Latency points in a Spanner request
This page gives an overview of the high-level components involved in aSpanner request and how each component can affect latency.
Spanner API requests
The high-level components that are used to make a Spanner APIrequest include:
Spanner clientlibraries, which provide a layer of abstraction on top of gRPC, andhandle server communication details, such as session management,transactions, and retries.
The Google Front End (GFE), which is an infrastructure service that's commonto all Google Cloud services, including Spanner. TheGFE verifies that all Transport Layer Security (TLS) connections are stoppedand applies protections against Denial of Service attacks. To learn moreabout the GFE, seeGoogle Front End Service.
The Spanner API frontend (AFE), which performs various checkson the API request (including authentication, authorization, and quotachecks) , and maintains sessions and transaction states.
The Spanner database, which executes reads and writes to thedatabase.
When you make a remote procedure call to Spanner, theSpanner client libraries prepare the API request. Then, the APIrequest passes through both the GFE and the Spanner AFE beforereaching the Spanner database.
By measuring and comparing the request latencies between different componentsand the database, you can determine which component is causing the problem.These latencies include client end-to-end, GFE, Spanner APIrequest, and query latencies.
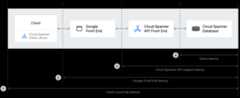
The following sections explain each type of latency you see in the previousdiagram.
End-to-end latency
End-to-end latency is the length of time (in milliseconds) between the firstbyte of the Spanner API request that the client sends to thedatabase (through both the GFE and the Spanner API front end),and the last byte of response that the client receives from the database.
Thespanner.googleapis.com/client/operation_latencies metricprovides the time between the first byte of the API requestsent to the last byte of the response received. This includes retries performedby the client library.
For more information, seeView and manage client-side metrics.
Note: You can also use OpenTelemetry to capture and visualize end-to-end latency. For more information, seeCapture custom client-side metrics using OpenTelemetry.GFE latency
Google Front End (GFE) latency is the length of time (in milliseconds) betweenwhen the Google network receives a remote procedure call from the client andwhen the GFE receives the first byte of the response. This latency doesn'tinclude any TCP/SSL handshake.

Every response from Spanner (REST or gRPC) includesa header that contains the total time between the GFE and the backend (theSpanner service) for the request and the response. Thishelps to differentiate better the source of the latency between the client andthe GFE.
Thespanner.googleapis.com/client/gfe_latenciesmetric captures and exposes GFE latency for Spanner requests.
For more information, seeView and manage client-side metrics.
Note: You can also use OpenTelemetry to capture and visualize GFE latency. For more information, seeCapture custom client-side metrics using OpenTelemetry.Spanner API request latency
Spanner API request latency is the length of time (in seconds)from when the Spanner AFE receives the first byte of a request towhen the Spanner API frontend sends the last byte of a response.The latency includes the time needed for processing API requests in boththe Spanner backend and the API layer. However, this latencydoesn't include network or reverse-proxy overhead between Spannerclients and servers.

Thespanner.googleapis.com/api/request_latencies metric capturesand exposes Spanner AFE latency for Spannerrequests. For more information, seeSpanner metrics.
Query latency
Query latency is the length of time (in milliseconds) that it takes to run SQLqueries in the Spanner database.
Query latency is available for theexecuteSqlAPI.
If theQueryModeparameter is set toWITH_STATS orWITH_PLAN_AND_STATS,then Spanner'sResultSetStatsare available in the responses.ResultSetStats includes the elapsedtime for running queries in the Spanner database.
To capture and visualize query latency, seeCapture query latency with OpenTelemetry.
What's next
- Learn how toidentify latency pointsin Spanner components.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
