
Korea has had administrative districts that can be considered provinces since the 7th century. These divisions were initially calledju (Korean: 주;Hanja: 州) inUnified Silla andLater Baekje, and there were nine in total. AfterGoryeo conquered these states in the 10th century, twelve divisions calledmok (목;牧) were established, although they were reorganized into tendo (도;道) in the 11th century.
AfterJoseon's conquest of Goryeo, it established theEight Provinces in 1413. These provincial boundaries closely reflected majorregional anddialect boundaries, and are still significant in contemporary Korea. In 1895, as part of theGabo Reform, the country was redivided into 23 districts (Bu; 부;府), which were replaced a year later by thirteen new provinces. The thirteen provinces of 1896 included three of the original eight provinces, with the five remaining original provinces divided into north and south halves (Bukdo (북도;北道) andNamdo (남도;南道) respectively). The thirteen provinces remained unchanged throughout theJapanese colonial period.
With the liberation of Korea in 1945, the Korean peninsula was divided intoNorth Korea andSouth Korea, with the dividing line established along the38th parallel. Three provinces—Hwanghae,Gyeonggi, andGangwon (Kangwŏn)—were modified or split as a part of this. The special cities ofSeoul (South Korea) andP'yŏngyang (North Korea) were formed in 1946. Between 1946 and 1954, five new provinces were created:Jeju in South Korea, andNorth andSouth Hwanghae,Chagang, andRyanggang in North Korea. With the freezing of theKorean War in 1953, provincial boundaries were again modified between the two Koreas, and have since remained mostly unchanged; new cities and special administrative regions have since been created in their provinces.
Although southern part of Korean peninsula was took over by Silla, northern part was not fully conquered by norTang dynasty andSilla. Under the leadership ofTae Joyŏng,Parhae was founded. The country was divided into 5 capitals, 15 provinces; and 62 prefectures. Its territory covered former regions ofGoguryeo while added territories ofOuter Manchuria.
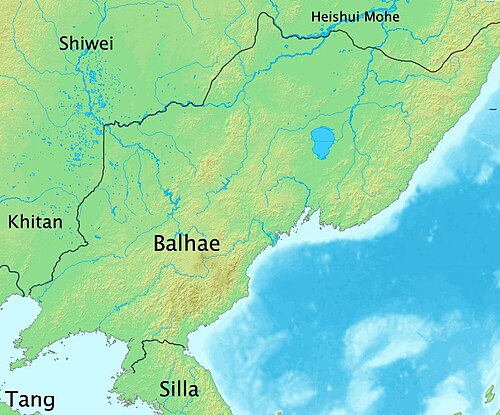
| Hanja | Hangul | RR,Pinyin | Modern location |
|---|---|---|---|
| 上京/龍州 | 상경/용주 | Sanggyeong/Yongju Shangjing/Longzhou | Ning'an (寧安市) (Manchu: Ninguta 寧古塔) |
| 中京/顯州 | 중경/현주 | Junggyeong/Hyeonju Zhongjing/Xianzhou | Helong/Dunhua (和龍市/敦化市) |
| 東京/慶州 | 동경/경주 | Donggyeong/Gyeongju Dongjing/Qingzhou | Hunchun |
| 南京/沃州 | 남경/옥주 | Namgyeong/Okju Nanjing/Wozhou | Hamheung |
| 西京/神州 | 서경/신주 | Seogyeong/Sinju Xijing/Shenzhou | Linjiang |
| 瑕州 | 하주 | Haju Xiazhou | Jingyu (靖宇县) |
| 扶州 | 부주 | Buju Fuzhou | Kaiyuan |
| 鄚州 | 막주 | Makju Mozhou | Acheng (阿城) |
| 定州 | 정주 | Jeongju/Dingzhou | Partizansk |
| 安州 | 안주 | Anju Anzhou | Olga |
| 華州 | 화주 | Hwaju Huazhou | Ussuriysk/Shuaibin |
| 伊州 | 이주 | Iju Yizhou | Dangbi (密山市/当壁鎮) |
| 德理鎮 | 덕리진 | Deongnijin/Delizhen | Yilan (依蘭郷) |
| 達州 | 달주 | Dalju | Tongjiang (同江市) |
| 寧州 | 영주 | Yeongju Ningzhou | Dalnerechensk |

