- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork39
Android app which let you stream various phone's sensors to websocket clients
License
umer0586/SensorServer
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
SensorServer transforms Android device into a versatile sensor hub, providing real-time access to its entire array of sensors. It allows multiple Websocket clients to simultaneously connect and retrieve live sensor data.The app exposes all available sensors of the Android device, enabling WebSocket clients to read sensor data related to device position, motion (e.g., accelerometer, gyroscope), environment (e.g., temperature, light, pressure), GPS location, and even touchscreen interactions.
Since this application functions as a Websocket Server, you will require a Websocket Client API to establish a connection with the application. To obtain a Websocket library for your preferred programming language clickhere.
To receive sensor data,Websocket client must connect to the app using followingURL.
ws://<ip>:<port>/sensor/connect?type=<sensor type here>Value for thetype parameter can be found by navigating toAvailable Sensors in the app.
For example
Foraccelerometer
/sensor/connect?type=android.sensor.accelerometer.Forgyroscope
/sensor/connect?type=android.sensor.gyroscope.Forstep detector
/sensor/connect?type=android.sensor.step_detectorso on...
Once connected, client will receive sensor data inJSON Array (float type values) throughwebsocket.onMessage.
A snapshot from accelerometer.
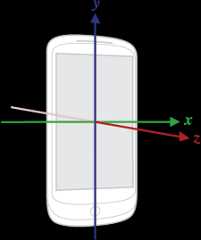
{"accuracy":2,"timestamp":3925657519043709,"values": [0.31892395,-0.97802734,10.049896]}where
| Array Item | Description |
|---|---|
| values[0] | Acceleration force along the x axis (including gravity) |
| values[1] | Acceleration force along the y axis (including gravity) |
| values[2] | Acceleration force along the z axis (including gravity) |
Andtimestamp is the time in nanoseconds at which the event happened
UseJSON parser to get these individual values.
Note :Use following links to know what each value invalues array corresponds to
- For motion sensors/topics/sensors/sensors_motion
- For position sensors/topics/sensors/sensors_position
- For Environmental sensors/topics/sensors/sensors_environment
Some Android devices have additional sensors likeCoarse Motion Classifier(com.qti.sensor.motion_classifier),Basic Gesture(com.qti.sensor.basic_gestures) etc which are not documented on offical android docs. Please refer to thisBlog for corresponding values invalues array
Multiple WebSocket clients can connect to a specific type of sensor. For example, by connecting to/sensor/connect?type=android.sensor.accelerometer multiple times, separate connections to the accelerometer sensor are created. Each connected client will receive accelerometer data simultaneously.
Additionally, it is possible to connect to different types of sensors from either the same or different machines. For instance, one WebSocket client object can connect to the accelerometer, while another WebSocket client object can connect to the gyroscope. To view all active connections, you can select the "Connections" navigation button.
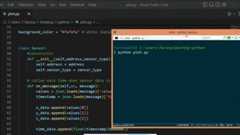
Here is a simple websocket client in python usingwebsocket-client api which receives live data from accelerometer sensor.
importwebsocketimportjsondefon_message(ws,message):values=json.loads(message)['values']x=values[0]y=values[1]z=values[2]print("x = ",x ,"y = ",y ,"z = ",z )defon_error(ws,error):print("error occurred ",error)defon_close(ws,close_code,reason):print("connection closed : ",reason)defon_open(ws):print("connected")defconnect(url):ws=websocket.WebSocketApp(url,on_open=on_open,on_message=on_message,on_error=on_error,on_close=on_close)ws.run_forever()connect("ws://192.168.0.103:8080/sensor/connect?type=android.sensor.accelerometer")
Your device's IP might be different when you tap start button, so make sure you are using correct IP address at client side
Also seeConnecting to Multiple Sensors Using Threading in Python
In networks using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), devices frequently receive different IP addresses upon reconnection, making it impractical to rely on hardcoded network configurations. To address this challenge, the app supports Zero-configuration networking (Zeroconf/mDNS), enabling automatic server discovery on local networks. This feature eliminates the need for clients to hardcode IP addresses and port numbers when connecting to the WebSocket server. When enabled by the app user, the server broadcasts its presence on the network using the service type_websocket._tcp, allowing clients to discover the server automatically. Clients can now implement service discovery to locate the server dynamically, rather than relying on hardcoded network configurations.
See complete python Example atConnecting To the Server Using Service Discovery
You can also connect to multiple sensors over single websocket connection. To use multiple sensors over single websocket connection use followingURL.
ws://<ip>:<port>/sensors/connect?types=["<type1>","<type2>","<type3>"...]By connecting using above URL you will receive JSON response containing sensor data along with a type of sensor. See complete example atUsing Multiple Sensors On Single Websocket Connection. Avoid connecting too many sensors over single connection
By connecting to the addressws://<ip>:<port>/touchscreen, clients can receive touch screen events in following JSON formate.
