- Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork0
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
AbdalkarimA/iClusterVB
Folders and files
| Name | Name | Last commit message | Last commit date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Repository files navigation
iClusterVB allows for fast integrative clustering and feature selectionfor high dimensional data.
Using a variational Bayes approach, its key features - clustering ofmixed-type data, automated determination of the number of clusters, andfeature selection in high-dimensional settings - address the limitationsof traditional clustering methods while offering an alternative andpotentially faster approach than MCMC algorithms, makingiClusterVBa valuable tool for contemporary data analysis challenges.
You can install iClusterVB from CRAN with:
install.packages("iClusterVB")You can install the development version of iClusterVB fromGitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")devtools::install_github("AbdalkarimA/iClusterVB")
Mandatory arguments
mydata: A list of length R, where R is the number of datasets,containing the input data.- Note: Forcategorical data,
0’s must be re-coded to another,non-0value.
- Note: Forcategorical data,
dist: A vector of length R specifying the type of data ordistribution. Options include: "gaussian" (for continuous data),"multinomial" (for binary or categorical data), and "poisson" (forcount data).
Optional arguments
K: The maximum number of clusters, with a default value of 10. Thealgorithm will converge to a model with dominant clusters, removingredundant clusters and automating the process of determining thenumber of clusters.initial_method: The method for the initial cluster allocation, whichthe iClusterVB algorithm will then use to determine the final clusterallocation. Options include "VarSelLCM" (default) for VarSelLCM,"random" for a random sample, "kproto" for k-prototypes, "kmeans" fork-means (continuous data only), "mclust" for mclust (continuous dataonly), or "lca" for poLCA (categorical data only).VS_method: The feature selection method. The options are 0 (default)for clustering without feature selection and 1 for clustering withfeature selectioninitial_cluster: The initial cluster membership. The default isNULL, which usesinitial_methodfor initial cluster allocation. Ifit is not NULL, it will overwrite the previous initial values settingfor this parameter.initial_vs_prob: The initial feature selection probability, ascalar. The default is NULL, which assigns a value of 0.5.initial_fit: Initial values based on a previously fitted iClusterVBmodel (an iClusterVB object). The default is NULL.initial_omega: Customized initial values for feature inclusionprobabilities. The default is NULL. If the argument is not NULL, itwill overwrite the previous initial values setting for this parameter.IfVS_method = 1,initial_omegais a list of length R, and eachelement of the list is an array with dim=c(N,p[[r]])). N is thesample size and p[[r]] is the number of features for dataset r, r= 1,…,R.initial_hyper_parameters: A list of the initial hyper-parameters ofthe prior distributions for the model. The default is NULL, whichassignsalpha_00 = 0.001, mu_00 = 0,s2_00 = 100, a_00 = 1, b_00 = 1, kappa_00 = 1, u_00 = 1, v_00 = 1.These are$\boldsymbol{\alpha}_0, \mu_0, s^2_0, a_0, b_0, \boldsymbol{\kappa}_0, c_0, \text{and } d_0$ described inhttps://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4971680.max_iter: The maximum number of iterations for the VB algorithm. Thedefault is 200.early_stop: Whether to stop the algorithm upon convergence or tocontinue untilmax_iteris reached. Options are 1 (default) to stopwhen the algorithm converges, and 0 to stop only whenmax_iterisreached.per: Print information every "per" iteration. The default is 10.convergence_threshold: The convergence threshold for the change inELBO. The default is 0.0001.
We will demonstrate the clustering and feature selection performance ofiClusterVB using a simulated dataset comprising
| Data View | Cluster | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (Continuous) | Cluster 1 | |
| Cluster 2 | ||
| Cluster 3 | ||
| Cluster 4 | ||
| 2 (Continuous) | Cluster 1 | |
| Cluster 2 | ||
| Cluster 3 | ||
| Cluster 4 | ||
| 3 (Count) | Cluster 1 | |
| Cluster 2 | ||
| Cluster 3 | ||
| Cluster 4 | ||
Distribution of relevant and noise features across clusters in each dataview
The simulated dataset is included as a list in the package.
library(iClusterVB)# Input data must be a listdat1<-list(gauss_1=sim_data$continuous1_data,gauss_2=sim_data$continuous2_data,multinomial_1=sim_data$binary_data)dist<- c("gaussian","gaussian","multinomial")
set.seed(123)fit_iClusterVB<- iClusterVB(mydata=dat1,dist=dist,K=8,initial_method="VarSelLCM",VS_method=1,# Variable Selection is onmax_iter=100,per=100)#> ------------------------------------------------------------#> Pre-processing and initializing the model#> ------------------------------------------------------------#> ------------------------------------------------------------#> Running the CAVI algorithm#> ------------------------------------------------------------#> iteration = 100 elbo = -21293757.232508
table(fit_iClusterVB$cluster,sim_data$cluster_true)#>#> 1 2 3 4#> 4 0 0 60 0#> 5 0 60 0 0#> 6 0 0 0 60#> 8 60 0 0 0
# We can obtain a summary using summary()summary(fit_iClusterVB)#> Total number of individuals:#> [1] 240#>#> User-inputted maximum number of clusters: 8#> Number of clusters determined by algorithm: 4#>#> Cluster Membership:#> 4 5 6 8#> 60 60 60 60#>#> # of variables above the posterior inclusion probability of 0.5 for View 1 - gaussian#> [1] "54 out of a total of 500"#>#> # of variables above the posterior inclusion probability of 0.5 for View 2 - gaussian#> [1] "59 out of a total of 500"#>#> # of variables above the posterior inclusion probability of 0.5 for View 3 - multinomial#> [1] "500 out of a total of 500"
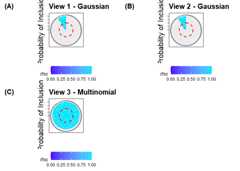
plot(fit_iClusterVB)# The `piplot` function can be used to visualize the probability of inclusionpiplot(fit_iClusterVB)
# The `chmap` function can be used to display heat maps for each data viewlist_of_plots<- chmap(fit_iClusterVB,rho=0,cols= c("green","blue","purple","red"),scale="none")
# The `grid.arrange` function from gridExtra can be used to display all the# plots togethergridExtra::grid.arrange(grobs=list_of_plots,ncol=2,nrow=2)
About
Resources
License
Unknown, MIT licenses found
Licenses found
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.
Stars
Watchers
Forks
Releases
Packages0
Uh oh!
There was an error while loading.Please reload this page.