- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork13
How to use Azure Kubernetes Service end-to-end for Java apps? Illustrates using a Microservice Architecture with Spring Boot, Spring Cloud and Docker -- Piggymetrics
License
Azure-Samples/java-on-aks
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
| page_type | languages | products | description | urlFragment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
sample |
|
| End-to-end experience for Java apps in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | java-on-aks |
This guide walks you through how to deploy and manage Java apps on the Azure Kubernetes Service.
You will:
- Build Piggymetrics - build a proof-of-concept application, which demonstratesmicro service architecture pattern using Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
- Create Mongodb and RabbitMQ on Azure
- Create Azure Kubernetes Service and Azure Container Registry
- Deploy Piggymetrics to Azure Kubernetes Service
- Troubleshoot Java apps in Azure Kubernetes Service
- Automate and rapidly deploy changes to Azure Kubernetes Service - using GitHub Actions or Azure Pipelines
- Rapidly deploy changes to Azure Kubernetes without disruption - blue-green deployments
- Scale out Java apps in Azure Kubernetes Service
- Learn about next steps to production
In order to deploy a Java Web app to cloud, you needan Azure subscription. If you do not already have an Azuresubscription, you can activate yourMSDN subscriber benefitsor sign up for afree Azure account.
In addition, you will need the following:
|Azure CLI|Java 8|Maven 3|Git|ACR Docker Credential Helper|Docker|Kubectl|Helm|dos2unix|
Clone this GitHub repo and change directory:
git clone https://github.com/Azure-Samples/java-on-aks.gitcd java-on-aksYou can create MongoDB and RabbitMQ on Azure by following steps outlinedhereand capture MongoDB and RabbitMQ coordinates and credentials insetup-env-variables-azure.sh.
If you have not yet setup the development environment,make a copy of the setup environment variables bash script:
cp .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure-template.sh .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.sh
Prep the dev environment by populating environment variables in.scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.shbash script:
# ====== Piggy Metrics Azure Coordinatesexport RESOURCE_GROUP=INSERT-your-resource-group-nameexport REGION=westus2export AKS_CLUSTER=INSERT-your-AKS-cluster-nameexport CONTAINER_REGISTRY=INSERT-your-Azure-Container-Registry-name## ===== Mongo DBexport MONGODB_DATABASE=INSERT-your-mongodb-database-nameexport MONGODB_USER=INSERT-your-cosmosdb-account-nameexport MONGODB_URI="INSERT-your-mongodb-connection-string"export MONGODB_RESOURCE_ID=INSERT-your-mongodb-resource-id## ===== Rabbit MQexport RABBITMQ_RESOURCE_GROUP=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-resource-group-nameexport RABBITMQ_VM_NAME=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-virtual-machine-nameexport RABBITMQ_ADMIN_USERNAME=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-admin-user-name# Rabbit MQexport RABBITMQ_HOST=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-host-public-ip-addressexport RABBITMQ_PORT=5672export RABBITMQ_USERNAME=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-usernameexport RABBITMQ_PASSWORD=INSERT-your-rabbitmq-password
Then, export these environment variables from thejava-on-aks directory:
source .scripts/setup-env-variables-azure.shCreate an Azure Container Registry instance using Azure CLI:
# Create a Resource Group, if you have not created oneaz group create --name${RESOURCE_GROUP} \ --location${REGION}# Create Azure Container Registryaz acr create --name${CONTAINER_REGISTRY} \ --resource-group${RESOURCE_GROUP} \ --sku basic --location${REGION}# Log into Azure Container Registryaz acr login -n${CONTAINER_REGISTRY}
Create an Azure Kubernetes Service instance and attach the Azure Container Registry using Azure CLI:
az aks create --name${AKS_CLUSTER} \ --resource-group${RESOURCE_GROUP} \ --location${REGION} \ --attach-acr${CONTAINER_REGISTRY} \ --node-vm-size Standard_DS3_v2 \ --node-count 5
Get access credentials for the AKS cluster:
az aks get-credentials --name${AKS_CLUSTER} \ --resource-group${RESOURCE_GROUP}
If you do not have an instance of Application Insights, seehow to create Application Insights.
Download Java agent (download link)for auto instrumenting for monitoring Java apps on an Azure Kubernetes Service.
