- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork108
Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (R port of original Python package)
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
tidymodels/lime
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
There once was a package called lime,
Whose models were simply sublime,
It gave explanations for their variations,
one observation at a time.
lime-rick by Mara Averick
This is an R port of the Python lime package(https://github.com/marcotcr/lime) developed by the authors of thelime (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) approach forblack-box model explanations. All credits for the invention of theapproach goes to the original developers.
The purpose oflime is to explain the predictions of black boxclassifiers. What this means is that for any given prediction and anygiven classifier it is able to determine a small set of features in theoriginal data that has driven the outcome of the prediction. To learnmore about the methodology oflime read thepaper and visit the repository oftheoriginal implementation.
Thelime package for R does not aim to be a line-by-line port of itsPython counterpart. Instead it takes the ideas laid out in the originalcode and implements them in an API that is idiomatic to R.
Out of the boxlime supports a long range of models, e.g. thosecreated with caret, parsnip, and mlr. Support for unsupported models areeasy to achieve by adding apredict_model andmodel_type method forthe given model.
The following shows how a random forest model is trained on the irisdata set and howlime is then used to explain a set of newobservations:
library(caret)library(lime)# Split up the data setiris_test<-iris[1:5,1:4]iris_train<-iris[-(1:5),1:4]iris_lab<-iris[[5]][-(1:5)]# Create Random Forest model on iris datamodel<- train(iris_train,iris_lab,method='rf')# Create an explainer objectexplainer<- lime(iris_train,model)# Explain new observationexplanation<- explain(iris_test,explainer,n_labels=1,n_features=2)# The output is provided in a consistent tabular format and includes the# output from the model.explanation#> # A tibble: 10 × 13#> model_type case label label_prob model_r2 model_intercept model_prediction#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>#> 1 classificat… 1 seto… 1 0.700 0.120 0.984#> 2 classificat… 1 seto… 1 0.700 0.120 0.984#> 3 classificat… 2 seto… 1 0.681 0.128 0.978#> 4 classificat… 2 seto… 1 0.681 0.128 0.978#> 5 classificat… 3 seto… 1 0.686 0.126 0.976#> 6 classificat… 3 seto… 1 0.686 0.126 0.976#> 7 classificat… 4 seto… 1 0.708 0.119 0.982#> 8 classificat… 4 seto… 1 0.708 0.119 0.982#> 9 classificat… 5 seto… 1 0.682 0.126 0.981#> 10 classificat… 5 seto… 1 0.682 0.126 0.981#> # ℹ 6 more variables: feature <chr>, feature_value <dbl>, feature_weight <dbl>,#> # feature_desc <chr>, data <list>, prediction <list># And can be visualised directlyplot_features(explanation)#> Warning: `aes_()` was deprecated in ggplot2 3.0.0.#> ℹ Please use tidy evaluation idioms with `aes()`#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the lime package.#> Please report the issue at <https://github.com/tidymodels/lime/issues>.#> This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.#> Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was#> generated.
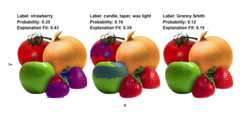
lime also supports explaining image and text models. For imageexplanations the relevant areas in an image can be highlighted:
explanation<- .load_image_example()plot_image_explanation(explanation)
Here we see that the second most probably class is hardly true, but isdue to the model picking up waxy areas of the produce and interpretingthem as wax-light surface.
For text the explanation can be shown by highlighting the importantwords. It even includes ashiny application for interactivelyexploring text models:
lime is available on CRAN and can be installed using the standardapproach:
install.packages('lime')To get the development version, install from GitHub instead:
# install.packages('pak')pak::pak('tidymodels/lime')
Please note that the ‘lime’ project is released with aContributor Codeof Conduct. Bycontributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
About
Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations (R port of original Python package)
Topics
Resources
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
Code of conduct
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.