| Geniohyoid muscle | |
|---|---|
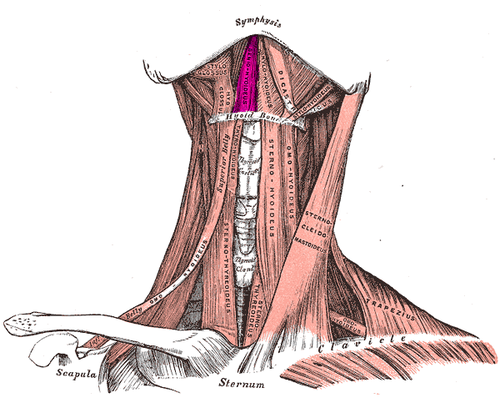 Anterior view. Geniohyoid muscle labeled at upper center left | |
 Extrinsic muscles of thetongue. Left side. | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Inferiormental spine ofmandible |
| Insertion | Hyoid bone |
| Artery | Branches of thelingual artery. |
| Nerve | C1 via thehypoglossal nerve |
| Actions | Carryhyoid bone and the tongue upward duringdeglutition |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | musculus geniohyoideus |
| TA98 | A04.2.03.007 |
| TA2 | 2166 |
| FMA | 46325 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
Thegeniohyoid muscle is a narrow pairedmuscle situated superior to the medial border of themylohyoid muscle. It is named for its passage from thechin ("genio-" is a standard prefix for "chin")[1] to thehyoid bone.
The geniohyoid is a paired short muscle that arises from the inferiormental spine, on the back of themandibular symphysis, and runs backward and slightly downward, to be inserted into the anterior surface of the body of thehyoid bone.[2]: 346 It lies in contact with its counterpart on the opposite side. It thus belongs to thesuprahyoid muscles. The muscle receives its blood supply from branches of thelingual artery.[3]
The geniohyoid muscle is innervated by fibres from thefirst cervical spinal nerve travelling alongside thehypoglossal nerve.[2][4][5] Although the first three cervical nerves give rise to theansa cervicalis, the geniohyoid muscle is said to be innervated by the first cervical nerve, as some of its efferent fibers do not contribute to ansa cervicalis.[clarification needed]
It may be blended with the one on opposite side or double; slips togreater cornu of hyoid bone andgenioglossus occur.[citation needed]
The geniohyoid muscle brings thehyoid bone forward and upwards.[2] This dilates theupper airway, assistingrespiration.[4] During the first act ofdeglutition, when the mass of food is being driven from the mouth into the pharynx, the hyoid bone, and with it the tongue, is carried upward and forward by the anterior bellies of the Digastrici, the Mylohyoidei, and Geniohyoidei. It also assists in depressing the mandible.[3]
The inclined position of the geniohyoid muscle has been contrasted to the horizontal position inneanderthals.[6]
![]() This article incorporates text in thepublic domain frompage 393 of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
This article incorporates text in thepublic domain frompage 393 of the 20th edition ofGray's Anatomy(1918)
Chin
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)