- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork2
License
thebrisklab/SparseICA
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Sparse ICA (Sparse Independent Component Analysis) is a novel ICA method that enables sparse estimation of independent source components.
We assume you are running R 4.1.0 or newer. There is no guarantee for backward or forward comparability. Please raise the issue on GitHub if something breaks.
The following R packages are required:
- RcppArmadillo (>= 14.2.2),
- Rcpp (>= 1.0.13),
- MASS (>= 7.3-58),
- irlba (>= 2.3.5),
- clue (>= 0.3),
- ciftiTools (>= 0.16),
- parallel (>= 4.1),
- devtools
You can install them by running this code:
if(!require(c("Rcpp","RcppArmadillo","MASS","irlba","clue","ciftiTools","parallel","devtools"))){ install.packages(c("Rcpp","RcppArmadillo","MASS","irlba","clue","ciftiTools","parallel","devtools"))}
Then you can install Sparse ICA from github with:
library(devtools)install_github("thebrisklab/SparseICA")# Load the packagelibrary(SparseICA)
ThesparseICA() is the main function of our Sparse ICA algorithm. It is implemented in both pure R and Rcpp.
sparseICA( xData, n.comp, nu = "BIC", nu_list = seq(0.1, 4, 0.1), U.list = NULL, whiten = c('eigenvec', 'sqrtprec', 'none'), lngca = FALSE, orth.method = c('svd', 'givens'), method = c("C", "R"), restarts = 40, use_irlba = TRUE, eps = 1e-06, maxit = 500, verbose = TRUE, BIC_verbose = FALSE, converge_plot = FALSE, col.stand = TRUE, row.stand = FALSE, iter.stand = 5, positive_skewness = TRUE)xData: A numeric matrix of input data with dimensions P x T, where P is the number of features and T is the number of samples.n.comp: An integer specifying the number of components to estimate.nu: A positive numeric value or a character"BIC"specifying the tuning parameter controlling the balance between accuracy and sparsity of the results. It can be selected using a BIC-like criterion ("BIC") or based on expert knowledge (a positive number). Default is "BIC".nu_list: A numeric vector specifying the list of candidate tuning parameters. Default isseq(0.1, 4, 0.1).U.list: An optional matrix specifying the initialization of the U matrix. Default isNULL.whiten: A character string specifying the method for whitening the inputxData. Options areeigenvec,sqrtprec,lngca, ornone. Default iseigenvec.lngca: A logical value indicating whether to perform Linear Non-Gaussian Component Analysis (LNGCA). Default isFALSE.orth.method: A character string specifying the method used for generating initial values for the U matrix. Default issvd.method: A character string specifying the computation method. IfC(default), C code is used for most computations for better performance. IfR, computations are performed entirely in R.restarts: An integer specifying the number of random initializations for optimization. Default is 40.use_irlba: A logical value indicating whether to use theirlbamethod for fast truncated Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) during whitening. This can improve memory efficiency for intermediate datasets. Default isTRUE.eps: A numeric value specifying the convergence threshold. Default is1e-6.maxit: An integer specifying the maximum number of iterations for the Sparse ICA method using Laplace density. Default is 500.verbose: A logical value indicating whether to print convergence information during execution. Default isTRUE.BIC_verbose: A logical value indicating whether to print BIC selection information. Default isFALSE.converge_plot: A logical value indicating whether to generate a line plot showing the convergence trace. Default isFALSE.col.stand: A logical value indicating whether to standardize columns. For each column, the mean of the entries in the column equals 0, and the variance of the entries in the column equals 1. Default isTRUE.row.stand: A logical value indicating whether to standardize rows. For each row, the mean of the entries in the row equals 0, and the variance of the entries in the row equals 1. Default isFALSE.iter.stand: An integer specifying the number of iterations for achieving both row and column standardization whencol.stand = TRUEandrow.stand = TRUE. Default is 5.positive_skewness: A logical value indicating whether to enforce positive skewness on the estimated components. Default isTRUE.
