Use the code editor for MQL
This section describes the features of the code editor for Monitoring Query Language (MQL), which is available in theGoogle Cloud console.
This page doesn't cover the MQL language; for a set of examplesand for more information about the language, seeExamples andAbout the MQL language.MQL Referenceprovides a comprehensive reference for the language.
Accessing the code editor
To access the code editor when using theMetrics Explorer,do the following:
In the Google Cloud console, go to theleaderboard Metrics explorer page:
If you use the search bar to find this page, then select the result whose subheading isMonitoring.
- In the toolbar of thequery-builder pane, select the button whose name is eithercode MQL orcode PromQL.
- Verify thatMQL is selectedin theLanguage toggle. The language toggle is in the same toolbar thatlets you format your query.
Using the code editor
To use the code editor, type your query into the query editor andclickRun Query:
Error messages
Error messages appear at the bottom of the editor pane.Some errors appear as you type. Others appear when you run the query.
Code folding
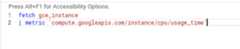
The editor provides code folding—the ability to collapse segments of yourqueries—so you can temporarily hide them from view.
The editor indicates foldable segments of your query with carets next to theline numbers, as shown in the following screenshot:
Find and replace
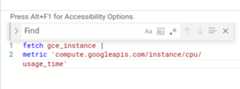
The editor supports a find-and-replace feature. To find, and optionallyreplace, terms in your query, pressControl+F (orCommand+F on Mac). Thefollowing screenshot shows the feature:
Editor controls
The editor has two controls that determine how it interacts with your query.
By default, your query is executed only when you clickRun Query.You can set up the code editor to automatically execute your query asyou type, but this option is disabled by default.
To enable the auto-run option, use theAuto-run toggle.When this option is enabled, the editor works as follows:
- TheRun Query button isn't displayed.
- Errors messages appear continuously as you type.
If your cursor is at the end of a query that is incomplete but has noerrors, the editor shows a yellow triangle in the control bar. If there isroom, the textIncomplete query also appears.
The code editor does not attempt to evaluate incomplete queries.
There is also a grab-bar between the code editor and the chart region.Use this bar to change the relative sizes of the two regions.
Exit the code editor
To exit the code editor without saving a chart or condition,clickarrow_back Return to query selector widget. Any query text in the editoris discarded, but you are given the option to save it to the clipboard.
View queries in strict form
To view a query in strict form when using the code editor,clickmore_vertMore optionsand selectSee strict form.
For more information, seeStrict-form queries.
Time ranges, charts, and the code editor
MQL queries in the code editor must include a time range.The time range specifies the subset of data to return as part ofthe query. The time range can be expressed implicitly by using the chart'stime-range selector or explicitly in your MQL query text.
By default, the time-range selector is set to one hour.
To change the time range of a chart, use the time-range selector. Forexample, if you want to view the data for the past week, then selectLast 1 week from the time-range selector. You can also specifya start and end time, or specify a time to view around.
Using chart settings for time selection
You can set the time period for a query by using the chart's time selector.This selector is the default way to set the time period. To change the timeperiod, select a different time option on the chart. If you select, for example,one week, then your query returns the data from now to a week ago.

When you use this default mechanism, you don't have to specify an explicittime range in the text of your query. The value on the chart is used implicitly.
Usingwithin for time selection
You can specify the time range for the query explicitly in the query by usingthewithin operation. This operation determines the range ofreturned data. If your query includes awithin operation, then thetime-selection options on the chart are disabled, and the time range specifiedin the query is used.
If you remove an explicitwithin operation from your query, the chartoptions are automatically re-enabled, ensuring that your query alwaysincludes a time period.
You must use explicit time selection if you want to use the API methodtimeSeries.query to issue the query. For more information, seeUsing MQL from the Monitoring API.
Query, alignment, and display periods
MQL has a number of potentially confusing operations that specify timeperiods. The following operations are related to the range of a query:
within: specifies the query-output window. Thisoperation determines how much data is returned. If, for example, you specifywithin 1h, then the query produces only points whose timestamps are withinthe last hour, which is why this operation overrides the chart'stime-selector options.The following operations relate to the alignment period of their outputtables. Both require an aligned table as input, or they supply a default:
every: specifies the period for aligned table output.window: specifies the window for alignment operations.
In both cases, if an
alignoperation is provided with an explicitalignment window, it must match the period specified for thewindowoperation, if provided. For thedeltaalignment function,the alignment window and period must be the same; if an explicit alignmentwindow is given, then theeveryoperation, if given, must agree. In allcases, the alignment window must be at least as large as the alignmentperiod or input data will be ignored.
MQL also has agraph_period operation, whichspecifies the period of output points for charts. This operation is useful inqueries given to the API whose output is being charted by third-party software.The Monitoring charting software ignores thegraph_periodoperation in queries, setting the period of points according to the width intime of the output chart.
In Monitoring charts, the graph period is set based on thevalue of the chart's time-range selector and the maximum number of pointsthat a chart can display. For example, if you select one week,the graph period might be one hour. For charts on dashboards, to viewthe graph period, clickquery_statsQuery stats.
The relationship between the query alignment period and the graph period canchange the way a chart looks. This relationship is described in the followingsection.
Min/max bands
When the query alignment period is close to the graph period, the chartrepresents each graphed time series with a single line. If the queryalignment period is less than half of the graph period of the chart, the chartincludes a shaded region around each line. This region, called amin/max band, shows the range of values that produced the mean value.
For example, assume the following MQL query:
fetchgce_instance::compute.googleapis.com/instance/cpu/utilization|group_by[zone],mean(val())|every1hThis query returns the mean CPU utilization of VMs by zone, with aone-hour alignment period.
If the chart's time selector is set to one week, then the graph period isone hour, which is indicated on a chip. For the example query, the graphperiod and alignment period are equal. Running the query produces a chartthat looks like the following:

For example, if you change the alignment period passed to theeveryoperation from1h to1m in the previous query, then the query produces achart that includes the min/max bands:

The chart lines are graphed with a graph period of one hour, based on theone-week selection for the chart, so the lines are the same as those in theprevious example. But the query produces a point every minute, so themin/max bands show the range of one-minute values from the query that fall intoeach one-hour graph point.
If theevery operation is omitted, the default query alignment period iseither the value of the alignment window or, if the alignment window is notspecified, one minute.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