From a Linux or MacOS terminal, execute init.sh from the release.
source init.shOpen the generatedvalues.yaml file in an editor and fill up Kubernetes Clustertarget namespace, saydefault, and Application InsightsInstrumentation Key. Like this:
namespaces: -target:"default"# kubernetes namespace where the Java apps will be auto-instrumentediKey:"c197cf6b-WWWW-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZZZZZZZZZ"# Instrumentation Key of the receiving Application Insights resource
Install the Java agent for auto instrumentation:
helm install ./helm-<version>.tgz -f values.yaml --generate-name
Build Java apps, container images and push images to Azure Container Registryusing Maven andJib:
cd configmvn compile jib:build \ -Djib.container.environment=CONFIG_SERVICE_PASSWORD=${CONFIG_SERVICE_PASSWORD}cd ../registrymvn compile jib:buildcd ../gatewaymvn compile jib:buildcd ../auth-servicemvn compile jib:buildcd ../account-servicemvn compile jib:build \ -Djib.container.environment=ACCOUNT_SERVICE_PASSWORD=${ACCOUNT_SERVICE_PASSWORD}cd ../statistics-servicemvn compile jib:build \ -Djib.container.environment=STATISTICS_SERVICE_PASSWORD=${STATISTICS_SERVICE_PASSWORD}cd ../notification-servicemvn compile jib:build \ -Djib.container.environment=NOTIFICATION_SERVICE_PASSWORD=${NOTIFICATION_SERVICE_PASSWORD}
Jib is configured to start from a production-ready distribution of Java. For example:
<plugin> <groupId>com.google.cloud.tools</groupId> <artifactId>jib-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.8.0</version> <configuration> <from><!-- production-ready distribution of Java--> <image>mcr.microsoft.com/java/jre-headless:8u232-zulu-alpine</image> </from> <to> <image>${CONTAINER_REGISTRY}.azurecr.io/${parent.artifactId}-${project.name}</image> </to> <container> <jvmFlags> <jvmFlag>-Xms2048m</jvmFlag> <jvmFlag>-Xmx2048m</jvmFlag> </jvmFlags> <ports> <port>${CONFIG_PORT}</port> </ports> <labels> <key1>${project.version}</key1> </labels> </container> </configuration></plugin>
Prepare Kubernetes manifest files using the suppliedbash script:
# cd to kubernetes foldercd ../kubernetessource ../.scripts/prepare-kubernetes-manifest-files.sh
You can create Secrets for deploying micro service apps in Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f deploy/0-secrets.yaml# you can view Secrets in Kubernetes using:kubectl get secret piggymetrics -o yamlYou can deploy the Spring Cloud Config Server to Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f deploy/1-config.yaml
You can deploy the Spring Cloud Service Registry to Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f deploy/2-registry.yaml
You can validate that a Spring Cloud Config Server is up and running byinvoking its REST API.
The Spring Cloud Config Server REST API has resources in the following form:
/{application}/{profile}[/{label}]/{application}-{profile}.yml/{label}/{application}-{profile}.yml/{application}-{profile}.properties/{label}/{application}-{profile}.propertiesYou can get IP addresses of Spring Cloud Config Server and Spring Cloud Service Registryusingkubectl:
kubectl get servicesNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEconfig LoadBalancer 10.0.34.171 51.143.50.77 8888:31892/TCP 3m15skubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1<none> 443/TCP 3h42mregistry LoadBalancer 10.0.198.13 52.137.96.211 8761:31689/TCP 6s
Try:
open http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-config>:8888/gateway/profileopen http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-config>:8888/account-service/profileopen http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-config>:8888/statistics-service/profileopen http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-config>:8888/notification-service/profile...open http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-config>:8888/notification-service/profile/development...
