Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork9
Training Keras Models by the Genetic Algorithm using PyGAD
ahmedfgad/KerasGA
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
KerasGA is part of thePyGAD library for training Keras models using the genetic algorithm (GA).
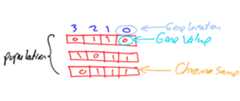
TheKerasGA project has a single module namedkerasga.py which has a class namedKerasGA for preparing an initial population of Keras model parameters.
PyGAD is an open-source Python library for building the genetic algorithm and training machine learning algorithms. Check the library's documentation atRead The Docs:https://pygad.readthedocs.io
- Credit/Debit Card:https://donate.stripe.com/eVa5kO866elKgM0144
- Open Collective:opencollective.com/pygad
- PayPal: Use either this link:paypal.me/ahmedfgad or the e-mail addressahmed.f.gad@gmail.com
- Interac e-Transfer: Use e-mail addressahmed.f.gad@gmail.com
To installPyGAD, simply use pip to download and install the library fromPyPI (Python Package Index). The library lives a PyPI at this pagehttps://pypi.org/project/pygad.
pip3installpygad
To get started with PyGAD, please read the documentation atRead The Docshttps://pygad.readthedocs.io.
The source code of thePyGAD modules is found in the following GitHub projects:
- pygad: (https://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython)
- pygad.nn:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyANN
- pygad.gann:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NeuralGenetic
- pygad.cnn:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/NumPyCNN
- pygad.gacnn:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/CNNGenetic
- pygad.kerasga:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/KerasGA
- pygad.torchga:https://github.com/ahmedfgad/TorchGA
The documentation of PyGAD is available atRead The Docshttps://pygad.readthedocs.io.
The documentation of the PyGAD library is available atRead The Docs at this link:https://pygad.readthedocs.io. It discusses the modules supported by PyGAD, all its classes, methods, attribute, and functions. For each module, a number of examples are given.
If there is an issue using PyGAD, feel free to post at issue in thisGitHub repositoryhttps://github.com/ahmedfgad/GeneticAlgorithmPython or by sending an e-mail toahmed.f.gad@gmail.com.
If you built a project that uses PyGAD, then please drop an e-mail toahmed.f.gad@gmail.com with the following information so that your project is included in the documentation.
- Project title
- Brief description
- Preferably, a link that directs the readers to your project
Please check theContact Us section for more contact details.
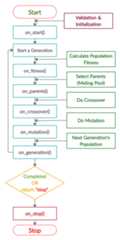
The next figure lists the different stages in the lifecycle of an instance of thepygad.GA class. Note that PyGAD stops when either all generations are completed or when the function passed to theon_generation parameter returns the stringstop.
The next code implements all the callback functions to trace the execution of the genetic algorithm. Each callback function prints its name.
importpygadimportnumpyfunction_inputs= [4,-2,3.5,5,-11,-4.7]desired_output=44deffitness_func(ga_instance,solution,solution_idx):output=numpy.sum(solution*function_inputs)fitness=1.0/ (numpy.abs(output-desired_output)+0.000001)returnfitnessfitness_function=fitness_funcdefon_start(ga_instance):print("on_start()")defon_fitness(ga_instance,population_fitness):print("on_fitness()")defon_parents(ga_instance,selected_parents):print("on_parents()")defon_crossover(ga_instance,offspring_crossover):print("on_crossover()")defon_mutation(ga_instance,offspring_mutation):print("on_mutation()")defon_generation(ga_instance):print("on_generation()")defon_stop(ga_instance,last_population_fitness):print("on_stop()")ga_instance=pygad.GA(num_generations=3,num_parents_mating=5,fitness_func=fitness_function,sol_per_pop=10,num_genes=len(function_inputs),on_start=on_start,on_fitness=on_fitness,on_parents=on_parents,on_crossover=on_crossover,on_mutation=on_mutation,on_generation=on_generation,on_stop=on_stop)ga_instance.run()
Based on the used 3 generations as assigned to thenum_generations argument, here is the output.
on_start()on_fitness()on_parents()on_crossover()on_mutation()on_generation()on_fitness()on_parents()on_crossover()on_mutation()on_generation()on_fitness()on_parents()on_crossover()on_mutation()on_generation()on_stop()Check thePyGAD's documentation for more examples information. You can also find more information about the implementation of the examples.
