- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork4
Visualizing Hypothesis Tests in Multivariate Linear Models,http://friendly.github.io/heplots/
friendly/heplots
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Version 1.8.0; documentation built forpkgdown 2025-12-05
Theheplots package provides functions for visualizing hypothesistests in multivariate linear models (“MLM” = {MANOVA, multivariatemultiple regression, MANCOVA, and repeated measures designs}). It alsoprovides other tools for analysis and graphical display of MLMs.
HE plots represent sums-of-squares-and-products matrices for linearhypotheses (H) and for error (E) using ellipses (in twodimensions), ellipsoids (in three dimensions), or by line segments inone dimension. For the theory and applications, see:
- Friendly (2007) for thebasic theory on which this is based.
- Fox, Friendly and Monette(2009) for abrief introduction,
- Friendly (2010) for theapplication of these ideas to repeated measure designs,
- Friendly, Monette and Fox(2013) for a generaldiscussion of the role of elliptical geometry in statisticalunderstanding,
- Friendly & Sigal (2017) foran applied R tutorial,
- Friendly & Sigal (2018)for theory and examples of visualizing equality of covariancematrices.
If you use this work in teaching or research, please cite it as given bycitation("heplots") or seeCitation.
Other topics now addressed here include:
- robust MLMs, using iteratively re-weighted least squared todown-weight observations with large multivariate residuals,
robmlm(). Mahalanobis()calculates classical androbust Mahalanobis squareddistances using MCD and MVE estimators of center and covariance.- visualizing tests for equality of covariance matrices in MLMs (Box’s Mtest),
boxM()andplot.boxM(). Also:bartlettTests()andLeveneTests()for homogeneity of variance for each response in aMLM. $\chi^2$ Q-Q plots for MLMs (cqplot()) to detect outliers and assessmultivariate normality of residuals.- bivariate coefficient plots showing elliptical confidence regions(
coefplot()).
In this respect, theheplots package now aims to provide a wide rangeof tools for analyzing and visualizing multivariate response linearmodels, together with other packages:
- The related
candiscpackageprovides HE plots incanonical discriminant space, the space oflinear combinations of the responses that show the maximum possibleeffects and for canonical correlation in multivariate regressiondesigns. See thepackagedocumentation for details.
- Another package,
mvinfluence, providesdiagnostic measures and plots forinfluential observations in MLMdesigns. See thepackagedocumentation for details.
Several tutorial vignettes are also included. Seevignette(package="heplots").
| CRAN version | install.packages("heplots") |
| R-universe | install.packages("heplots", repos = c('https://friendly.r-universe.dev') |
| Development version | remotes::install_github("friendly/heplots") |
The graphical functions contained here all display multivariate modeleffects in variable (data) space, for one or more response variables(or contrasts among response variables in repeated measures designs).
heplot()constructs two-dimensional HE plots for model terms andlinear hypotheses for pairs of response variables in multivariatelinear models.heplot3d()constructs analogous 3D plots for triples of responsevariables.The
pairsmethod,pairs.mlm()constructs a scatterplot matrix ofpairwise HE plots.heplot1d()constructs 1-dimensional analogs of HE plots for modelterms and linear hypotheses for single response variables.
glance.mlm()extendsbroom::glance.lm()to multivariate responsemodels, giving a one-line statistical summary for each responsevariable.uniStats()does something similar, but formatted more likea ANOVA table.boxM()Calculates Box’sM test for homogeneity of covariancematrices in a MANOVA design. Aplotmethod displays a visualrepresentation of the components of the test. Associated with this,bartletTests()andlevineTests()give the univariate tests ofhomogeneity of variance for each response measure in a MLM.covEllipses()draw covariance (data) ellipses for one or more group,optionally including the ellipse for the pooled within-groupcovariance.coefplot()for an MLM object draws bivariate confidence ellipses.
For repeated measure designs, between-subject effects and within-subjecteffects must be plotted separately, because the error terms (Ematrices) differ. For terms involving within-subject effects, thesefunctions carry out a linear transformation of the matrixY ofresponses to a matrixY M, whereM is the model matrix for aterm in the intra-subject design and produce plots of theH andE matrices in this transformed space. The vignette"repeated"describes these graphical methods for repeated measures designs. (ThispaperHE plots for repeated measuresdesigns is now provided as aPDF vignette.)
