- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork6
📘 CHAPTER-1 📘 Github Training: Introduction to Github 101 🚀
License
CodeMacrocosm/Github-Training
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
🌟🌟🌟🌟
🌟🌟🌟🌟
- Introduction
- What will you Learn?
- What is GitHub?
- No Coding Necessary
- How to start?
- Why this Training
- License
- Star this Repo
- Celebrate!
TheHello World project Training is hosted byShreya Malogi , is a time-honored tradition in computer programming. It is a simple exercise that gets you started when learning something new. Let’s get started with GitHub! 🌐
By the end of this training, you will be able to make your own Codecosmers rep0,
P.S : CodeCosmers are the Stakeholders in Codemacrocosm
Enjoy your journey into GitHub! 🚀✨
- Create and use a repository 📁
- Start and manage a new branch 🌿
- Make changes to a file and push them to GitHub as commits 💻
- Open and merge a pull request 🔄
GitHub is a code hosting platform for version control and collaboration. It lets you and others work together on projects from anywhere. 🌍
This tutorial teaches you GitHub essentials likerepositories,branches,commits, andPull Requests. You’ll create your own Hello CodeCosmers repository and learn GitHub’s Pull Request workflow, a popular way to create and review code. 📝
To complete this tutorial, you need aGitHub.com account and Internet access. You don’t need to know how to code, use the command line, or install Git (the version control software GitHub is built on). 🌐
Tip: Open this guide in a separate browser window (or tab) so you can see it while you complete the steps in the tutorial. 🌟
Click here
Arepository is usually used to organize a single project. Repositories can contain folders and files, images, videos, spreadsheets, and data sets – anything your project needs. We recommend including aREADME, or a file with information about your project. GitHub makes it easy to add one at the same time you create your new repository. 📁
Yourhello-CodeCosmers repository can be a place where you store ideas, resources, or even share and discuss things with others. 🤝
- To create a new repository 🌟
- In the upper right corner, next to your avatar or identicon, clickand then selectNew repository. 📅
- Name your repository
hello-CodeCosmers. 🌐 - Write a short description. 📝
- SelectInitialize this repository with a README. 📂
ClickCreate repository. 🚀
Branching is the way to work on different versions of a repository at one time. 🔄
By default, your repository has one branch named
masterwhich is considered to be the definitive branch. We use branches to experiment and make edits before committing them tomaster. 🎨When you create a branch off the
masterbranch, you’re making a copy, or snapshot, ofmasteras it was at that point in time. If someone else made changes to themasterbranch while you were working on your branch, you could pull in those updates. 🔄This diagram shows:
The
masterbranch 🌟A new branch called
feature(because we’re doing ‘feature work’ on this branch) 🌟The journey that
featuretakes before it’s merged intomaster🌟
Have you ever saved different versions of a file? Something like:
story.txt📖story-shreya-edit.txt✏️story-shreya-edit-reviewed.txt📝
Branches accomplish similar goals in GitHub repositories. 🌟
Here at GitHub, our developers, writers, and designers use branches for keeping bug fixes and feature work separate from our
master(production) branch. When a change is ready, they merge their branch intomaster. 🤝To create a new branch 🌿
- Go to your new repository
hello-CodeCosmers. 🚀 - Click the drop down at the top of the file list that saysbranch: master. 🌿
- Type a branch name,
readme-edits, into the new branch text box. 📝 - Select the blueCreate branch box or hit “Enter” on your keyboard. 🚀
- Now you have two branches,
masterandreadme-edits. They look exactly the same, but not for long! Next, we’ll add our changes to the new branch. 🌟
Bravo! Now, you’re on the code view for your
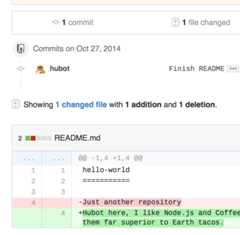
readme-editsbranch, which is a copy ofmaster. Let’s make some edits. 💻On GitHub, saved changes are calledcommits. Each commit has an associatedcommit message, which is a description explaining why a particular change was made. Commit messages capture the history of your changes, so other contributors can understand what you’ve done and why. 📜
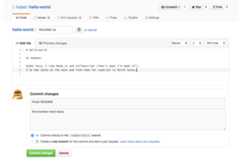
Make and commit changes 📝
- Click the
README.mdfile. 📖
- Click the
- Click thepencil icon in the upper right corner of the file view to edit. ✏️
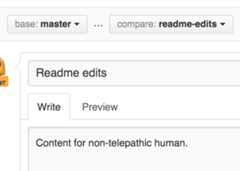
- In the editor, write a bit about yourself. 🤖
- Write a commit message that describes your changes. 📝
- ClickCommit changes button. 🚀
- These changes will be made to just the README file on your
readme-editsbranch, so now this branch contains content that’s different frommaster. 🌟
Nice edits! Now that you have changes in a branch off of
master, you can open apull request. 🌟Pull Requests are the heart of collaboration on GitHub. When you open apull request, you’re proposing your changes and requesting that someone review and pull in your contribution and merge them into their branch. Pull requests showdiffs, or differences, of the content from both branches. The changes, additions, and subtractions are shown in green and red. 🌟
As soon as you make a commit, you can open a pull request and start a discussion, even before the code is finished. 🌟
By using GitHub’s@mention system in your pull request message, you can ask for feedback from specific people or teams, whether they’re down the hall or 10 time zones away. 🌟
You can even open pull requests in your own repository and merge them yourself. It’s a great way to learn the GitHub Flow before working on larger projects. 🌟
- Open a Pull Request for changes to the README 📜
Click on the image for a larger version 🌟
- When you’re done with your message, clickCreate pull request! 🌟
Tip: You can useemoji anddrag and drop images and gifs onto comments and Pull Requests. 🌟
- In this final step, it’s time to bring your changes together – merging your
readme-editsbranch into themasterbranch. 🌟
- Click the greenMerge pull request button to merge the changes into
master. 🔄 - ClickConfirm merge. 🌟
- Go ahead and delete the branch, since its changes have been incorporated, with theDelete branch button in the purple box. ❌
Whether you're a coding novice or an experienced developer looking to enhance your GitHub skills, this hands-on experience is tailored to ensure effective learning. This training provides a comprehensive understanding of GitHub's fundamental concepts and workflows. From creating repositories to making pull requests, you'll gain practical insights that are valuable for both beginners and seasoned developers. Join us on this coding adventure and elevate your collaboration game! 🚀💻🌐📘🌟
This repository is open-source and distributed under the MIT License.
MIT License
Copyright (c) 2020 CodeMacrocosm
If you find this training program helpful and valuable, don't forget to star this repository to show your support!
By completing this training, you’ve learned to create a project and make a pull request on GitHub! 🌟
Here’s what you accomplished in this tutorial:
- Created an open-source repository 📁
- Started and managed a new branch 🌿
- Changed a file and committed those changes to GitHub 💻
- Opened and merged a Pull Request 🔄
Take a look at your GitHub profile, and you’ll see your newcontribution squares! 🌟
To learn more about the power of Pull Requests, we recommend reading theGitHub Flow Guide. You might also visitGitHub Explore and get involved in an Open Source project
We hope you find these resources engaging and beneficial. If you have any questions or suggestions, feel free to reach out.
Happy Learning! 🌟
About
📘 CHAPTER-1 📘 Github Training: Introduction to Github 101 🚀
Topics
Resources
License
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.