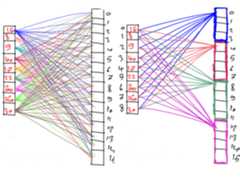
importtensorflow.kerasimportpygad.kerasgaimportnumpyimportpygaddeffitness_func(ga_instance,solution,sol_idx):globaldata_inputs,data_outputs,keras_ga,modelmodel_weights_matrix=pygad.kerasga.model_weights_as_matrix(model=model,weights_vector=solution)model.set_weights(weights=model_weights_matrix)predictions=model.predict(data_inputs)mae=tensorflow.keras.losses.MeanAbsoluteError()abs_error=mae(data_outputs,predictions).numpy()+0.00000001solution_fitness=1.0/abs_errorreturnsolution_fitnessdefcallback_generation(ga_instance):print("Generation = {generation}".format(generation=ga_instance.generations_completed))print("Fitness = {fitness}".format(fitness=ga_instance.best_solution()[1]))input_layer=tensorflow.keras.layers.Input(3)dense_layer1=tensorflow.keras.layers.Dense(5,activation="relu")(input_layer)output_layer=tensorflow.keras.layers.Dense(1,activation="linear")(dense_layer1)model=tensorflow.keras.Model(inputs=input_layer,outputs=output_layer)keras_ga=pygad.kerasga.KerasGA(model=model,num_solutions=10)# Data inputsdata_inputs=numpy.array([[0.02,0.1,0.15], [0.7,0.6,0.8], [1.5,1.2,1.7], [3.2,2.9,3.1]])# Data outputsdata_outputs=numpy.array([[0.1], [0.6], [1.3], [2.5]])# Prepare the PyGAD parameters. Check the documentation for more information: https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pygad.html#pygad-ga-classnum_generations=250# Number of generations.num_parents_mating=5# Number of solutions to be selected as parents in the mating pool.initial_population=keras_ga.population_weights# Initial population of network weightsga_instance=pygad.GA(num_generations=num_generations,num_parents_mating=num_parents_mating,initial_population=initial_population,fitness_func=fitness_func,on_generation=callback_generation)ga_instance.run()# After the generations complete, some plots are showed that summarize how the outputs/fitness values evolve over generations.ga_instance.plot_fitness(title="PyGAD & Keras - Iteration vs. Fitness",linewidth=4)# Returning the details of the best solution.solution,solution_fitness,solution_idx=ga_instance.best_solution()print("Fitness value of the best solution = {solution_fitness}".format(solution_fitness=solution_fitness))print("Index of the best solution : {solution_idx}".format(solution_idx=solution_idx))# Fetch the parameters of the best solution.best_solution_weights=pygad.kerasga.model_weights_as_matrix(model=model,weights_vector=solution)model.set_weights(best_solution_weights)predictions=model.predict(data_inputs)print("Predictions :\n",predictions)mae=tensorflow.keras.losses.MeanAbsoluteError()abs_error=mae(data_outputs,predictions).numpy()print("Absolute Error : ",abs_error)
importtensorflow.kerasimportpygad.kerasgaimportnumpyimportpygaddeffitness_func(ga_instance,solution,sol_idx):globaldata_inputs,data_outputs,keras_ga,modelmodel_weights_matrix=pygad.kerasga.model_weights_as_matrix(model=model,weights_vector=solution)model.set_weights(weights=model_weights_matrix)predictions=model.predict(data_inputs)bce=tensorflow.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()solution_fitness=1.0/ (bce(data_outputs,predictions).numpy()+0.00000001)returnsolution_fitnessdefcallback_generation(ga_instance):print("Generation = {generation}".format(generation=ga_instance.generations_completed))print("Fitness = {fitness}".format(fitness=ga_instance.best_solution()[1]))# Build the keras model using the functional API.input_layer=tensorflow.keras.layers.Input(2)dense_layer=tensorflow.keras.layers.Dense(4,activation="relu")(input_layer)output_layer=tensorflow.keras.layers.Dense(2,activation="softmax")(dense_layer)model=tensorflow.keras.Model(inputs=input_layer,outputs=output_layer)# Create an instance of the pygad.kerasga.KerasGA class to build the initial population.keras_ga=pygad.kerasga.KerasGA(model=model,num_solutions=10)# XOR problem inputsdata_inputs=numpy.array([[0,0], [0,1], [1,0], [1,1]])# XOR problem outputsdata_outputs=numpy.array([[1,0], [0,1], [0,1], [1,0]])# Prepare the PyGAD parameters. Check the documentation for more information: https://pygad.