numpy.random.lognormal(mean=0.0,sigma=1.0,size=None)¶Draw samples from a log-normal distribution.
Draw samples from a log-normal distribution with specified mean,standard deviation, and array shape. Note that the mean and standarddeviation are not the values for the distribution itself, but of theunderlying normal distribution it is derived from.
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: |
|
See also
scipy.stats.lognormNotes
A variablex has a log-normal distribution iflog(x) is normallydistributed. The probability density function for the log-normaldistribution is:
p(x) = \frac{1}{\sigma x \sqrt{2\pi}}e^{(-\frac{(ln(x)-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2})}
where\mu is the mean and\sigma is the standarddeviation of the normally distributed logarithm of the variable.A log-normal distribution results if a random variable is theproductof a large number of independent, identically-distributed variables inthe same way that a normal distribution results if the variable is thesum of a large number of independent, identically-distributedvariables.
References
| [1] | Limpert, E., Stahel, W. A., and Abbt, M., “Log-normalDistributions across the Sciences: Keys and Clues,”BioScience, Vol. 51, No. 5, May, 2001.http://stat.ethz.ch/~stahel/lognormal/bioscience.pdf |
| [2] | Reiss, R.D. and Thomas, M., “Statistical Analysis of ExtremeValues,” Basel: Birkhauser Verlag, 2001, pp. 31-32. |
Examples
Draw samples from the distribution:
>>>mu,sigma=3.,1.# mean and standard deviation>>>s=np.random.lognormal(mu,sigma,1000)
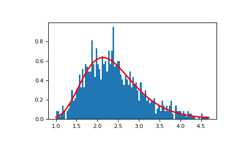
Display the histogram of the samples, along withthe probability density function:
>>>importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt>>>count,bins,ignored=plt.hist(s,100,density=True,align='mid')
>>>x=np.linspace(min(bins),max(bins),10000)>>>pdf=(np.exp(-(np.log(x)-mu)**2/(2*sigma**2)).../(x*sigma*np.sqrt(2*np.pi)))
>>>plt.plot(x,pdf,linewidth=2,color='r')>>>plt.axis('tight')>>>plt.show()

Demonstrate that taking the products of random samples from a uniformdistribution can be fit well by a log-normal probability densityfunction.
>>># Generate a thousand samples: each is the product of 100 random>>># values, drawn from a normal distribution.>>>b=[]>>>foriinrange(1000):...a=10.+np.random.random(100)...b.append(np.product(a))
>>>b=np.array(b)/np.min(b)# scale values to be positive>>>count,bins,ignored=plt.hist(b,100,density=True,align='mid')>>>sigma=np.std(np.log(b))>>>mu=np.mean(np.log(b))
>>>x=np.linspace(min(bins),max(bins),10000)>>>pdf=(np.exp(-(np.log(x)-mu)**2/(2*sigma**2)).../(x*sigma*np.sqrt(2*np.pi)))
>>>plt.plot(x,pdf,color='r',linewidth=2)>>>plt.show()