Build a one-to-many Pub/Sub system
This tutorial walks you through setting up a set of applications thatcommunicate by sending messages through Pub/Sub rather thansynchronous RPCs. By decoupling applications, messaging:
- Makes applications more robust
- Might simplify development
For example, the caller (publisher) does not need the receiver (subscriber) tobe up and available. The publisher sends a message to Pub/Sub.The publisher doesn't need to know which and how many subscriber applicationsneed to receive the message. As a result, the service can be relied upon todeliver the message to one or more subscriber applications whenever they areavailable.
System overview
In this tutorial, you start a publisher application that sendsa "Hello, World!" message to two subscribers usingone-to-many communication,as illustrated in the following diagram:
The two subscriber applications use the same code, but you start themat different times. This process demonstrates howPub/Sub enables asynchronous communication. To build thissystem, you complete the following steps:
- Create an IAM service account that the applicationsuse for authentication.
- Set up IAM permissions.
- Create a Pub/Sub topic and a subscription.
- Start three independent applications: one publisher and two subscribers.
Before you begin
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
Create or select a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Create a Google Cloud project:
gcloud projects createPROJECT_ID
Replace
PROJECT_IDwith a name for the Google Cloud project you are creating.Select the Google Cloud project that you created:
gcloud config set projectPROJECT_ID
Replace
PROJECT_IDwith your Google Cloud project name.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the Pub/Sub API:
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.gcloudservicesenablepubsub.googleapis.comCreate local authentication credentials for your user account:
gcloudauthapplication-defaultlogin
If an authentication error is returned, and you are using an external identity provider (IdP), confirm that you have signed in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Grant roles to your user account. Run the following command once for each of the following IAM roles:
roles/pubsub.publisher, roles/pubsub.subscribergcloudprojectsadd-iam-policy-bindingPROJECT_ID--member="user:USER_IDENTIFIER"--role=ROLE
Replace the following:
PROJECT_ID: Your project ID.USER_IDENTIFIER: The identifier for your user account. For example,myemail@example.com.ROLE: The IAM role that you grant to your user account.
Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
Create or select a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Create a Google Cloud project:
gcloud projects createPROJECT_ID
Replace
PROJECT_IDwith a name for the Google Cloud project you are creating.Select the Google Cloud project that you created:
gcloud config set projectPROJECT_ID
Replace
PROJECT_IDwith your Google Cloud project name.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the Pub/Sub API:
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.gcloudservicesenablepubsub.googleapis.comCreate local authentication credentials for your user account:
gcloudauthapplication-defaultlogin
If an authentication error is returned, and you are using an external identity provider (IdP), confirm that you have signed in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Grant roles to your user account. Run the following command once for each of the following IAM roles:
roles/pubsub.publisher, roles/pubsub.subscribergcloudprojectsadd-iam-policy-bindingPROJECT_ID--member="user:USER_IDENTIFIER"--role=ROLE
Replace the following:
PROJECT_ID: Your project ID.USER_IDENTIFIER: The identifier for your user account. For example,myemail@example.com.ROLE: The IAM role that you grant to your user account.
Install Python
This tutorial uses thePub/Sub Client Libraries, which requiresPython 3.7 or higher. Complete the instructions forinstalling Python.
Set up your Pub/Sub project
To manage message flow between publishing and subscribing applications, youcreate a topic and two different subscriptions.
Create a Pub/Sub topic
Create a topic with the IDhello_topic:
gcloudpubsubtopicscreatehello_topic
Create Pub/Sub subscriptions
Create two subscriptions and attach them to your topic.
These subscriptions are aStreamingPull subscription, which is atype ofpull subscription.
Subscription 1
Create a subscription with the IDsub_one and attach it tohello_topic.
gcloudpubsubsubscriptionscreatesub_one--topic=hello_topicSubscription 2
Create a subscription with the IDsub_two and attach it tohello_topic.
gcloudpubsubsubscriptionscreatesub_two--topic=hello_topicBuild the one-to-many system
Download the publisher and subscriber code
Download the Pub/Sub Python filesneeded for this tutorial.
gitclonehttps://github.com/googleapis/python-pubsub.git
Close any open terminals before proceeding.
