Flutter 3.41 is live! Check out theFlutter 3.41 blog post!
Integrate a Flutter module into your Android project
Learn how to integrate a Flutter module into your existing Android project.
Flutter can be embedded into your existing Android application piecemeal, as a source code Gradle subproject or as AARs.
The integration flow can be done using the Android Studio IDE with theFlutter plugin or manually.
Your existing Android app might support architectures such asmips orx86. Flutter currentlyonly supports building ahead-of-time (AOT) compiled libraries forx86_64,armeabi-v7a, andarm64-v8a.
Consider using theabiFilters Android Gradle Plugin API to limit the supported architectures in your APK. Doing this avoids a missinglibflutter.so runtime crash, for example:
android{//...defaultConfig{ndk{// Filter for architectures supported by FlutterabiFilters+=listOf("armeabi-v7a","arm64-v8a","x86_64")}}}android{// ...defaultConfig{ndk{// Filter for architectures supported by FlutterabiFilters"armeabi-v7a","arm64-v8a","x86_64"}}} The Flutter engine also has anx86_64 version. When using an emulator in debug Just-In-Time (JIT) mode, the Flutter module still runs correctly.
Integrate your Flutter module
#Integrate with Android Studio
#The Android Studio IDE can help integrate your Flutter module. Using Android Studio, you can edit both your Android and Flutter code in the same IDE.
You can also use IntelliJ Flutter plugin functionality like Dart code completion, hot reload, and widget inspector.
To build your app, the Android Studio plugin configures your Android project to add your Flutter module as a dependency.
Open your Android project in Android Studio.
Go toFile >New >New Project.... TheNew Project dialog displays.
ClickFlutter.
If asked to provide yourFlutter SDK path, do so and clickNext.
Complete the configuration of your Flutter module.
If you have an existing project:
- To choose an existing project, click... to the right of theProject location box.
- Navigate to your Flutter project directory.
- ClickOpen.
If you need to create a new Flutter project:
- Complete the configuration dialog.
- In theProject type menu, selectModule.
ClickFinish.
By default, your project's Project pane might show the 'Android' view. If you can't see your new Flutter files in the Project pane, set your Project pane to displayProject Files. This shows all files without filtering.
Integrate without Android Studio
#To integrate a Flutter module with an existing Android app manually, without using Flutter's Android Studio plugin, follow these steps:
Create a Flutter module
# Assuming that you have an existing Android app atsome/path/MyApp, and that you want your Flutter project as a sibling, do the following:
cd some/path/flutter create -t module --org com.example flutter_module This creates asome/path/flutter_module/ Flutter module project with some Dart code to get you started and a.android/ hidden subfolder. The.android folder contains an Android project that can both help you run a barebones standalone version of your Flutter module withflutter run and it's also a wrapper that helps bootstrap the Flutter module an embeddable Android library.
Do not edit files in.android/ to add native functionality. This folder is generated for testing purposes andwill be overwritten whenever you runflutter pub get or build the module.
- To add native code that you can use across apps/modules, create aFlutter Plugin and depend on it.
- To addapp-specific native code, add it directly to your existing Android host application.
The.android directory contains a generated Android project that uses Java to bootstrap the Flutter module, sodo not add it to source control. This approach helps you run a barebones standalone version of your Flutter module (withflutter run) and verify basic functionality. Using Java here doesn't prevent you from using Kotlin in your host app or plugins.
To avoid Dex merging issues,flutter.androidPackage should not be identical to your host app's package name.
Java version requirement
#Flutter requires your project to declare compatibility with Java 17 or later.
Before attempting to connect your Flutter module project to your host Android app, ensure that your host Android app declares the following source compatibility within your app'sbuild.gradle file, under theandroid { } block.
android{// ...compileOptions{sourceCompatibility=JavaVersion.VERSION_17// The minimum valuetargetCompatibility=JavaVersion.VERSION_17// The minimum value}// ...}Centralize repository settings
# Starting with Gradle 7, Android recommends using centralized repository declarations insettings.gradle instead of project or module level declarations inbuild.gradle files.
Before attempting to connect your Flutter module project to your host Android app, make the following changes to your host app:
Remove the
repositoriesblock in all of your app'sbuild.gradlefiles.groovy// Remove the following block, starting on the next linerepositories{google()mavenCentral()}// ...to the previous lineAdd the
dependencyResolutionManagementdisplayed in this step to thesettings.gradlefile.
dependencyResolutionManagement{repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.PREFER_SETTINGS)valstorageUrl:String=System.getenv("FLUTTER_STORAGE_BASE_URL")?:"https://storage.googleapis.com"repositories{google()mavenCentral()maven("$storageUrl/download.flutter.io")}}dependencyResolutionManagement{repositoriesMode=RepositoriesMode.PREFER_SETTINGSStringstorageUrl=System.env.FLUTTER_STORAGE_BASE_URL?:"https://storage.googleapis.com"repositories{google()mavenCentral()maven{url=uri("$storageUrl/download.flutter.io")}}}Add the Flutter module as a dependency
#Add the Flutter module as a dependency of your existing app in Gradle. You can achieve this in two ways.