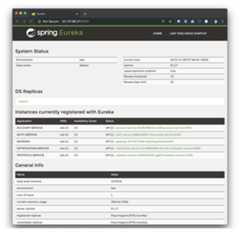
You can validate that a Spring Cloud Service Registry is up and running byopening the Service Registry Dashboard:
open http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-registry>:8761/
You can deploy the Spring Cloud Gateway to Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f deploy/3-gateway.yaml
You can deploy Spring Cloud micro service apps to Kubernetes:
kubectl apply -f deploy/4-auth-service.yamlkubectl apply -f deploy/5-account-service.yamlkubectl apply -f deploy/6-statistics-service.yamlkubectl apply -f deploy/7-notification-service.yaml
You can validate that Spring Cloud middleware components and micro service apps are running:
kubectl get servicesNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGEaccount-service ClusterIP 10.0.215.174<none> 6000/TCP 108sauth-service ClusterIP 10.0.164.45<none> 5000/TCP 2m26sconfig LoadBalancer 10.0.34.171 51.143.50.77 8888:31892/TCP 24mgateway LoadBalancer 10.0.154.13 52.143.88.12 80:31412/TCP 4m3skubernetes ClusterIP 10.0.0.1<none> 443/TCP 4h3mnotification-service ClusterIP 10.0.169.231<none> 8000/TCP 63sregistry LoadBalancer 10.0.198.13 52.137.96.211 8761:31689/TCP 21mstatistics-service ClusterIP 10.0.217.229<none> 7000/TCP 76s
You can also validate that byopening the Spring Cloud Service Registry Dashboard
open http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-registry>:8761/
Open the Piggymetrics landing page by using thegateway app'sEXTERNAL-IP.
open http://<EXTERNAL-IP-of-gateway>/
For example:
With out-of-the-box support for aggregating logs, metrics, anddistributed app traces into Azure Monitor, you can easily visualizehow your applications are performing, detect and diagnose issuesacross micro service applications and their dependencies, drillinto monitoring data for troubleshooting and gain betterunderstanding of what end-users do with your apps.
You can run Spring Cloud Config, Spring Cloud Service Registry,Spring Cloud Gateway and other Spring Cloud components on their dev machine.You can attach debuggers to Spring Cloud micro service apps and step through them. You canlook at logs and metrics. Use Java Flight Recorder, etc.
You can stream logs from micro service apps running on Kubernetes to yourdevelopment machine usingkubectl, like:
# Stream logs from Spring Cloud Config Serverkubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=config# Stream logs from Spring Cloud Service Registrykubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=registry# Stream logs from Spring Cloud Gatewaykubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=gateway# Stream logs from Spring Cloud micro service appskubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=auth-servicekubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=account-servicekubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=statistics-servicekubectl logs -f --timestamps=true -l app=notification-service
You can aggregate logs in Azure Log Analytics and retrieve themusing Kusto queries. If you do not have a Log Analytics Workspace in Azure,seehow to create a Log Analytics Workspace
You can onboard your Kubernetes cluster to Azure Monitor for monitoring, by clickingon theLogs blade in the Azure Portal and choosing your Log Analytics Workspace:
Then, you can view logs using Kusto queries in theLogs blade of yourLog Analytics Workspace:
Here are some sample Kusto queries for viewing logs for each of the micro service apps -please replacejava-on-aks with your Azure Kubernetes cluster name:
-- Logs for Spring Cloud Config Serverlet ContainerIdList= KubePodInventory|where ContainerName contains'config'|where ClusterId contains'java-on-aks'| distinct ContainerID;ContainerLog|where ContainerIDin (ContainerIdList)|where LogEntry !contains"AI:" | project LogEntrySource, LogEntry, TimeGenerated, Computer, Image, Name, ContainerID|order by TimeGenerateddesc| render table-- Logs for Spring Cloud Service Registrylet ContainerIdList= KubePodInventory|where ContainerName contains'registry'|where ClusterId contains'java-on-aks'| distinct ContainerID;ContainerLog|where ContainerIDin (ContainerIdList)|where LogEntry !contains"AI:" | project LogEntrySource, LogEntry, TimeGenerated, Computer, Image, Name, ContainerID|order by TimeGenerateddesc| render table-- Logs for Spring Cloud Gatewaylet ContainerIdList= KubePodInventory|where ContainerName contains'gateway'|where ClusterId contains'java-on-aks'| distinct ContainerID;ContainerLog|where ContainerIDin (ContainerIdList)|where LogEntry !contains"AI:" | project LogEntrySource, LogEntry, TimeGenerated, Computer, Image, Name, ContainerID|order by TimeGenerateddesc| render table-- Logs for Account Service micro service applet ContainerIdList= KubePodInventory|where ContainerName contains'account-service'|where ClusterId contains'java-on-aks'| distinct ContainerID;ContainerLog|where ContainerIDin (ContainerIdList)|where LogEntry !contains"AI:" | project LogEntrySource, LogEntry, TimeGenerated, Computer, Image, Name, ContainerID|order by TimeGenerateddesc| render table-- Logs for Auth Service micro service applet ContainerIdList= KubePodInventory|where ContainerName contains'auth-service'|where ClusterId contains'java-on-aks'| distinct ContainerID;ContainerLog|where ContainerIDin (ContainerIdList)|where LogEntry !contains"AI:" | project LogEntrySource, LogEntry, TimeGenerated, Computer, Image, Name, ContainerID|order by TimeGenerateddesc| render table
You can use Application Insights to monitor your live web application. It willautomatically detect performance anomalies. It includes powerful analytics tools tohelp you diagnose issues and to understand what users actually do with your app. It is designed tohelp you continuously improve performance and usability.
