- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork10
[NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight] Code and data for the paper "Finding Transformer Circuits with Edge Pruning".
License
princeton-nlp/Edge-Pruning
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
UPDATE: The code for GPT-2 circuits does not always initialize the
log_alphascorrectly with newertransformersversions. We have provided a modified version of allfpt2_*.pyscripts that work with newer versions, and have also updated the arguments inrun_scripts/*_sweep.shto reflect this. The eval scripts have also been updated. For these updated scripts, please use therequirements-experimental.txtfile for the python environment.
 This repository contains the code and data for the paper"Finding Transformer Circuits with Edge Pruning".
This repository contains the code and data for the paper"Finding Transformer Circuits with Edge Pruning".
After installingPyTorch, run
pip install -r requirements.txtto install the required packages.
The method itself is described in depth in our paper. Here we outline the implementation.
We expand the hidden state tensor from(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim) to(node, batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim). This array acts as a sort of outbox for every node. Then, a downstream node can read its input via muxing these outboxes with a binary mask. The masks and their optimization are implemented with theL0 trick (described further in our paper)---this part of the code is insrc/modeling/l0.py. We also provide some additional implementation comments here: since the "target" sparsities specified to the pruning scripts are just numbers, we can (and sometimes do) specify values above1 to strongly push the model to be as sparse as possible. Also note that at the end of the training, we discretize the masks to0 or1 from their floating point values by rounding w.r.t a threshold. Instead of fixing the threshold to0.5, we perform a binary search during evaluating so that the final threshold causes a sparsity of exactly1 - <average mask value>.
Note: Please unzip the
data.zipfile to thedata/directory before running the code!
The repository is structured as follows.
- The
data/folder contains everything related to datasets and their generation. Specifically,data/datasets/has the datasets for the various tasks used in our evaluation, while the scripts indata/scripts/use the seed data indata/helper_filesto generate these datasets programmatically.data/tracr_modelscontains the precompiled weights of the tracr models we use, whiledata/runsprovides the final checkpoints of the pruned versions. src/houses the code related to actually performing the pruning, and evaluating the pruned circuits. In particular,src/modelingdefines the model classes we use.src/pruneprovides fine-tuning scripts andsrc/eval/contains scripts that evaluate the produced circuits (or the whole model).run_scripts/contain helper scripts that both demonstrate and help with launching pruning and evaluation runs.tracrx/has a slightly modifiedTracr implementation. The modifications allow us to return the embedding matrix entries when calling the model, so that we can save all weights for future use in our equivalent Tracr class in PyTorch.assets/contains images used in this README.
The datasets forIOI-t1 /IOI (Indirect Object Identification),GT (Greater Than) andGP (Gendered Pronoun) are underdata/datasets/{ioi-t1/ioi/gt/gp}. If you wish to re-generate these, use the scripts indata/scripts/prepare_{ioi/gt/gp}.py. The modeling file for GPT-2 issrc/modeling/modeling_fpt2.py, and the pruning scripts are found atsrc/prune/fpt2_{ioi/gt/gp}.py. The IOI pruning script can also be used for IOI-t1.
A demonstration of how to use these scripts, along with the hyperparameters we used, is provided inrun_scripts/{ioi/gt/gp}_sweep.sh. There are further explanations in these files, and flags for enabling a node loss (along with an edge loss) or to disallow removing edges of the formembedding -> node. Please note that---in contrast to some prior methods---we disallow removing edges of the formhead.Q/K/V -> head since it is equivalent to removing all incoming edges of the former node.
Evaluation scripts are found insrc/eval/{ioi/gt/gp}.py. To evaluate a circuit found with the default settings above, you can simply run, for example,
python src/eval/ioi.py -m /path/to/pruned_model -wThe-w flag signifies that embedding nodes were allowed to be pruned in the circuit. You can also use this script with the original GPT-2 model (or any GPT-2 checkpoint).
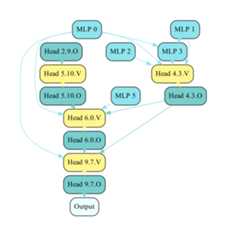
An example circuit
Visualizing a GPT-2 circuit: The following two steps will let you generate a drawing of a circuit. First, save the circuit edges usingsrc/modeling/vis_fpt2.py as follows:
python src/modeling/vis_fpt2.py -i /path/to/checkpoint/dir/ -wThis will save the edges (by default to/path/to/checkpoint/dir/edges.json), and-w tells the script that you model masks over embedding edges as well. Then, you can draw the circuit with
python src/modeling/draw_fpt2.py -i /path/to/checkpoint/dir/edges.jsonThe default output path is/path/to/checkpoint/dir/edges.pdf; please look at the scripts for other arguments. An example circuit is shown above.
