each of the four content domains
- 56 to 64 seconds of response time per item
To yield decent routing accuracy, the first two stages are required toinclude at least 8 items. The model is solved by lp_solve under a timelimit of 5minutes.
x<- mst(item_pool(),design='1-2-3',n_panels=2,method='topdown',test_len=40,max_use=4)x<- mst_route(x, c(1,2,6),"-")x<- mst_route(x, c(1,3,4),"-")x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-1.96,-0.64,length.out=3),'max',indices=1)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-0.64,0.64,length.out=3),'max',indices=2:3)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(0.64,1.96,length.out=3),'max',indices=4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=34,max=38,level='3PL')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=1,max=3,level='GPCM')x<- mst_constraint(x,'type',min=1,max=3,level='GRM')for(iin1:4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'content',min=8,max=12,level=i)x<- mst_constraint(x,'time',min=56*40,max=64*40)x<- mst_stage_length(x,1:2,min=8)x<- mst_assemble(x,'lpsolve',time_limit=60*5)
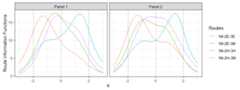
## the model is sub-optimal, optimum: 8.258 (12.837, 4.579)# Plot the route information functionsplot(x,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.96,1.96,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
# Plot the module information functionsplot(x,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)+ geom_vline(xintercept=seq(-1.96,1.96,length.out=3),linetype=2,color='gray60')
Examine the compliance of the assembly results with the contentconstraints.
rs<-NULLfor(pin1:x$n_panels)for(iin1:x$n_routes) {items<- mst_get_items(x,panel_ix=p,route_ix=i)item_content<- rowSums(sapply(items,function(x) freq(x$content,1:4)$freq)) names(item_content)<- paste('content',1:4,sep='')item_type<- unlist(Map(nrow,items))item_time<- mean(unlist(sapply(items,function(x)x$time)))rs<- rbind(rs, c(panel=p,route=i,item_content,item_type,time=item_time)) }rs
## panel route content1 content2 content3 content4 3pl gpcm grm time## [1,] 1 1 9 10 9 12 35 3 2 56.450## [2,] 1 2 9 8 12 11 36 2 2 60.025## [3,] 1 3 11 10 10 9 37 2 1 58.400## [4,] 1 4 11 12 8 9 35 2 3 57.100## [5,] 2 1 10 8 10 12 35 3 2 56.850## [6,] 2 2 12 10 9 9 36 2 2 57.500## [7,] 2 3 12 11 8 9 35 2 3 57.825## [8,] 2 4 11 10 8 11 37 1 2 57.825Map(function(x) mutate(x,module=paste(stage,label,sep='')) %>% select(id,panel,module,type),x$items) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>% group_by(panel,module) %>% summarise(n=n(),n_3pl=sum(type=='3PL'),n_gpcm=sum(type=='GPCM'),n_grm=sum(type=='GRM')) %>% as.data.frame()
## panel module n n_3pl n_gpcm n_grm## 1 1 1M 9 8 1 0## 2 1 2E 12 11 0 1## 3 1 2H 12 12 0 0## 4 1 3E 19 16 2 1## 5 1 3H 19 15 1 3## 6 1 3M 19 17 1 1## 7 2 1M 13 12 0 1## 8 2 2E 14 14 0 0## 9 2 2H 14 13 0 1## 10 2 3E 13 9 3 1## 11 2 3H 13 12 1 0## 12 2 3M 13 10 2 1Administer the assembled panels to 3,000 students drawn from thestandard normal distribution using the maximum information routing rule.
