lstsq#
- scipy.linalg.lstsq(a,b,cond=None,overwrite_a=False,overwrite_b=False,check_finite=True,lapack_driver=None)[source]#
Compute least-squares solution to the equation
a@x=b.Compute a vector x such that the 2-norm
|b-Ax|is minimized.The documentation is written assuming array arguments are of specified“core” shapes. However, array argument(s) of this function may have additional“batch” dimensions prepended to the core shape. In this case, the array is treatedas a batch of lower-dimensional slices; seeBatched Linear Operations for details.
- Parameters:
- a(M, N) array_like
Left-hand side array
- b(M,) or (M, K) array_like
Right hand side array
- condfloat, optional
Cutoff for ‘small’ singular values; used to determine effectiverank of a. Singular values smaller than
cond*largest_singular_valueare considered zero.- overwrite_abool, optional
Discard data ina (may enhance performance). Default is False.
- overwrite_bbool, optional
Discard data inb (may enhance performance). Default is False.
- check_finitebool, optional
Whether to check that the input matrices contain only finite numbers.Disabling may give a performance gain, but may result in problems(crashes, non-termination) if the inputs do contain infinities or NaNs.
- lapack_driverstr, optional
Which LAPACK driver is used to solve the least-squares problem.Options are
'gelsd','gelsy','gelss'. Default('gelsd') is a good choice. However,'gelsy'can be slightlyfaster on many problems.'gelss'was used historically. It isgenerally slow but uses less memory.Added in version 0.17.0.
- Returns:
- x(N,) or (N, K) ndarray
Least-squares solution.
- residues(K,) ndarray or float
Square of the 2-norm for each column in
b-ax, ifM>Nandrank(A)==n(returns a scalar ifbis 1-D). Otherwise a(0,)-shaped array is returned.- rankint
Effective rank ofa.
- s(min(M, N),) ndarray or None
Singular values ofa. The condition number of
aiss[0]/s[-1].
- Raises:
- LinAlgError
If computation does not converge.
- ValueError
When parameters are not compatible.
See also
scipy.optimize.nnlslinear least squares with non-negativity constraint
Notes
When
'gelsy'is used as a driver,residues is set to a (0,)-shapedarray ands is alwaysNone.Examples
>>>importnumpyasnp>>>fromscipy.linalgimportlstsq>>>importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt
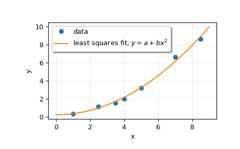
Suppose we have the following data:
>>>x=np.array([1,2.5,3.5,4,5,7,8.5])>>>y=np.array([0.3,1.1,1.5,2.0,3.2,6.6,8.6])
We want to fit a quadratic polynomial of the form
y=a+b*x**2to this data. We first form the “design matrix” M, with a constantcolumn of 1s and a column containingx**2:>>>M=x[:,np.newaxis]**[0,2]>>>Marray([[ 1. , 1. ], [ 1. , 6.25], [ 1. , 12.25], [ 1. , 16. ], [ 1. , 25. ], [ 1. , 49. ], [ 1. , 72.25]])
We want to find the least-squares solution to
M.dot(p)=y,wherepis a vector with length 2 that holds the parametersaandb.>>>p,res,rnk,s=lstsq(M,y)>>>parray([ 0.20925829, 0.12013861])
Plot the data and the fitted curve.
>>>plt.plot(x,y,'o',label='data')>>>xx=np.linspace(0,9,101)>>>yy=p[0]+p[1]*xx**2>>>plt.plot(xx,yy,label='least squares fit, $y = a + bx^2$')>>>plt.xlabel('x')>>>plt.ylabel('y')>>>plt.legend(framealpha=1,shadow=True)>>>plt.grid(alpha=0.25)>>>plt.show()