- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork255
Benchmarking Knowledge Transfer in Lifelong Robot Learning
License
Lifelong-Robot-Learning/LIBERO
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
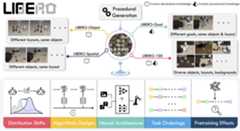
LIBERO is designed for studying knowledge transfer in multitask and lifelong robot learning problems. Successfully resolving these problems require both declarative knowledge about objects/spatial relationships and procedural knowledge about motion/behaviors.LIBERO provides:
- a procedural generation pipeline that could in principle generate an infinite number of manipulation tasks.
- 130 tasks grouped into four task suites:LIBERO-Spatial,LIBERO-Object,LIBERO-Goal, andLIBERO-100. The first three task suites have controlled distribution shifts, meaning that they require the transfer of a specific type of knowledge. In contrast,LIBERO-100 consists of 100 manipulation tasks that require the transfer of entangled knowledge.LIBERO-100 is further splitted intoLIBERO-90 for pretraining a policy andLIBERO-10 for testing the agent's downstream lifelong learning performance.
- five research topics.
- three visuomotor policy network architectures.
- three lifelong learning algorithms with the sequential finetuning and multitask learning baselines.
Please run the following commands in the given order to install the dependency forLIBERO.
conda create -n libero python=3.8.13conda activate liberogit clone https://github.com/Lifelong-Robot-Learning/LIBERO.gitcd LIBEROpip install -r requirements.txtpip install torch==1.11.0+cu113 torchvision==0.12.0+cu113 torchaudio==0.11.0 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113Then install thelibero package:
pip install -e .We provide high-quality human teleoperation demonstrations for the four task suites inLIBERO. To download the demonstration dataset, run:
pythonbenchmark_scripts/download_libero_datasets.py
By default, the dataset will be stored under theLIBERO folder and all four datasets will be downloaded. To download a specific dataset, use
pythonbenchmark_scripts/download_libero_datasets.py--datasetsDATASET
whereDATASET is chosen from[libero_spatial, libero_object, libero_100, libero_goal.
NEW!!!
Alternatively, you can download the dataset from HuggingFace by using:
pythonbenchmark_scripts/download_libero_datasets.py--use-huggingface
This option can also be combined with the specific dataset selection:
pythonbenchmark_scripts/download_libero_datasets.py--datasetsDATASET--use-huggingface
The datasets hosted on HuggingFace are available athere.
For a detailed walk-through, please either refer to the documentation or the notebook examples provided under thenotebooks folder. In the following, we provide example scripts for retrieving a task, training and evaluation.
The following is a minimal example of retrieving a specific task from a specific task suite.
fromlibero.liberoimportbenchmarkfromlibero.libero.envsimportOffScreenRenderEnvbenchmark_dict=benchmark.get_benchmark_dict()task_suite_name="libero_10"# can also choose libero_spatial, libero_object, etc.task_suite=benchmark_dict[task_suite_name]()# retrieve a specific tasktask_id=0task=task_suite.get_task(task_id)task_name=task.nametask_description=task.languagetask_bddl_file=os.path.join(get_libero_path("bddl_files"),task.problem_folder,task.bddl_file)print(f"[info] retrieving task{task_id} from suite{task_suite_name}, the "+ \f"language instruction is{task_description}, and the bddl file is{task_bddl_file}")# step over the environmentenv_args= {"bddl_file_name":task_bddl_file,"camera_heights":128,"camera_widths":128}env=OffScreenRenderEnv(**env_args)env.seed(0)env.reset()init_states=task_suite.get_task_init_states(task_id)# for benchmarking purpose, we fix the a set of initial statesinit_state_id=0env.set_init_state(init_states[init_state_id])dummy_action= [0.]*7forstepinrange(10):obs,reward,done,info=env.step(dummy_action)env.close()
Currently, we only support sparse reward function (i.e., the agent receives+1 when the task is finished). As sparse-reward RL is extremely hard to learn, currently we mainly focus on lifelong imitation learning.
To start a lifelong learning experiment, please choose:
BENCHMARKfrom[LIBERO_SPATIAL, LIBERO_OBJECT, LIBERO_GOAL, LIBERO_90, LIBERO_10]POLICYfrom[bc_rnn_policy, bc_transformer_policy, bc_vilt_policy]ALGOfrom[base, er, ewc, packnet, multitask]
then run the following:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=GPU_ID&& \export MUJOCO_EGL_DEVICE_ID=GPU_ID&& \python libero/lifelong/main.py seed=SEED \ benchmark_name=BENCHMARK \ policy=POLICY \ lifelong=ALGO
Please see the documentation for the details of reproducing the study results.
By default the policies will be evaluated on the fly during training. If you have limited computing resource of GPUs, we offer an evaluation script for you to evaluate models separately.
python libero/lifelong/evaluate.py --benchmark BENCHMARK_NAME \ --task_id TASK_ID\ --algo ALGO_NAME \ --policy POLICY_NAME \ --seed SEED \ --ep EPOCH \ --load_task LOAD_TASK \ --device_id CUDA_IDIf you findLIBERO to be useful in your own research, please consider citing our paper:
@article{liu2023libero,title={LIBERO: Benchmarking Knowledge Transfer for Lifelong Robot Learning},author={Liu, Bo and Zhu, Yifeng and Gao, Chongkai and Feng, Yihao and Liu, Qiang and Zhu, Yuke and Stone, Peter},journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.03310},year={2023}}
| Component | License |
|---|---|
| Codebase | MIT License |
| Datasets | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) |
About
Benchmarking Knowledge Transfer in Lifelong Robot Learning
Topics
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Contributors4
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.