Prebuilt search spaces
A Neural Architecture Search search space is key to achieving a good performance.It defines all thepotential architectures or parameters to explore and search. Neural Architecture Searchprovides a set of default search spaces in thesearch_spaces.pyfile:
MnasnetEfficientnet_v2NasfpnSpinenetSpinenet_v2Spinenet_mbconvSpinenet_scalingRandaugment_detectionRandaugment_segmentationAutoAugmentation_detectionAutoAugmentation_segmentation
In addition, we also provide the following search space examples:
- Lidar search space for 3D point clouds
- PyTorch 3D medical image segmentation search space example
- PyTorch MnasNet search space example
The Lidar notebook publishes verification results in the notebook.The rest of the PyTorch search spaces code are to be usedas an example onlyand not for benchmarking.
Each of these search spaces has a specific use case:
- MNasNet search space is used for image classification and object detection tasks andis based uponMobileNetV2 architecture.
- EfficientNetV2 search space is used for object detection tasks.EfficientNetV2 adds new operations, such as Fused-MBConv. See theEfficientNetV2 paper for more details.
- NAS-FPN search space is typically used for object detection.You can find a detailed description in thissection.
The SpineNet family of search spaces include
spinenet,spinenet_v2,spinenet_mbconv, andspinenet_scaling.These are typically used for object detection as well.You can find a detailed description for SpineNet in thissection.spinenetis the base search space in this family, offeringbothresidual andbottleneck block candidates during search.spinenet_v2offers a smaller version ofspinenet, which canhelp in faster convergence, offering onlybottleneck block candidatesduring search.spinenet_mbconvoffers a version ofspinenetfor mobileplatforms and usesmbconv block candidates during search.spinenet_scalingis typically usedafter finding a goodarchitecture by usingspinenetsearch space to scale it up or down to meetlatency requirements. This search is done over things such as image size, number of filters,filter size, and number of block repeats.
RandAugment andAutoAugment searchspaces let you search for optimumdata augmentation operations for detection and segmentation, respectively.Note: Data augmentation is typically usedafter a good model has beensearched already. You can find a detailed description for DataAugmentationin thissection.
Lidar search space for 3D point cloudsshows end-to-end search on featurizer, backbone, decoder and detection head.
PyTorch 3D medical image segmentation search space exampleshows search on UNet encoder and UNet decoder.
Most of the time, these default search spaces are sufficient.However, if needed, you cancustomizethese existing ones, or add a new one asrequired using the PyGlove library. See theexamplecode to specify the NAS-FPN search space.
MNasnet and EfficientNetV2 search space
The MNasNet and EfficientV2 search spaces define differentbackbone buildingoptions such asConvOps,KernelSize, andChannelSize. Thebackbone can beused for different tasks like classification and detection.
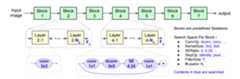
NAS-FPN search space
The NAS-FPN search space defines the searchspace in the FPN layers that connect different levels of features for objectdetection as shown in the following figure.

SpineNet search space
The SpineNet search space enables searchingfor a backbone with scale-permuted intermediate features and cross-scaleconnections, achieving state-of-the-art performance of one-stage object detectionon COCO with 60% less computation, and outperforms ResNet-FPN counterparts by 6%AP. The following are connections of backbone layers in the searched SpineNet-49architecture.

Data augmentation search space
After the best architecture has been searched already, you can also search for abest data augmentation policy. Data augmentation can further improve theaccuracy of the previously searched architecture.
The Neural Architecture Search platform provides RandAugment and AutoAugment augmentation searchspaces for two tasks: (a) randaugment_detection for object detection and (b)randaugment_segmentation for segmentation. It internally chooses between a listof augmentation operations such as auto-contrast, shear, or rotation to beapplied to the training data.
RandAugment search space
The RandAugment search space is configured by two parameters: (a)Nwhich is the number of successive augmentation operations to be applied toan image and (b)M which is the magnitude of ALL of those operations. Forexample, the following image shows an example where N=2 operations (Shear andContrast) with different M=magnitude are applied to an image.

For a given value of N, the list of operations are picked at random from theoperation bank. The augmentation search finds the best value ofN andM forthe training job at hand. The search doesn't use a proxy task and thereforeruns the training jobs to the end.
AutoAugment search space
The AutoAugment search space lets you search forchoice,magnitude, andprobability of operations, to optimize your model training.The AutoAugment search space lets you search for the choices of the policy,which RandAugment doesn't support.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.