The output will be a list with the following components as such:
loglik: The minimal log-likelihood value among the random initializations.estS: A numeric matrix of estimated sparse independent components with dimensions P x Q.estM: The estimated mixing matrix with dimensions Q x T.estU: The estimated U matrix with dimensions Q x Q.whitener: The whitener matrix used for data whitening.converge: The convergence trace of the difference norm of the U matrix.BIC: A numeric vector of BIC values corresponding to each candidatenuinnu_list.nu_list: A numeric vector of candidate tuning parameter values.best_nu: The optimal nu selected based on the BIC-like criterion.
Load the example data:
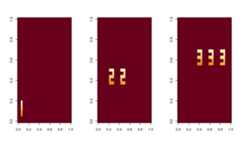
data(example_sim123)- The true "source signals" -
smat:
par(mfrow=c(1,3))image(matrix(-example_sim123$smat[,1],33))image(matrix(-example_sim123$smat[,2],33))image(matrix(-example_sim123$smat[,3],33))
- The true time series in the mixing matrix -
mmat:
par(mfrow=c(3,1))plot(example_sim123$mmat[1,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")plot(example_sim123$mmat[2,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")plot(example_sim123$mmat[3,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")
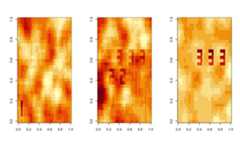
- The simulated data matrix at time points T = 12, 23, and 35 -
xmat:
par(mfrow=c(1,3))image(matrix(example_sim123$xmat[,12],33))image(matrix(example_sim123$xmat[,23],33))image(matrix(example_sim123$xmat[,35],33))
- Perform our Sparse ICA algorithm using
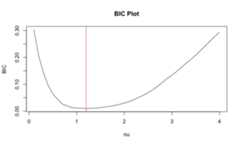
sparseICAfunction. The tuning parameternuis selected using the BIC-like criterion.
my_sparseICA= sparseICA(xData=example_sim123$xmat,n.comp=3,nu="BIC",method="C",restarts=40,eps=1e-6,maxit=500,verbose=TRUE)
The selected optimalnu is 1.1.
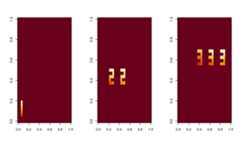
- Match the order of the estimated components with the truth.
matched_res=matchICA(my_sparseICA$estS,example_sim123$smat,my_sparseICA$estM)
- Check the estimated source signals.
par(mfrow=c(1,3))image(matrix(-matched_res$S[,1],33,33))image(matrix(-matched_res$S[,2],33,33))image(matrix(-matched_res$S[,3],33,33))
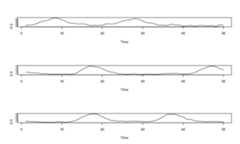
- Check the estimated time series in the mixing matrix.
par(mfrow=c(3,1))plot(matched_res$M[1,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")plot(matched_res$M[2,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")plot(matched_res$M[3,],type="l",xlab="Time",ylab="")
- Check the correlations.
> cor(example_sim123$smat[,1],matched_res$S[,1])[1]0.9970362> cor(example_sim123$smat[,2],matched_res$S[,2])[1]0.9962684> cor(example_sim123$smat[,3],matched_res$S[,3])[1]0.9856885> cor(example_sim123$mmat[1,],matched_res$M[1,])[1]0.964416> cor(example_sim123$mmat[2,],matched_res$M[2,])[1]0.9910054> cor(example_sim123$mmat[3,],matched_res$M[3,])[1]0.9922269
Those using theSparseICA software should cite:
Wang Z., Gaynanova, I., Aravkin, A., Risk, B. B. (2024). Sparse Independent Component Analysis with an Application to Cortical Surface fMRI Data in Autism. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 119(548), 2508-2520.
About
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Contributors2
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.