The package also provides a large collection of data sets illustrating avariety of multivariate linear models of the types listed above,together with graphical displays. The table below classifies these withmethod tags. Their names are linked to their documentation withgraphical output on thepkgdown website,[http://friendly.github.io/heplots].
| dataset | rows | cols | title | tags |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AddHealth | 4344 | 3 | Adolescent Health Data | MANOVA ordered |
| Adopted | 62 | 6 | Adopted Children | MMRA repeated |
| Bees | 246 | 6 | Captive and maltreated bees | MANOVA |
| Diabetes | 145 | 6 | Diabetes Dataset | MANOVA |
| dogfood | 16 | 3 | Dogfood Preferences | MANOVA contrasts candisc |
| FootHead | 90 | 7 | Head measurements of football players | MANOVA contrasts |
| Headache | 98 | 6 | Treatment of Headache Sufferers for Sensitivity to Noise | MANOVA repeated |
| Hernior | 32 | 9 | Recovery from Elective Herniorrhaphy | MMRA candisc |
| Iwasaki_Big_Five | 203 | 7 | Personality Traits of Cultural Groups | MANOVA |
| mathscore | 12 | 3 | Math scores for basic math and word problems | MANOVA |
| MockJury | 114 | 17 | Effects Of Physical Attractiveness Upon Mock Jury Decisions | MANOVA candisc |
| NeuroCog | 242 | 10 | Neurocognitive Measures in Psychiatric Groups | MANOVA candisc |
| NLSY | 243 | 6 | National Longitudinal Survey of Youth Data | MMRA |
| oral | 56 | 5 | Effect of Delay in Oral Practice in Second Language Learning | MANOVA |
| Oslo | 332 | 14 | Oslo Transect Subset Data | MANOVA candisc |
| Overdose | 17 | 7 | Overdose of Amitriptyline | MMRA cancor |
| Parenting | 60 | 4 | Father Parenting Competence | MANOVA contrasts |
| peng | 333 | 8 | Size measurements for adult foraging penguins near Palmer Station | MANOVA |
| Plastic | 20 | 5 | Plastic Film Data | MANOVA |
| Pottery2 | 48 | 12 | Chemical Analysis of Romano-British Pottery | MANOVA candisc |
| Probe | 11 | 5 | Response Speed in a Probe Experiment | MANOVA repeated |
| RatWeight | 27 | 6 | Weight Gain in Rats Exposed to Thiouracil and Thyroxin | MANOVA repeated |
| ReactTime | 10 | 6 | Reaction Time Data | repeated |
| Rohwer | 69 | 10 | Rohwer Data Set | MMRA MANCOVA |
| RootStock | 48 | 5 | Growth of Apple Trees from Different Root Stocks | MANOVA contrasts |
| Sake | 30 | 10 | Taste Ratings of Japanese Rice Wine (Sake) | MMRA |
| schooldata | 70 | 8 | School Data | MMRA robust |
| Skulls | 150 | 5 | Egyptian Skulls | MANOVA contrasts |
| SocGrades | 40 | 10 | Grades in a Sociology Course | MANOVA candisc |
| SocialCog | 139 | 5 | Social Cognitive Measures in Psychiatric Groups | MANOVA candisc |
| TIPI | 1799 | 16 | Data on the Ten Item Personality Inventory | MANOVA candisc |
| VocabGrowth | 64 | 4 | Vocabulary growth data | repeated |
| WeightLoss | 34 | 7 | Weight Loss Data | repeated |
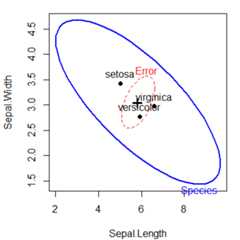
This example illustrates HE plots using the classiciris data set. Howdo the means of the flower variables differ bySpecies? This datasetwas the impetus for R. A. Fisher (1936) to propose a method ofdiscriminant analysis using data collected by Edgar Anderson (1928).Though some may rightly deprecate Fisher for being a supporter ofeugenics, Anderson’siris dataset should not be blamed.
A basic HE plot shows theH andE ellipses for the first tworesponse variables (here:Sepal.Length andSepal.Width). Themultivariate test is significant (by Roy’s test)iff theH ellipseprojectsanywhere outside theE ellipse.
The positions of the group means show how they differ on the tworesponse variables shown, and provide an interpretation of theorientation of theH ellipse: it is long in the directions ofdifferences among the means.
iris.mod<- lm(cbind(Sepal.Length,Sepal.Width,Petal.Length,Petal.Width)~Species,data=iris)heplot(iris.mod)
Contrasts or other linear hypotheses can be shown as well, and theellipses look better if they are filled. We create contrasts to test thedifferences betweenversacolor andvirginca and also betweensetosa and the average of the other two. Each 1 df contrast plots asdegenerate 1D ellipse– a line.
