Localize Messages
This documentation outlines the use ofFCM localization fields(*_loc_key and*_loc_args) to deliver notifications that automatically adaptto a user's language settings on Android and iOS. This lets your server send asingle, language-agnostic payload, delegating the translation to the clientdevice.
FCM Localization Overview
To localize your app, you can send a key that corresponds to a string resourceentry inside the user's application. The device's operating system (OS) handlesthe lookup and insertion of dynamic arguments.
Note: SeeAndroidNotificationandApnsConfigin theHTTP v1 referencedocumentationfor complete detail on the keys available in platform-specific blocks in themessage body. For keys supported by APNS, see Apple'sPayload KeyReference.| FCM Field | Description | Client Action |
|---|---|---|
title_loc_key | The key for the title string in the client app's string resources. | The OS finds the corresponding string in the app's localized files. |
body_loc_key | The key for the body string in the client app's string resources. | The OS finds the corresponding string in the app's localized files. |
title_loc_args | An array of dynamic string values to be substituted into thetitle_loc_key string. | The OS inserts these arguments into the localized string's format specifiers. |
body_loc_args | An array of dynamic string values to be substituted into thebody_loc_key string. | The OS inserts these arguments into the localized string's format specifiers. |
Step 1: Define localized string resources in your apps
To get started withFCM localization, it is important to make sure that you have the necessarytranslations available in your Android and iOS projects.
Android Setup
Define string resources: Enter your default language strings inres/values/strings.xml.Use format specifiers (%1$s,%2$d, etc.) for any dynamic values you plan topass in the*_loc_args.
Default (res/values/strings.xml):
<resources><stringname="welcome_title">Welcome,%1$s!</string><stringname="new_message_body">Youhave%1$dnewmessage(s)from%2$s.</string></resources>Add translations: Create language-specific directories using the ISO languagecodes (e.g.,values-fr for French,values-es for Spanish) and translate the keys.
French (res/values-fr/strings.xml):
<resources><stringname="welcome_title">Bienvenue,%1$s!</string><stringname="new_message_body">Vousavez%1$dnouveau(x)message(s)de%2$s.</string></resources>For more information, use the following documentation:
iOS Setup
Define string resources: Define your base strings in theLocalizable.stringsfile (typically in theBase.lproj folder or a String Catalog). Use formatspecifiers (%@,%ld, etc.) for dynamic values. Keys are often defined inall capital letters for convention.
Default (EnglishLocalizable.strings):
"WELCOME_TITLE"="Welcome, %@!";"NEW_MESSAGE_BODY"="You have %ld new message(s) from %@.";Add translations: Create language-specific.lproj folders (or addlocalizations using a String Catalog) and translate the keys.
French (fr.lproj/Localizable.strings):
"WELCOME_TITLE"="Bienvenue, %@!";"NEW_MESSAGE_BODY"="Vous avez %ld nouveau(x) message(s) de %@.";For more information, use the following documentation:
Step 2: Construct theFCM message payload
When sending the notification using theFCM HTTP v1 API, your serverconstructs a single payload that uses the resource keys (*_loc_key) and thedynamic data (*_loc_args) as an array of strings.
ExampleFCM HTTP v1 Payload
The localization keys are placed within the platform-specific override blocks(android.notification andapns.payload.aps.alert).
{"message":{"token":"DEVICE_REGISTRATION_TOKEN","android":{"notification":{// Android keys match strings.xml resource names"title_loc_key":"welcome_title","title_loc_args":["Alice"],"body_loc_key":"new_message_body","body_loc_args":["3","Bob"]}},"apns":{"payload":{"aps":{"alert":{// iOS uses 'title-loc-key' and 'loc-key' (for the body)"title-loc-key":"WELCOME_TITLE","title-loc-args":["Alice"],"loc-key":"NEW_MESSAGE_BODY","loc-args":["3","Bob"]}}}}}}Key considerations for payload arguments
Order matters: The strings in
*_loc_argsmust be in the exact orderrequired by the placeholders in the string resource file (e.g.,%1$s,%2$s).Strings only: All elements in the
*_loc_argsarray must be strings, evenif they represent numbers (like"3"in the example). The client OS's stringformatter handles the final type conversion based on the format specifier(%ldor%1$d).
Step 3: Client processing and display
When the device receives the notification, the following steps occur automatically:
Language check: The device identifies the user's primary locale (e.g.,German, Italian).
Key lookup: The OS uses the
*_loc_keyvalue (welcome_title) to look upthe corresponding translated string in the app's resource files for thedevice's locale.Argument insertion: The OS takes the array from
*_loc_args(["Alice"])and inserts the values into the localized string, respecting the locale'sformatting rules (punctuation, word order, etc.).
| Device Locale | title_loc_key: welcome_title | title_loc_args: ["Alice"] | Final Title Display |
|---|---|---|---|
| English | "Welcome, %1$s!" | Alice | "Welcome, Alice!" |
| French | "Bienvenue, %1$s!" | Alice | "Bienvenue, Alice!" |
| German | "Willkommen, %1$s!" | Alice | "Willkommen, Alice!" |
This process makes sure that every user receives a message tailored to theirlanguage preferences, using the correct linguistic structure, all whilemaintaining a standardized payload from your server.
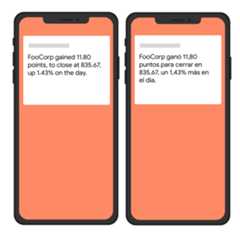
Example: notification message with localization options
The following example send request sends a notification to theTech topic,including localization options for the client to display localized messages.Here's an example of the visual effect on a user's device:
Node.js
vartopicName='industry-tech';varmessage={android:{ttl:3600000,notification:{bodyLocKey:'STOCK_NOTIFICATION_BODY',bodyLocArgs:['FooCorp','11.80','835.67','1.43']}},apns:{payload:{aps:{alert:{locKey:'STOCK_NOTIFICATION_BODY',locArgs:['FooCorp','11.80','835.67','1.43']}}}},topic:topicName,};getMessaging().send(message).then((response)=>{// Response is a message ID string.console.log('Successfully sent message:',response);}).catch((error)=>{console.log('Error sending message:',error);});REST
POST https://fcm.googleapis.com/v1/projects/myproject-b5ae1/messages:send HTTP/1.1Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Bearer ya29.ElqKBGN2Ri_Uz...HnS_uNreA{ "message": { "topic":"Tech", "android": { "ttl":"3600s", "notification": { "body_loc_key": "STOCK_NOTIFICATION_BODY", "body_loc_args": ["FooCorp", "11.80", "835.67", "1.43"] } }, "apns": { "payload": { "aps": { "alert": { "loc-key": "STOCK_NOTIFICATION_BODY", "loc-args": ["FooCorp", "11.80", "835.67", "1.43"] } } } } }}'To learn more, seeAndroidNotificationandApnsConfigin theHTTP v1 referencedocumentationfor complete detail on the keys available in platform-specific blocks in themessage body. For keys supported by APNS, see Apple'sPayload KeyReference.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.