- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork0
Ebrahim-Farrington Binary logistic regression goodness of fit test
License
ebrahimkhaled/ebrahim.gof
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Theebrahim.gof package implements the Ebrahim-Farrington goodness-of-fit test for logistic regression models. This test is particularly effective for binary data and sparse datasets, providing an improved alternative to the traditional Hosmer-Lemeshow test.
- Ebrahim-Farrington Test: Simplified implementation for binary data with automatic grouping
- Original Farrington Test: Full implementation for grouped data
- Robust Performance: Particularly effective with sparse data and binary outcomes
- Easy to Use: Simple function interface similar to other goodness-of-fit tests
- Well Documented: Comprehensive documentation with examples
Copy and paste this in R or R-studio.
# Install devtools if you haven't alreadyif (!requireNamespace("devtools",quietly=TRUE)) { install.packages("devtools")}# Install ebrahim.gof from GitHubdevtools::install_github("ebrahimkhaled/ebrahim.gof")
Another way to install the R-Libarary, but itsnot avaialbe yet.
# Will be available after CRAN submissioninstall.packages("ebrahim.gof")
library(ebrahim.gof)# Example with binary dataset.seed(123)n<-500x<- rnorm(n)linpred<-0.5+1.2*xprob<-1/ (1+ exp(-linpred))y<- rbinom(n,1,prob)# Fit logistic regressionmodel<- glm(y~x,family= binomial())predicted_probs<- fitted(model)# Perform Ebrahim-Farrington testresult<- ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=10)print(result)
The main function that performs the goodness-of-fit test:
ef.gof(y,predicted_probs ,G=10,model=NULL,m=NULL)
Parameters:
y: Binary response vector (0/1) or success counts for grouped datapredicted_probs: Vector of predicted probabilities from logistic modelG: Number of groups for binary data (default: 10)model: Optional glm object (required for original Farrington only, not for Ebrahim-Farrington test)m: Optional vector of trial counts (for grouped data) (required for original Farrington only, not for Ebrahim-Farrington test)
Returns:A data frame with test name, test statistic, and p-value.
library(ebrahim.gof)# Simulate binary dataset.seed(42)n<-1000x1<- rnorm(n)x2<- rnorm(n)linpred<--0.5+0.8*x1+0.6*x2prob<- plogis(linpred)y<- rbinom(n,1,prob)# Fit logistic regressionmodel<- glm(y~x1+x2,family= binomial())predicted_probs<- fitted(model)# Test goodness of fitresult<- ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=10)print(result)#> Test Test_Statistic p_value#> 1 Ebrahim-Farrington -0.8944 0.8143
# Test with different numbers of groupsresults<-data.frame(Groups= c(4,10,20),P_value= c( ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=4)$p_value, ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=10)$p_value, ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=20)$p_value ))print(results)
library(ResourceSelection)# Ebrahim-Farrington testef_result<- ef.gof(y,predicted_probs,G=10)# Hosmer-Lemeshow testhl_result<- hoslem.test(y,predicted_probs,g=10)# Compare resultscomparison<-data.frame(Test= c("Ebrahim-Farrington","Hosmer-Lemeshow"),P_value= c(ef_result$p_value,hl_result$p.value))print(comparison)
# Function to simulate misspecified modelsimulate_power<-function(n,beta_quad=0.1,n_sims=100) {rejections<-0for (iin1:n_sims) {x<- runif(n,-2,2)# True model has quadratic termlinpred_true<-0+x+beta_quad*x^2prob_true<- plogis(linpred_true)y<- rbinom(n,1,prob_true)# Fit misspecified linear modelmodel_mis<- glm(y~x,family= binomial())pred_probs<- fitted(model_mis)# Test goodness of fittest_result<- ef.gof(y,pred_probs,G=10)if (test_result$p_value<0.05) {rejections<-rejections+1 } }return(rejections/n_sims)}# Calculate power for different sample sizespower_results<-data.frame(n= c(100,200,500,1000),power= sapply(c(100,200,500,1000),simulate_power))print(power_results)
The Ebrahim-Farrington test is based on Farrington's (1996) theoretical framework but simplified for practical implementation with binary data. The test uses a modified Pearson chi-square statistic:
For binary data with automatic grouping, the test statistic is:
Z_EF = (T_EF - (G - 2)) / sqrt(2(G - 2))Where:
T_EFis the modified Pearson chi-square statisticGis the number of groups- The test statistic follows a standard normal distribution under H₀
- Better Power: More sensitive to model misspecification
- Sparse Data Handling: Specifically designed for sparse data situations
- Computational Efficiency: Simplified calculations for binary data
- Theoretical Foundation: Based on rigorous asymptotic theory
Simulation results consistently demonstrate that the Ebrahim-Farrington test outperforms the Hosmer-Lemeshow test, even when the model misspecification is minimal—such as with a missing interaction or omitted quadratic term—when usingG = 10 groups (Ebrahim, 2025).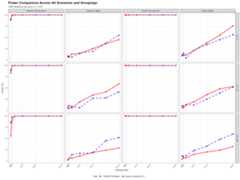
The following two figures illustrate that, under the null hypothesis, the Ebrahim-Farrington test statistic is asymptotically standard normal for both single-predictor and multiple-predictor logistic regression models. This property holds even in sparse data settings, confirming the theoretical foundation of the test and supporting its use for model assessment. (see (Ebrahim,2025))
- Figure 1: Empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the Ebrahim-Farrington test statistic under the null for a single predictor, compared to the standard normal CDF.
- Figure 2: Empirical CDF for the test statistic under the null for a multiple independent predictors scenario, again compared to the standard normal.
These results demonstrate that the Ebrahim-Farrington test maintains the correct type I error rate and its statistic converges to the standard normal distribution as sample size increases, validating its asymptotic properties.
Farrington, C. P. (1996). On Assessing Goodness of Fit of Generalized Linear Models to Sparse Data.Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B (Methodological), 58(2), 349-360.
Ebrahim, Khaled Ebrahim (2025). Goodness-of-Fits Tests and Calibration Machine Learning Algorithms for Logistic Regression Model with Sparse Data.Master's Thesis, Alexandria University.
Hosmer, D. W., & Lemeshow, S. (2000). Applied Logistic Regression, Second Edition. New York: Wiley.
If you use this package in your research, please cite:
Ebrahim, K. E. (2025). ebrahim.gof: Ebrahim-Farrington Goodness-of-Fit Test for Logistic Regression. R package version 1.0.0. https://github.com/ebrahimkhaled/ebrahim.gofContributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
This project is licensed under the GPL-3 License - see theLICENSE file for details.
Ebrahim Khaled Ebrahim
Alexandria University
Email:ebrahim.khaled@alexu.edu.eg
- Prof. Osama Abd ElAziz Hussien (Alexandria University) for supervision
- Dr. Ahmed El-Kotory (Alexandria University) for guidance and supervision
- The R community for continuous support and feedback
About
Ebrahim-Farrington Binary logistic regression goodness of fit test
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
.png&f=jpg&w=240)
.png&f=jpg&w=240)