We use the original source codes ofACDC andEAP (the minimal implementation branch), with thin wrappers. Example wrappers are included inbaselines_examples/.
The Tracr data and model preparation involves two steps (or you can use the datasets and models provided underdata/datasets/ anddata/tracr_models/). We will illustrate them for the case of the taskreverse (the files/steps forxproportion are the same, with the changereverse -> xproportion). You can calldata/scripts/prepare_reverse.py to generate the dataset for the task. The model itself can be compiled by callingdata/scripts/prepare_reverse_tracr-model.py. This will compile the tracr models using thetracrx/ code and then save the weights as pickle files (by default underdata/tracr_models/).
These weights are now compatible with our PyTorch model, defined insrc/modeling/modeling_erazr.py. The pruning code insrc/prune/erazr_{reverse/xproportion}.py is called upon by the helper scripts inrun_scripts/tracr_{reverse/xproportion}.sh. The evaluation is performed at the end of the run by the pruning code itself. Please refer to the helper scripts for an example of how to launch a pruning run.
Extension to other tracr models should be straightforward by modifying the pruning scripts above. However, note that Tracr seems to map the BOS token to a random index in its vocabulary for each task, and figuring out the specific index for may need an inspection of a few outputs.
The data preparation scripts for Boolean Expressions are provided underdata/datasets/, and the dataset itself indata/datasets/boolean_expressions/. The modeling code is insrc/modeling/modeling_fllama.py and the pruning code is insrc/prune/fllama_boolean_expressions_{fs/ip}.py for instruction prompting and few-shot (in-context learning) settings. To directly evaluate the obtained checkpoints, usesrc/eval/boolean_expressions.py just like the GPT-2 evaluation scripts. This script has the following differences from the GPT-2 evaluation scripts:
- Use the flag
-mor--modeto specify the mode of evaluation (fewshotorinstruction). - The
-e/--edgesflag allows you to specify a JSON file with a list of edges that are loaded into the model first: this lets you evaluate, e.g., the intersection of two models found with the filesrc/modeling/vis_fllama.py(use the-m1,-m2and-oflags to specify model paths and the output JSON path). - You will probably need to launch this script with
4(or more) GPUs:run_scripts/launch_fllama_eval.shshows how to do this.For the pruning itself, the helper scripts inrun_scripts/launch_fllama_{instr/fs}_prune.shuse PyTorch FSDP and call uponsrc/prune/fllama_boolean_expressions_{ip/fs}.py. Note that these are sbatch scripts (despite having the.shextension). Please refer to them for the hyperparameters we used (and find the FSDP config files underrun_scripts/fsdp_configs/). The runs are quite resource-intensive and required us to use multi-node training with 32 GPUs.
Note 1: We are aware of a bug in the CodeLlama pruning code due to which the loss starts out as a large negative number sometimes (when using multi-node training and initializing from a Llama checkpoint instead of our class). Terminating the run and re-launching it fixes the issue. Additionally, initializing from an Fllama class (load Llama into our class, then save to disk with
save_pretrainedand load that checkpoint instead) seems to help. We are looking into this bug and will fix it soon!
Note 2: To facilitate use with other models, we plan on releasing modeling files for a few popular architectures soon. Stay tuned!
Extension to other models should be straightforward by mimickingmodeling_{fpt2/fllama}.py in modiyfing the corresponding HuggingFace model files (e.g.,modeling_gpt2.py).
Using a custom dataset with, e.g., the GPT-2 pruning script is as straightforward as writing into a JSONL file (data/datasets/example_custom.jsonl)
{ "clean": "1 + 2 = <predict>3</predict>", "corrupted": "1 + 4 = <predict>5</predict>"}{ "clean": "5 + 1 = <predict>6</predict>", "corrupted": "1 + 1 = <predict>2</predict>"}{ "clean": "2 + 2 = <predict>4</predict>", "corrupted": "2 + 4 = <predict>6</predict>"}and calling thesrc/prune/fpt2_custom.py as inrun_scripts/custom_example.sh. The clean and corrupted text must be filled into the entriesclean andcorrupted. The part meant for the model to predict must be enclosed in<predict></predict>. You can also add asplit key in your examples with valuetrain/validation. If this key is missing, the entire dataset is used for both training and validation.
Please reach out to Adithya<adithyab@princeton.edu> with any questions or bug reports.
If you use our work or found it useful, please consider citing us:
@inproceedings{bhaskar2024finding, title={Finding Transformer Circuits with Edge Pruning}, author={Adithya Bhaskar and Alexander Wettig and Dan Friedman and Danqi Chen}, booktitle={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)}, year={2024}}About
[NeurIPS 2024 Spotlight] Code and data for the paper "Finding Transformer Circuits with Edge Pruning".
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.