The Korean peninsula was mostly unified for the first time by the stateSilla in the 7th century.[1] Silla's capital was Geumseong (nowGyeongju).[2] It had five sub-capitals (소경;小京;sogyeong) at Geumgwan-gyeong (금관경, nowGimhae), Namwon-gyeong (남원경,Namwon), Seowon-gyeong (서원경,Cheongju), Jungwon-gyeong (중원경,Chungju), and Bugwon-gyeong (북원경,Wonju).[3]
The country was divided into nine provinces (주;ju): three in the pre-660 territory of Silla, and three each in the territories of the former kingdomsBaekje andGoguryeo.[4]
| Province | Hangul | Hanja | Capital | Modern equivalent | Former kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangju [ko] | 양주 | 良州 | Yangju | EasternGyeongsang | Silla |
| Gangju [ko] | 강주 | 康州 | Gangju | WesternSouth Gyeongsang | |
| Sangju [ko] | 상주 | 尙州 | Sangju | WesternNorth Gyeongsang | |
| Muju [ko] | 무주 | 武州 | Muju | South Jeolla | Baekje |
| Jeonju [ko] | 전주 | 全州 | Jeonju | North Jeolla | |
| Ungju [ko] | 웅주 | 熊州 | Gongju | South Chungcheong | |
| Hanju [ko] | 한주 | 漢州 | Hanju | North Chungcheong,Gyeonggi,Hwanghae | Goguryeo |
| Sakju [ko] | 삭주 | 朔州 | Sakju | WesternGangwon | |
| Myeongju [ko] | 명주 | 溟州 | Myeongju | EasternGangwon |

Goryeo was established in the 10th century, and had its capital at Gaegyeong (nowKaesong). It conquered Silla andLater Baekje, and also conquered parts of the former territory ofGoguryeo.[5] Goryeo had three subcapitals: Donggyeong (nowGyeongju), Namgyeong (nowSeoul), and Seogyeong (nowPyongyang).[6]
Goryeo reorganized its provinces several times. Originally, the country had one royal district (기내;畿內;ginae) around Gaegyeong and twelve administrative districts (목;牧;mok).[7] In 995, the twelve districts were redivided into ten provinces (도;道;do).[8] In 1005,[8][clarification needed] the ten provinces were again redivided, this time into five provinces and two frontier districts (계;界;gye). Gyojudo later became its own province after 1178, making it six provinces and two frontier districts.
| Provinces (pre-995)[7] | Provinces (995–1005)[8] | Provinces (post-1005)[9] | Modern equivalent | Silla equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yangju-mok (揚州牧) | Gwannae-do (관내도) | Seohae-do (西海道,서해도) | Hwanghae | Hanju |
| Hwangju-mok (黃州牧) | North Hwanghae | |||
| Haeju-mok (海州牧) | South Hwanghae | |||
| Gwangju-mok (廣州牧) | Yanggwang-do(楊廣道,양광도) | Gyeonggi | ||
| Chungju-mok (忠州牧) | Jungwon-do (중원도) | North Chungcheong | ||
| Cheongju-mok | Ungju | |||
| Gongju-mok | Hanam-do (하남도) | South Chungcheong | ||
| Jeonju-mok (全州牧) | Gangnam-do (강남도) | Jeolla-do(전라도) | Jeonbuk | Jeonju |
| Naju-mok | Haeyang-do (해양도) | South Jeolla | Muju | |
| Seungju-mok | ||||
| Sangju-mok | Yeongnam-do (영남도) | Gyeongsang-do(경상도) | North Gyeongsang | Sangju |
| Jinju-mok | Sannam-do (산남도) | WesternSouth Gyeongsang | Gangju | |
| Yeongdong-do (영동도) | EasternSouth Gyeongsang | Yangju | ||
| — | Sakbang-do (삭방도) | Gyoju-do(교주도,交州道),also known as gyoju gangneungdo(交州江陵道,교주강릉도)[a] | Gangwon | Sakju |
| — | Donggye(東界,동계),also known as Dongbukmyeon(東北面,동북면) | Myeongju | ||
| — | Paeseo-do (패서도) | Bukgye(北界,북계),Also known as Seobukmyeon(西北面,서북면)) | Pyeongan | — |