# simulationtrue_t<- rnorm(3000,0,1)sims<- Map(function(t) mst_sim(x,t),true_t)rs<- Map(function(xx) { cbind(true=xx$true,est=xx$theta,panel=xx$admin$'3pl'$panel[1],se=xx$stats$se[x$n_stages],info=xx$stats$info[x$n_stages],route=x$module[xx$stats$route, c('stage','label')] %>% apply(.,1,paste,collapse='') %>% paste(.,collapse='-'),n_items=sum(xx$stats$n_items))},sims) %>% Reduce(rbind,.) %>%data.frame(.,stringsAsFactors=FALSE)rs$true<- as.numeric(rs$true) %>% round(.,4)rs$est<- as.numeric(rs$est) %>% round(.,4)rs$info<- as.numeric(rs$info) %>% round(.,4)rs$se<- as.numeric(rs$se) %>% round(.,4)rs$panel<- as.integer(rs$panel)rs$n_items<- as.integer(rs$n_items)# Panel usagefreq(rs$panel) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 1 1532 0.51 1532 0.51## 2 2 1468 0.49 3000 1.00# Route usagefreq(rs$route) %>% mutate(perc=round(perc,2),cum_perc=round(cum_perc,2))
## value freq perc cum_freq cum_perc## 1 1M-2E-3E 632 0.21 632 0.21## 2 1M-2E-3M 1169 0.39 1801 0.60## 3 1M-2H-3H 221 0.07 2022 0.67## 4 1M-2H-3M 978 0.33 3000 1.00# Compare true and estimated thetaswith(rs, c(corr=cor(true,est),rmse=rmse(true,est))) %>% round(.,2)
## corr rmse ## 0.96 0.26mutate(rs,lb=est-1.96*se,ub=est+1.96*se) %>% ggplot(aes(true,est,ymin=lb,ymax=ub,color=route))+ geom_linerange(color='skyblue',alpha=.5)+ geom_point(alpha=.5)+ facet_wrap(~panel)+ xlab(expression(paste('True',theta)))+ ylab(expression(paste('Estimated',theta)))+ theme_bw()+ scale_color_discrete(guide=guide_legend('Routes'))
Assemble 2 panels of 1-3 MST using a hybrid assembly approach that setsconstraints on routes but test information functions on modules. Inparticular, module 1M is required to have a flat TIF of 6 over theregion from -1.28 to 1.28, module 2E, 2M, and 2H to hit the TIF targetof 8 at -1.28, 0, and 1.28 respectively. Additionally, each route isrequired to have 4 to 6 items in each content domain and 20 items intotal.
x<- mst(item_pool(),'1-3',n_panels=2,method='topdown',test_len=20,max_use=1)x<- mst_objective(x, seq(-1.28,1.28,length.out=3),target=6,indices=1,method='bottomup')x<- mst_objective(x,-1.28,target=8,indices=2,method='bottomup')x<- mst_objective(x,0,target=8,indices=3,method='bottomup')x<- mst_objective(x,1.28,target=8,indices=4,method='bottomup')for(iin1:4)x<- mst_constraint(x,'content',min=4,max=6,level=i)x<- mst_assemble(x,'lpsolve',time_limit=30)
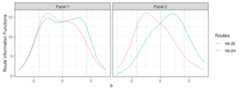
## the model is sub-optimal, optimum: 1.869 (0.988, 0.881)# plot the route information functionsplot(x,byroute=FALSE,label=TRUE)
# plot the module information functionsplot(x,byroute=TRUE,label=TRUE)
# check the content distributionrs<-NULLfor(pin1:x$n_panels)for(rin1:x$n_routes){x_items<- mst_get_items(x,panel_ix=p,route_ix=r)x_content<- Map(function(x)if(is.null(x)) rep(0,4)else with(x, freq(content,1:4)$freq),x_items)x_content<- colSums(Reduce(rbind,x_content)) names(x_content)<- paste('content',1:4,sep='')rs<- rbind(rs, c(panel=p,route=r,x_content)) }rs
## panel route content1 content2 content3 content4## [1,] 1 1 6 6 4 4## [2,] 1 2 5 5 4 6## [3,] 1 3 6 5 4 5## [4,] 2 1 4 6 4 6## [5,] 2 2 4 6 4 6## [6,] 2 3 4 6 4 6If you encounter a bug, please post a code example that exposes the bugongithub. You can post yourquestions and feature requests ongithub or to theauthor.
About
Assemble and Simulate multistage testing in R
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.