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pygad.html#pygad-ga-classnum_generations=250# Number of generations.num_parents_mating=5# Number of solutions to be selected as parents in the mating pool.initial_population=keras_ga.population_weights# Initial population of network weights.# Create an instance of the pygad.GA classga_instance=pygad.GA(num_generations=num_generations,num_parents_mating=num_parents_mating,initial_population=initial_population,fitness_func=fitness_func,on_generation=callback_generation)# Start the genetic algorithm evolution.ga_instance.run()# After the generations complete, some plots are showed that summarize how the outputs/fitness values evolve over generations.ga_instance.plot_fitness(title="PyGAD & Keras - Iteration vs. Fitness",linewidth=4)# Returning the details of the best solution.solution,solution_fitness,solution_idx=ga_instance.best_solution()print("Fitness value of the best solution = {solution_fitness}".format(solution_fitness=solution_fitness))print("Index of the best solution : {solution_idx}".format(solution_idx=solution_idx))# Fetch the parameters of the best solution.best_solution_weights=pygad.kerasga.model_weights_as_matrix(model=model,weights_vector=solution)model.set_weights(best_solution_weights)predictions=model.predict(data_inputs)print("Predictions :\n",predictions)# Calculate the binary crossentropy for the trained model.bce=tensorflow.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()print("Binary Crossentropy : ",bce(data_outputs,predictions).numpy())# Calculate the classification accuracy for the trained model.ba=tensorflow.keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy()ba.update_state(data_outputs,predictions)accuracy=ba.result().numpy()print("Accuracy : ",accuracy)
There are different resources that can be used to get started with the building CNN and its Python implementation.
To start with coding the genetic algorithm, you can check the tutorial titledGenetic Algorithm Implementation in Python available at these links:
This tutorial is prepared based on a previous version of the project but it still a good resource to start with coding the genetic algorithm.
Get started with the genetic algorithm by reading the tutorial titledIntroduction to Optimization with Genetic Algorithm which is available at these links:
Read about building neural networks in Python through the tutorial titledArtificial Neural Network Implementation using NumPy and Classification of the Fruits360 Image Dataset available at these links:
Read about training neural networks using the genetic algorithm through the tutorial titledArtificial Neural Networks Optimization using Genetic Algorithm with Python available at these links:
To start with coding the genetic algorithm, you can check the tutorial titledBuilding Convolutional Neural Network using NumPy from Scratch available at these links:
This tutorial) is prepared based on a previous version of the project but it still a good resource to start with coding CNNs.
Get started with the genetic algorithm by reading the tutorial titledDerivation of Convolutional Neural Network from Fully Connected Network Step-By-Step which is available at these links:
You can also check my book cited asAhmed Fawzy Gad 'Practical Computer Vision Applications Using Deep Learning with CNNs'. Dec. 2018, Apress, 978-1-4842-4167-7 which discusses neural networks, convolutional neural networks, deep learning, genetic algorithm, and more.
Find the book at these links:
If you used PyGAD, please consider adding a citation to the following paper about PyGAD:
@misc{gad2021pygad, title={PyGAD: An Intuitive Genetic Algorithm Python Library}, author={Ahmed Fawzy Gad}, year={2021}, eprint={2106.06158}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.NE}}About
Training Keras Models by the Genetic Algorithm using PyGAD
Topics
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Sponsor this project
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Packages0
Contributors2
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.