Because these contrasts are orthogonal, they add to the total 2 dfeffect ofSpecies. Note how the first contrast, labeledV:V,distinguishes the means ofversicolor fromvirginica; the secondcontrast,S:VV distinguishessetosa from the other two.
par(mar=c(4,4,1,1)+.1)contrasts(iris$Species)<-matrix(c(0,-1,1,2,-1,-1),nrow=3,ncol=2)contrasts(iris$Species)#> [,1] [,2]#> setosa 0 2#> versicolor -1 -1#> virginica 1 -1iris.mod<- lm(cbind(Sepal.Length,Sepal.Width,Petal.Length,Petal.Width)~Species,data=iris)hyp<-list("V:V"="Species1","S:VV"="Species2")heplot(iris.mod,hypotheses=hyp,fill=TRUE,fill.alpha=0.1)
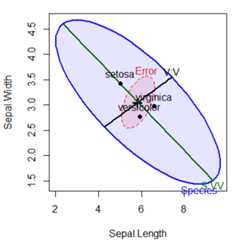
HE plot of sepal length and Sepal width for the iris data, showing linesreflecting two contrasts among iris species.
All pairwise HE plots are produced using thepairs() method for MLMobjects.In the plot, note how the means of most pairs of variables arevery highly correlated, in the order Setosa < Versicolor < Virginica,but this pattern doesn’t hold for relations withSepal.Width.
pairs(iris.mod,hypotheses=hyp,hyp.labels=FALSE,fill=TRUE,fill.alpha=0.1)
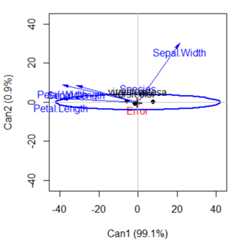
For more than two response variables, a multivariate effect can beviewed more simply by projecting the data into canonical space — thelinear combinations of the responses which show the greatest differencesamong the group means relative to within-group scatter. The computationsare performed with thecandiscpackage, which has anheplot.candisc() method.
library(candisc)iris.can<- candisc(iris.mod)|> print()#>#> Canonical Discriminant Analysis for Species:#>#> CanRsq Eigenvalue Difference Percent Cumulative#> 1 0.96987 32.19193 31.907 99.12126 99.121#> 2 0.22203 0.28539 31.907 0.87874 100.000#>#> Test of H0: The canonical correlations in the#> current row and all that follow are zero#>#> LR test stat approx F numDF denDF Pr(> F)#> 1 0.02344 199.145 8 288 < 2.2e-16 ***#> 2 0.77797 13.794 3 145 5.794e-08 ***#> ---#> Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
The HE plot in canonical space shows that the differences among speciesare nearly entirely one-dimensional. The weights for the variables onthe first dimension show howSepal.Width differs from the other sizevariables.
# HE plot in canonical spaceheplot(iris.can,var.pos=1,scale=40)
MANOVA relies on the assumption that within-group covariance matricesare all equal. It is useful to visualize these in the space of some ofthe predictors.covEllipses() provides this both for classical androbust (method="mve") estimates. The figure below shows these for thethree Iris species and the pooled covariance matrix, which is the sameas theE matrix used in MANOVA tests.
covEllipses(iris[,1:4],iris$Species)covEllipses(iris[,1:4],iris$Species,fill=TRUE,method="mve",add=TRUE,labels="")
Anderson, E. (1928). The Problem of Species in the Northern Blue Flags,Iris versicolor L. and Iris virginica L.Annals of the MissouriBotanical Garden,13, 241–313.
Fisher, R. A. (1936). The Use of Multiple Measurements in TaxonomicProblems.Annals of Eugenics,8, 379–388.
Friendly, M. (2006).Data Ellipses, HE Plots and Reduced-Rank Displaysfor Multivariate Linear Models: SAS Software andExamples.Journal ofStatistical Software,17, 1-42.
Friendly, M. (2007).HE plots for Multivariate General LinearModels.Journal ofComputational and Graphical Statistics,16(2) 421-444. DOI:10.1198/106186007X208407.
Fox, J., Friendly, M. & Monette, G. (2009).Visualizing hypothesistests in multivariate linear models: The heplots package forRComputationalStatistics,24, 233-246.
Friendly, M. (2010).HE plots for repeated measuresdesigns.Journal ofStatistical Software,37, 1–37.
Friendly, M.; Monette, G. & Fox, J. (2013).Elliptical Insights:Understanding Statistical Methods Through EllipticalGeometryStatisticalScience,28, 1-39.
Friendly, M. & Sigal, M. (2017).Graphical Methods for MultivariateLinear Models in Psychological Research: An RTutorial.The QuantitativeMethods for Psychology,13, 20-45.
Friendly, M. & Sigal, M. (2018):Visualizing Tests for Equality ofCovariance Matrices,TheAmerican Statistician,DOI
About
Visualizing Hypothesis Tests in Multivariate Linear Models,http://friendly.github.io/heplots/
Topics
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Contributors3
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.