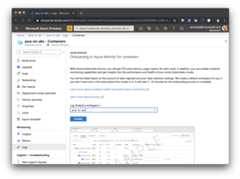
After some time, you can see distributed tracing in theconfigured Application Insights instance. Go to the `Application Map' blade in the Azure Portal: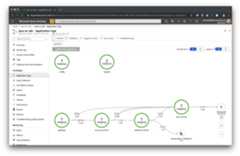
Also, you can view the performance and call drill downs in thePerformance blade: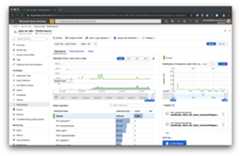
Create an Azure Pipelines CI/CD pipeline that automatically builds the code and deploys it to the Azure Kubernetes Cluster whenever there's a commit to the repository.
There are some additional prerequisites for this automation:
- GitHub Account
- Azure DevOps Organization
- Environment with AKS resource which creates a service account in the chosen cluster and namespace, which will be used by Azure DevOps account to deploy to AKS
- Azure service connection using service principal to establish authentication between Azure & Azure DevOps services
Important
To simplify the service connection, use the same email address for Azure DevOps as you use for Azure.
- Create an Azure KeyVault and upload secrets. Ensure the service principal used in the service connection above has GET, LISTpermissions on the vault. Use below command for that:
az keyvault set-policy -n $KV_NAME --secret-permissions get list --spn <clientId from the Azure SPN JSON>Sign into Azure Pipelines and Create a Pipeline using the
azure-pipelines.ymlfile.Take a look at the pipeline to see what it does. Make sure that all the default inputs are appropriate for your code.
The azure-pipelines.yml file contains the following key elements:
- The
triggerat the top indicates the commits that trigger the pipeline, such as commits to themasterbranch. - The
variableswhich parameterize the YAML template - The
stages- Build
stage, which builds your app, and a Deploystage, which deploys it to AKS cluster. - Deploy
stagealso refers the Environment with Kubernetes resource. Ensure to modify the environment name to the one that you have created.
- Build
- AzureKeyVault task is used in both the stages to fetch the secrets from Azure Key Vault instance and set as variables. In the
Deploystage, these variables are used to set secrets in the pods. - Kubernetes Manifest task has the added benefits of being able to check for object stability before marking a task as success/failure, perform artifact substitution, add pipeline traceability-related annotations onto deployed objects, simplify creation and referencing of imagePullSecrets
- The
After you've looked at what the pipeline does, select Save and run, after which you're prompted for a commit message because Azure Pipelines adds the azure-pipelines.yml file to your repository. After editing the message, select Save and run again to see your pipeline in action.
As your pipeline runs, watch as your build stage, and then your deployment stage, go from blue (running) to green (completed). You can select the stages and jobs to watch your pipeline in action.
Additionally, you can also explore Kubernetes objects created and the deployment history for the App by navigating to the "Environment".
- From the pipelinesummary -> Select theEnvironments tab -> SelectView environment
- Resources view within the environment provides a glimpse of the status of objects within the namespace mapped to the resource. It also overlays pipeline traceability on top of these objects so that one can trace back from a Kubernetes object to the pipeline and then back to the commit.
You can also configure aWorkflow to automate build and deployin GitHubusing theworkflow.yml.