Set up three terminals
Start one terminal for each tutorial application (one publisher and twosubscribers). For convenience, this tutorial calls these terminals:
- publisher terminal
- sub_one terminal
- sub_two terminal
In thepublisher terminal, create and activate aPython virtual environment named
pyenv-qs.Bash
python-mvenvpyenv-qssourcepyenv-qs/bin/activatePowerShell
py-mvenvpyenv-qs.\pyenv-qs\Scripts\activate
In thesub_one andsub_two terminals, run the following command:
Bash
sourcepyenv-qs/bin/activatePowerShell
.\pyenv-qs\Scripts\activate
After you run the activate command, your command prompt includes the followingvalue
(pyenv-qs) $.In thepublisher terminal, install the Pub/Sub Python client library using
pip:python-mpipinstall--upgradegoogle-cloud-pubsub
In all three terminals, set up an environment variable with your currentproject ID. This gcloud command determines your selected project IDand sets it as a variable:
Bash
exportPROJECT=`gcloudconfigget-valueproject`
PowerShell
$env:PROJECT=$(gcloudconfigget-valueproject)
In all three terminals, change to the project path that contains the sample code.
cdpython-pubsub/samples/snippets/quickstart/
Start the apps and observe message flow
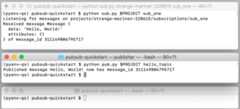
Start the Subscriber 1 application
In thesub_one terminal, startSubscriber 1:
Bash
pythonsub.py$PROJECTsub_onePowerShell
pysub.py$env:PROJECTsub_oneOnce started, this application opens a bidirectional streaming connection withthe server. Pub/Sub delivers messages over the stream.

Start the Publisher application
In thepublisher terminal, start thePublisher application:
Bash
pythonpub.py$PROJECThello_topicPowerShell
pypub.py$env:PROJECThello_topicAfter the publisher application starts, the Pub/Sub system doesthe following:
ThePublisher application sends a "Hello, World!" message toPub/Sub while remaining unaware of any existingsubscriptions. The server also assigns a message ID.
TheSubscriber 1 application receives the 'Hello World' message, printsit, and sends an acknowledgment to Pub/Sub.
ThePublisher application prints the acknowledgment. The acknowledgmenttells Pub/Sub that the message has been processedsuccessfully and does not need to be re-sent to this or any othersub_one subscriber.
Pub/Sub removes the message fromsub_one.
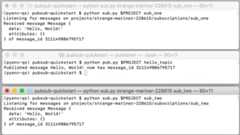
Start the Subscriber 2 application
In thesub_two terminal, startSubscriber 2:
Bash
pythonsub.py$PROJECTsub_twoPowerShell
pysub.py$env:PROJECTsub_twoThis subscriber receives messages delivered to thesub_two subscription.Subscriber 2 reuses thesub.py script. The difference is thatSubscriber2 isn't started until after the Publisher has sent the message to the topicand subscriptions. IfPublisher were callingSubscriber 2 directly, thepublishing application would either have to wait untilSubscriber 2 comes upor it would have to time out. Pub/Sub manages this process byeffectively saving the message forSubscriber 2.
You are now ready to develop with Pub/Sub!
How did it go?
Additional resources and links are available on thePub/Sub support page.
Clean up
- Stop all running applications.
- Delete the sample code directory from your local environment.
Delete the topic.
gcloudpubsubtopicsdeletehello_topic
Delete the subscriptions.
gcloudpubsubsubscriptionsdeletesub_one
gcloudpubsubsubscriptionsdeletesub_two
Shut down the tutorial project in theIAM & admin section of the Google Cloud console.
Optional: Revoke the authentication credentials that you created, and delete the local credential file.
gcloudauthapplication-defaultrevoke
Optional: Revoke credentials from the gcloud CLI.
gcloudauthrevoke
What's next
Here are some things that you can try:
Examine the tutorial's
pub.pyandsub.pycode and browse otherPub/Sub samples onGitHub. As an exercise, create a version ofpub.pythat publishes the local time every second.Learn tobatch messages.
UsingPush subscriptions, receive messages thattriggerApp Engine endpoints orCloud Functions.
Retrieve previously acknowledged messages usingreplay.By default, Pub/Sub removes acknowledged messages fromsubscriptions. In this tutorial, for instance, you wouldn't be able torerun
sub.pyto receive the "Hello, World!" message again. The replayfeature lets you set up subscriptions so that you can receive messagesafter they have been acknowledged.Get started with client libraries inother languages.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.
