numpy.logspace(start,stop,num=50,endpoint=True,base=10.0,dtype=None)[source]¶Return numbers spaced evenly on a log scale.
In linear space, the sequence starts atbase**start(base to the power ofstart) and ends withbase**stop(seeendpoint below).
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: |
|
See also
arangelinspacegeomspaceNotes
Logspace is equivalent to the code
>>>y=np.linspace(start,stop,num=num,endpoint=endpoint)...>>>power(base,y).astype(dtype)...
Examples
>>>np.logspace(2.0,3.0,num=4)array([ 100. , 215.443469 , 464.15888336, 1000. ])>>>np.logspace(2.0,3.0,num=4,endpoint=False)array([ 100. , 177.827941 , 316.22776602, 562.34132519])>>>np.logspace(2.0,3.0,num=4,base=2.0)array([ 4. , 5.0396842 , 6.34960421, 8. ])
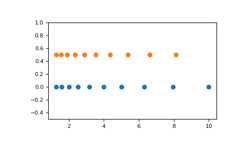
Graphical illustration:
>>>importmatplotlib.pyplotasplt>>>N=10>>>x1=np.logspace(0.1,1,N,endpoint=True)>>>x2=np.logspace(0.1,1,N,endpoint=False)>>>y=np.zeros(N)>>>plt.plot(x1,y,'o')[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>]>>>plt.plot(x2,y+0.5,'o')[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D object at 0x...>]>>>plt.ylim([-0.5,1])(-0.5, 1)>>>plt.show()