Android archive The AAR mechanism creates generic Android AARs as intermediaries that packages your Flutter module. This is good when your downstream app builders don't want to have the Flutter SDK installed. But, it adds one more build step if you build frequently.
Module source code The source code subproject mechanism is a convenient one-click build process, but requires the Flutter SDK. This is the mechanism used by the Android Studio IDE plugin.
Depend on the Android Archive (AAR)
#This option packages your Flutter library as a generic local Maven repository composed of AARs and POMs artifacts. This option allows your team to build the host app without installing the Flutter SDK. You can then distribute the artifacts from a local or remote repository.
Let's assume you built a Flutter module atsome/path/flutter_module, and then run:
cd some/path/flutter_moduleflutter build aarThen, follow the on-screen instructions to integrate.
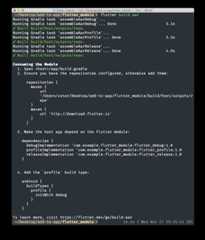
More specifically, this command creates (by default all debug/profile/release modes) alocal repository, with the following files:
build/host/outputs/repo
com
example
flutter_module
flutter_release
1.0
- flutter_release-1.0.aar
- flutter_release-1.0.aar.md5
- flutter_release-1.0.aar.sha1
- flutter_release-1.0.pom
- flutter_release-1.0.pom.md5
- flutter_release-1.0.pom.sha1
- maven-metadata.xml
- maven-metadata.xml.md5
- maven-metadata.xml.sha1
flutter_profile
- …
flutter_debug
- …
To depend on the AAR, the host app must be able to find these files.
To do that, editsettings.gradle in your host app so that it includes the local repository and the dependency:
dependencyResolutionManagement{repositoriesMode.set(RepositoriesMode.PREFER_SETTINGS)repositories{google()mavenCentral()maven("https://storage.googleapis.com/download.flutter.io")maven(url="<some/path/flutter_module>/build/host/outputs/repo")}}dependencyResolutionManagement{repositoriesMode=RepositoriesMode.PREFER_SETTINGSrepositories{google()mavenCentral()// Add the new repositories starting on the next line...maven{url=uri("<some/path/flutter_module>/build/host/outputs/repo")// This is relative to the location of the build.gradle file// if using a relative path.}maven{url=uri("https://storage.googleapis.com/download.flutter.io")}// ...to before this line}}Kotlin DSL based Android Project
# After anaar build of a Kotlin DSL-based Android project, follow these steps to add the flutter_module.
Include the flutter module as a dependency in the host app'sapp/build.gradle file.
android{buildTypes{release{...}debug{...}create("profile"){initWith(getByName("debug"))}}dependencies{// ...debugImplementation("com.example.flutter_module:flutter_debug:1.0")releaseImplementation("com.example.flutter_module:flutter_release:1.0")add("profileImplementation","com.example.flutter_module:flutter_profile:1.0")} Add the customprofileImplementation dependency configuration to the end of the same app-level build.gradle file.
configurations{getByName("profileImplementation"){}} If you're located in China, use a mirror site rather than thestorage.googleapis.com domain. To learn more about mirror sites, check outUsing Flutter in China page.
You can also build an AAR for your Flutter module in Android Studio using theBuild > Flutter > Build AAR menu.

Depend on the module's source code
#This option enables a one-step build for both your Android project and Flutter project. This option is convenient when you work on both parts simultaneously and rapidly iterate, but your team must install the Flutter SDK to build the host app.
By default, the host app provides the:app Gradle project. To change the name of this project, setflutter.hostAppProjectName in the Flutter module'sgradle.properties file. Include this project in the host app'ssettings.gradle file.
Updatingsettings.gradle
# Include the Flutter module as a subproject in the host app'ssettings.gradle. This example assumesflutter_module andMyApp exist in the same directory
If you are using Kotlin, apply the following changes:
// Include the host app project. Assumed existing content.include(":app")// Replace "flutter_module" with whatever package_name you supplied when you ran:// `$ flutter create -t module [package_name]valfilePath=settingsDir.parentFile.toString()+"/flutter_module/.android/include_flutter.groovy"apply(from=File(filePath)) The ability to invokeinclude_flutter.groovy from Kotlin code requires Flutter 3.27. To determine your current Flutter version, runflutter --version. If it isn't at least version 3.27, consider changing to either themain orbeta channels.
If you are using Groovy, apply the following changes:
// Include the host app project.include(":app")// assumed existing contentsetBinding(newBinding([gradle:this]))// newdeffilePath=settingsDir.parentFile.toString()+"/flutter_module/.android/include_flutter.groovy"// newapplyfrom:filePath// new The binding and script evaluation allows the Flutter module toinclude itself (as:flutter) and any Flutter plugins used by the module (such as:package_info and:video_player) in the evaluation context of yoursettings.gradle.
Updatingapp/build.gradle
# Introduce animplementation dependency on the Flutter module from your app:
dependencies{implementation(project(":flutter"))}This code is identical between Groovy and Kotlin.
Your app now includes the Flutter module as a dependency.
Continue to theAdding a Flutter screen to an Android app guide.
Unless stated otherwise, the documentation on this site reflects Flutter 3.38.6. Page last updated on 2026-02-05.View source orreport an issue.