- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork394
An open source library and framework for deep learning on satellite and aerial imagery.
License
azavea/raster-vision
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Raster Vision is an open source Pythonlibrary andframework for building computer vision models on satellite, aerial, and other large imagery sets (including oblique drone imagery).
It has built-in support for chip classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation with backends using PyTorch.
As a library, Raster Vision provides a full suite of utilities for dealing with all aspects of a geospatial deep learning workflow: reading geo-referenced data, training models, making predictions, and writing out predictions in geo-referenced formats.
As a low-code framework, Raster Vision allows users (who don't need to be experts in deep learning!) to quickly and repeatably configure experiments that execute a machine learning pipeline including: analyzing training data, creating training chips, training models, creating predictions, evaluating models, and bundling the model files and configuration for easy deployment.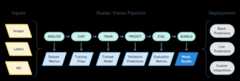
Raster Vision also has built-in support for running experiments in the cloud usingAWS Batch as well asAWS Sagemaker.
See thedocumentation for more details.
For more details, see theSetup documentation.
You can install Raster Vision directly viapip.
pip install rastervision
Alternatively, you may use a Docker image. Docker images are published toquay.io (see thetags tab).
We publish a new tag per merge intomaster, which is tagged with the first 7 characters of the commit hash. To use the latest version, pull thelatest suffix, e.g.raster-vision:pytorch-latest. Git tags are also published, with the Github tag name as the Docker tag suffix.
You can also build a Docker image from scratch yourself. After cloning this repo, rundocker/build, and run then the container usingdocker/run.
Non-developers may find it easiest to use Raster Vision as a low-code framework where Raster Vision handles all the complexities and the user only has to configure a few parameters. TheQuickstart guide is a good entry-point into this. More advanced examples can be found on theExamples page.
Fordevelopers and those looking to dive deeper or combine Raster Vision with their own code, the best starting point isUsage Overview, followed byBasic Concepts andTutorials.
You can ask questions and talk to developers (let us know what you're working on!) at:
To set up the development environment:
- For and clone the repo and navigate to it.
- Create and activate a new Python virtual environment via your environment manager of choice (
mamba,uv,pyenv, etc.). - Run
scripts/setup_dev_env.shto install all Raster Vision plugins in editable mode along with all the dependencies.
For more information, seeContributing.
We are happy to take contributions! It is best to get in touch with the maintainersabout larger features or design changesbefore starting the work,as it will make the process of accepting changes smoother.
Everyone who contributes code to Raster Vision will be asked to sign a Contributor License Agreement. SeeContributing for instructions.
Raster Vision is licensed under the Apache 2 license. See licensehere.
3rd party licenses for all dependecies used by Raster Vision can be foundhere.
About
An open source library and framework for deep learning on satellite and aerial imagery.
Topics
Resources
License
Code of conduct
Contributing
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.