In 1413, Korea (at that time called Joseon) was divided into eight provinces:Chungcheong,Gangwon,Gyeonggi,Gyeongsang,Jeolla,Hamgyŏng (originally called Yeonggil),Hwanghae (originally called P'unghae), andP'yŏngan.
| RR Romaja | M–R Romaja | Hangul | Hanja | Name origin | Capital | Region | Korean dialect | Post-1896 Provinces |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chungcheong | Ch'ungch'ŏng | 충청도 | 忠淸道 | Chungju (충주 忠州), Cheongju (청주 淸州) | Gongju | Hoseo | Chungcheong dialect | North Chungcheong South Chungcheong |
| Gangwon | Kangwŏn | 강원도 | 江原道 | Gangneung (강릉 江陵), Wonju (원주 原州) | Wonju | Gwandong (Yeongseo,Yeongdong[b] | Gangwon dialect | Gangwon |
| Gyeonggi | Kyŏnggi | 경기도 | 京畿道 | (See note) | Hanseong (Seoul) | Gijeon[c] | Seoul dialect | Gyeonggi |
| Gyeongsang | Kyŏngsang | 경상도 | 慶尙道 | Gyeongju (경주 慶州), Sangju (상주 尙州) | Daegu | Yeongnam | Gyeongsang dialect | North Gyeongsang South Gyeongsang |
| Hamgyeong | Hamgyŏng | 함경도 | 咸鏡道 | Hamhung (함흥 咸興), Kyongsong (경성 鏡城) | Hamhung | Kwanbuk,Kwannam[d] | Hamgyŏng dialect | North Hamgyong South Hamgyong |
| Hwanghae | Hwanghae | 황해도 | 黃海道 | Hwangju (황주 黃州), Haeju (해주 海州) | Haeju | Haeso | Hwanghae dialect | Hwanghae[e] |
| Jeolla | Chŏlla | 전라도 | 全羅道 | Jeonju (전주 全州), Naju (나주 羅州)[f] | Jeonju | Honam | Jeolla dialect; Jeju language[g] | North Jeolla South Jeolla |
| Pyeongan | P'yŏngan | 평안도 | 平安道 | Pyongyang (평양 平壤), Anju (안주 安州) | Pyongyang | Kwanso | Pyongan dialect | North Pyongan South Pyongan |
In 1895, Korea was redivided into 23 districts (Bu; 부;府), each named for the city or county that was its capital. The districts were short-lived, however, as the following year, the provincial system was restored.
In 1896, the former eight provinces were restored, with five of them (Chungcheong, Gyeongsang, Jeolla, Hamgyŏng, and P'yŏngan) being divided into North and South Provinces (Bukdo (북도;北道) andNamdo (남도;南道) respectively). The resulting system of thirteen provinces lasted until theDivision of Korea in 1945.
The thirteen provinces were:North andSouth Chungcheong,Gangwon,Gyeonggi,North andSouth Gyeongsang,North andSouth Hamgyŏng,Hwanghae,North andSouth Jeolla, andNorth andSouth P'yŏngan.

Under ColonialJapanese rule, Korean provinces ofKorean Empire, remained much the same, only taking on theJapanese reading of thehanja. The Provinces of Chōsen were:
| Japanese name | Kanji | Kana | Korean name | Hangul |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chūseihoku-dō | 忠清北道 | ちゅうせいほくどう | Chungcheongbuk-do | 충청북도 |
| Chūseinan-dō | 忠淸南道 | ちゅうせいなんどう | Chungcheongnam-do | 충청남도 |
| Keishōhoku-dō | 慶尚北道 | けいしょうほくどう | Gyeongsangbuk-do | 경상북도 |
| Keishōnan-dō | 慶尚南道 | けいしょうなんどう | Gyeongsangnam-do | 경상남도 |
| Heianhoku-dō | 平安北道 | へいあんほくどう | Pyeonganbuk-do | 평안북도 |
| Heian'nan-dō | 平安南道 | へいあんなんどう | Pyeongannam-do | 평안남도 |
| Kōgen-dō | 江原道 | こうげんどう | Gangwon-do | 강원도 |
| Kōkai-dō | 黃海道 | こうかいどう | Hwanghae-do | 황해도 |
| Kankyōhoku-dō | 咸鏡北道 | かんきょうほくどう | Hamgyeongbuk-do | 함경북도 |
| Kankyōnan-dō | 咸鏡南道 | かんきょうなんどう | Hamgyeongnam-do | 함경남도 |
| Zenranan-dō | 全羅南道 | ぜんらなんどう | Jeollanam-do | 전라남도 |
| Zenrahoku-dō | 全羅北道 | ぜんらほくどう | Jeollabuk-do | 전라북도 |
| Keiki-dō | 京畿道 | けいきどう | Gyeonggi-do | 경기도 |

At the end ofWorld War II in 1945, Korea was divided into Northern Korea and Southern Korea under trusteeship of theSoviet Union and theUnited States. The peninsula was divided at the38th parallel in 1945. In 1948, the two zones became the independent countries ofNorth Korea andSouth Korea.
Three provinces—Hwanghae, Gyeonggi, and Gangwon—were divided by the 38th parallel.
Also in 1946, the cities ofSeoul in the south andPyongyang in the north separated from Gyeonggi and South Pyongan Provinces respectively to become Special Cities. BothNorth Korea andSouth Korea have subsequently upgraded other cities to a level equal to a province, and these cities (special cities of North Korea andspecial cities of South Korea [qq.v.]) are sometimes counted along with provinces.
Finally, the new provinces ofJeju Province (in the south, in 1946) andChagang Province (in the north, 1949) were formed, from parts of South Jeolla and North Pyongan respectively. In 1954,Ryanggang Province was split from South Hamgyong and Hwanghae was divided intoNorth andSouth Hwanghae Provinces.
The following table lists the present provincial divisions in theKorean Peninsula.