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
| x | x coordinate of touch |
| y | y coordinate of touch |
| action | ACTION_MOVE or ACTION_UP or ACTION_DOWN |
"ACTION_DOWN" indicates that a user has touched the screen."ACTION_UP" means the user has removed their finger from the screen."ACTION_MOVE" implies the user is sliding their finger across the screen.SeeControlling Mouse Movement Using SensorServer app
You can access device location through GPS using following URL.
ws://<ip>:<port>/gpsSeeGetting Data From GPS for more details
SeeReal Time Plot of Accelerometer (Python) using this app
sensor.plotting.240p.mp4
You can also view your phone's sensor data in a Web Browser. Open the app's navigation drawer menu and enableTest in a Web Browser.Once the web server is running, the app will display an address on your screen. This address will look something likehttp://<ip>:<port>.On your device or another computer on the same network, open a web browser and enter that address. The web browser will now display a list of all the sensors available on your device. The web interface have options to connect to and disconnect from individual sensors, allowing you to view their real-time data readings.

This web app is built using Flutter and its source could be found undersensors_dashboard. However, there's one current limitation to be aware of. The app is built with Flutter using the--web-renderer canvaskit option. This means that the resulting app will have some dependencies that need to be downloaded from the internet. This means that any device accessing the web app through a browser will require an internet connection to function properly.
The web app is built and deployed to Android's assets folder viapython deploy_web_app.py
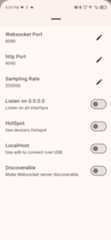
If you don't have Wifi network at your work place you can directly connect websocket clients to the app by enablingHotspot Option from settings. Just make sure that websocket clients are connected to your phone's hotspot
To connect over USB make sureUSB debugging option is enable in your phone andADB (android debug bridge) is available in your machine
- Step 1 : Enable
Local Hostoption in app - Step 2 : Run adb command
adb forward tcp:8081 tcp:8081(8081 is just for example) from client - Step 3 : use address
ws://localhost:8081:/sensor/connect?type=<sensor type here>to connect
Make sure you have installed your android device driver andadb devices command detects your connected android phone.
- Utilizing smartphone IMU sensors for controlling a robot via ROS (http://www.rc.is.ritsumei.ac.jp/FILES/PBL5/2024/IMU_based_control/)
- Use smartphone as "sensor" into RTMaps studio (https://github.com/Intempora/smartphone-sensors)
- Streams IMU and GPS data via WebSocket from Android app and integrates with MinIO CSI server for building-scale WiFi sensing testbeds. (https://github.com/WS-UB/WiSense-Mobile-Client)
- SLAM System with IMU and Wifi Synchronization. (https://github.com/WS-UB/imu_publisher)
- Middleware for Streaming Real Device Sensor Data to Android Emulators. (https://github.com/ingmarfjolla/android-sensor-injection)
- A Python graphical user interface to visualize real-time data streams from a generic WebSocket & HTTP source (https://github.com/AlyShmahell/robolytics)
- Tool designed to address the current limitations of passthrough mode in modern virtual reality (VR) headsets.(https://github.com/LucasHartmanWestern/Screen-Sight)
- Real-Time Sensor Data Streaming, Storage, and Visualization System with Kafka, InfluxDB, and Grafana.(https://github.com/TouradBaba/Iot_sensors_streaming)
- A project that uses data from IMU, GPS and Barometer modules to estimate position based on space state filters implementationhttps://github.com/Peterex08/IMUGPS
- A Windows desktop application that transforms a smartphone into a gesture‑based remote control. It streams real‑time sensor (gyroscope) data over WebSockets, recognizes swipe gestures, and maps them to system or media actions on the desktophttps://github.com/Guerric9018/Frogmote
- PHASETIMER (https://github.com/zenbooster/phasetimer)
- Score real-time walking data of users wearing an Andriod device. (https://github.com/eliasHw/BME450W_Fall2022)
- Wireless Steering wheel using python and android with paddles and breaks. (https://rutube.ru/video/03d53de54054337a8c54b825f7fcc3fe/)
- https://github.com/strets123/walking-pictionary
If you're using this app in a project and would like to share the link, feel free to submit a pull request with the link and a brief description so that it can be helpful to others.
- SensaGram. For streaming realtime sensor data over UDP
- DroidPad. Android app for creating customizable control interfaces for Bluetooth Low energy,WebSocket, MQTT, TCP, and UDP protocols.
Send Bitcoin at 1NHkiJmjUdjqbCKJf6ZksGKMvYu52Q5tew
OR
Scan following QR code with bitcoin wallet app to send bitcoins
About
Android app which let you stream various phone's sensors to websocket clients
Topics
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.