Create secrets for every parameter in
.scripts/setup-env-variables-azure-template.sh.- SetGitHub Repo Secrets AZURE_CREDENTIALS, AKS_CLUSTER_NAME, AKS_RESOURCE_GROUP and AKS_NAMESPACE with Azure creds, AKS cluster name, resource group name and namespace
- For configuring App secrets, You could either set them asGitHub Secrets or fetch them from an Azure Key Vault instance.
workflow.ymlcontains the following key elements:- The
on: [push]at the top indicates the commits that trigger the pipeline, such as every commit to the branch. - The
env:with variables which parameterize the YAML template - The
jobs: Buildjob, which builds your app, and a Deployjob, which deploys it to AKS cluster. Each job hasstepswhich eitherusesanactionorruna script, all of which execute on a hosted-runner defined byruns-on. - AzureKeyVault action is used in both the jobs to fetch the secrets from Azure Key Vault instance and set as environment variables. In the
Deployjob, these variables are used to set secrets in the pods. - Actions to deploy to AKS are then used to create imagepullsecret, set secrets on pods and finally to deploy to AKS cluster.
- The
- To be supplied
You can scale out micro service apps in Azure Kubernetes Service:
kubectl scale deployment gateway --replicas=4kubectl describe deployment gatewayName: gatewayNamespace: defaultCreationTimestamp: Sat, 07 Dec 2019 22:36:27 -0800Labels: app=gateway project=piggymetrics tier=frontendAnnotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1 kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: {"apiVersion":"extensions/v1beta1","kind":"Deployment","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"app":"gateway","project":"piggymetrics","ti...Selector: app=gateway,project=piggymetrics,tier=frontendReplicas: 4 desired | 4 updated | 4 total | 4 available | 0 unavailableCongratulations!!
You built, deployed, scaled out and setup monitoring for Spring Cloud micro service appsusing Spring Boot and Spring Cloud, Azure Kubernetes Service, Azure Container Registry,Azure Monitor, Log Analytics and Application Insights.
To advance Java deployments on Kubernetes to production, you should thinkabout the following next steps:
- Frame a scalable infrastructure with Azure Kubernetes Service and Azure Container Registryto satisfy your deployments' business and technical requirements. SeeMicroservices architecture on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Frame a plan to assume infrastructure management -- including load balancers, clustering,security, SSL offloading, domain name mapping, etc.
- Define an application lifecyle for apps on Azure Kubernetes Service and use themacross developer and DevOps automation tools. This lifecyle should include asource-to-container strategy
- Frame a plan to assume service management -- including configuration, managing secrets, backup & restore,monitoring & log shipping, upgrades, auto-restart, auto-scale or manual-scale, etc. If you are deployingSpring Cloud micro service apps, service management should includestrategies for manually or dynamically scaling Spring Cloud middleware components -Spring Cloud Config Server,Spring Cloud Service Registry, Spring Cloud Gateway, etc.
- Azure Kubernetes Story
- Azure Container Registry
- Production Ready and Supported Java Container Images
- Kusto Query Language
kubectlCheat Sheet 1kubectlCheat Sheet 2- Debugging Applications in Kubernetes Cluster
- Triage Micro Service Applications using Application Map
- Azure for Java Cloud Developers
- Spring Cloud Azure
- Spring Cloud
- Azure Pipelines - Build and Deploy to Azure Kubernetes Service
- Azure Pipelines - Azure Key Vault Task
- GitHub Actions - Workflow to automate build and deploy
- ...
This Java micro services sample is forked fromsqshq/Piggymetrics - seePiggymetrics README.
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to aContributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant usthe rights to use your contribution. For details, visithttps://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to providea CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructionsprovided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted theMicrosoft Open Source Code of Conduct.For more information see theCode of Conduct FAQ orcontactopencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
About
How to use Azure Kubernetes Service end-to-end for Java apps? Illustrates using a Microservice Architecture with Spring Boot, Spring Cloud and Docker -- Piggymetrics
Topics
Resources
License
Code of conduct
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Contributors3
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Languages
- Java40.4%
- CSS26.8%
- JavaScript19.2%
- HTML10.1%
- Shell2.9%
- Dockerfile0.6%