- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork8
SleekPanther/kruskals-algorithm-minimum-spanning-tree-mst
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
Java Implementation of Kruskal's Algorithm usingdisjoing sets
Kruskal's algorithm: Start withT = ∅. Consider edges in ascending order of weight. Insert edgee intoT unless doing so would create a cycle.
- Works onUN-directed graphs
- Algorithm still works on edges with identical weight
Edges are sorted by weight first. Depending on the order they are entered into theedge list in theconstructor, you may get different Minimum Spanning Trees (but all still optimal solutions)
Current code runs on this sample graph It produces this Minimum Spanning Tree
It produces this Minimum Spanning Tree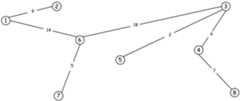
- Requiresdistinct nodes named with consecutive integers. If they reallydo have the same "name", convert them to integer ID's to use this algorithm
Example graph has 8 nodes numbered 1-8 (array ignores the 0th index) - Graph is created as an Edge List
- Make sure
nodeCountis accurate. There's no error checking betweennodeCount& the actual edge list DisjointSet nodeSet = new DisjointSet(nodeCount+1);skips the 0th index by creating a Disjoint Set1 larger than the number of verticesoutputMessageis a string that records the steps the algorithm takes. It's printed to the screen & to a file once complete- My implementation hasearly termination (A Spanning Tree of a graph hasN-1 edges so the algorithm stops whenn it has addedN-1 Edges)Hence
&& mstEdges.size()<(nodeCount-1)in my loop - The
Edgeclass simply packages an edge's weight & 2 vertices together as 1 object
- Disjoint Sets by Mark Allen Weiss Author ofData Structures and Algorithm Analysis in Java (3rd Edition), 2011
He also has other helpfulJava Data Structures implementations
About
Kruskal's Algorithm (greedy) to find a Minimum Spanning Tree on a graph
Topics
Resources
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
No releases published
Packages0
No packages published

