- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork117
Tools for ggplot2 scales
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
r-lib/scales
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
One of the most difficult parts of any graphics package is scaling,converting from data values to perceptual properties. The inverse ofscaling, making guides (legends and axes) that can be used to read thegraph, is often even harder! The scales packages provides the internalscaling infrastructure used byggplot2, and gives you tools tooverride the default breaks, labels, transformations and palettes.
# Scales is installed when you install ggplot2 or the tidyverse.# But you can install just scales from CRAN:install.packages("scales")# Or the development version from Github:# install.packages("pak")pak::pak("r-lib/scales")
The most common use of the scales package is to control the appearanceof axis and legend labels. Use abreak_ function to control how breaksare generated from the limits, and alabel_ function to control howbreaks are turned in to labels.
library(ggplot2)library(dplyr,warn.conflicts=FALSE)library(lubridate,warn.conflicts=FALSE)txhousing %>% mutate(date= make_date(year,month,1)) %>% group_by(city) %>% filter(min(sales)>5e2) %>% ggplot(aes(date,sales,group=city))+ geom_line(na.rm=TRUE)+ scale_x_date(NULL,breaks=scales::breaks_width("2 years"),labels=scales::label_date("'%y") )+ scale_y_log10("Total sales",labels=scales::label_number(scale_cut=scales::cut_short_scale()) )
economics %>% filter(date< ymd("1970-01-01")) %>% ggplot(aes(date,pce))+ geom_line()+ scale_x_date(NULL,breaks=scales::breaks_width("3 months"),labels=scales::label_date_short() )+ scale_y_continuous("Personal consumption expenditures",breaks=scales::breaks_extended(8),labels=scales::label_dollar() )
Generally, I don’t recommend runninglibrary(scales) because when youtype (e.g.)scales::label_ autocomplete will provide you with a listof labelling functions to jog your memory.
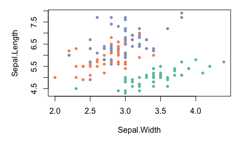
Scales colour palettes are used to power the scales in ggplot2, but youcan use them in any plotting system. The following example shows how youmight apply them to a base plot.
library(scales)# pull a list of colours from any palettepal_viridis()(4)#> [1] "#440154FF" "#31688EFF" "#35B779FF" "#FDE725FF"# use in combination with baseR `palette()` to set new defaultspalette(pal_brewer(palette="Set2")(4))par(mar= c(5,5,1,1))plot(Sepal.Length~Sepal.Width,data=iris,col=Species,pch=20)
scales also gives users the ability to define and apply their own customtransformation functions for repeated use.
# use new_transform to build a new transformationtransform_logp3<- new_transform(name="logp",transform=function(x) log(x+3),inverse=function(x) exp(x)-3,breaks= log_breaks())dsamp<- sample_n(diamonds,100)ggplot(dsamp, aes(carat,price,colour=color))+ geom_point()+ scale_y_continuous(trans=transform_logp3)
About
Tools for ggplot2 scales
Topics
Resources
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
Code of conduct
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.