Workflow using Cloud Composer
- Create a Dataprocworkflow template that runs aSpark PI job
- Create an Apache Airflow DAG thatCloud Composerwill use to start the workflow at a specific time.
In this document, you use the following billable components of Google Cloud:
- Dataproc
- Compute Engine
- Cloud Composer
To generate a cost estimate based on your projected usage, use thepricing calculator.
Before you begin
Set up your project
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the Dataproc, Compute Engine, and Cloud Composer APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the Dataproc, Compute Engine, and Cloud Composer APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
Create a Dataproc workflow template
Copy and run the following commands in a local terminal window or inCloud Shell to create anddefine aworkflow template.
- Create the
sparkpiworkflow template.gcloud dataproc workflow-templates create sparkpi \ --region=us-central1
- Add the spark job to the
sparkpiworkflow template. The "compute"step-idflag identifies the SparkPi job.gcloud dataproc workflow-templates add-job spark \ --workflow-template=sparkpi \ --step-id=compute \ --class=org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \ --jars=file:///usr/lib/spark/examples/jars/spark-examples.jar \ --region=us-central1 \ -- 1000
- Use amanaged,single-nodecluster to run the workflow. Dataproc will create the cluster,run the workflow on it, then delete the cluster when the workflow completes.
gcloud dataproc workflow-templates set-managed-cluster sparkpi \ --cluster-name=sparkpi \ --single-node \ --region=us-central1
- Confirm workflow template creation.
Console
Click the
sparkpiname on the DataprocWorkflows page in the Google Cloud console to open theWorkflow template details page. Click the name of your workflow template to confirm thesparkpitemplate attributes.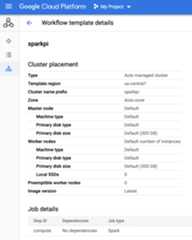
gcloud command
Run the following command:
gcloud dataproc workflow-templates describe sparkpi --region=us-central1
Create and upload a DAG to Cloud Storage
- Create or use an existingCloud Composer environment.
- Set environment variables.
Airflow UI
- In the toolbar, clickAdmin > Variables.
- ClickCreate.
- Enter the following information:
- Key:
project_id - Val:PROJECT_ID — your Google Cloud project ID
- Key:
- ClickSave.
gcloud command
Enter the following commands:
ENVIRONMENTis the name of the Cloud Composer environmentLOCATIONis the region where the Cloud Composer environment is locatedPROJECT_IDis the project ID for the project that contains the Cloud Composer environment
gcloud composer environments runENVIRONMENT --locationLOCATION variables set -- project_idPROJECT_ID
- In the toolbar, clickAdmin > Variables.
- Copy the following DAG code locally into a file titled "composer-dataproc-dag.py",which uses theDataprocInstantiateWorkflowTemplateOperator.
Airflow 2
"""Example Airflow DAG that kicks off a Cloud Dataproc Template that runs aSpark Pi Job.This DAG relies on an Airflow variablehttps://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/concepts/variables.html* project_id - Google Cloud Project ID to use for the Cloud Dataproc Template."""importdatetimefromairflowimportmodelsfromairflow.providers.google.cloud.operators.dataprocimport(DataprocInstantiateWorkflowTemplateOperator,)fromairflow.utils.datesimportdays_agoproject_id="{{var.value.project_id}}"default_args={# Tell airflow to start one day ago, so that it runs as soon as you upload it"start_date":days_ago(1),"project_id":project_id,}# Define a DAG (directed acyclic graph) of tasks.# Any task you create within the context manager is automatically added to the# DAG object.withmodels.DAG(# The id you will see in the DAG airflow page"dataproc_workflow_dag",default_args=default_args,# The interval with which to schedule the DAGschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),# Override to match your needs)asdag:start_template_job=DataprocInstantiateWorkflowTemplateOperator(# The task id of your jobtask_id="dataproc_workflow_dag",# The template id of your workflowtemplate_id="sparkpi",project_id=project_id,# The region for the templateregion="us-central1",)Airflow 1
"""Example Airflow DAG that kicks off a Cloud Dataproc Template that runs aSpark Pi Job.This DAG relies on an Airflow variablehttps://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/concepts/variables.html* project_id - Google Cloud Project ID to use for the Cloud Dataproc Template."""importdatetimefromairflowimportmodelsfromairflow.contrib.operatorsimportdataproc_operatorfromairflow.utils.datesimportdays_agoproject_id="{{var.value.project_id}}"default_args={# Tell airflow to start one day ago, so that it runs as soon as you upload it"start_date":days_ago(1),"project_id":project_id,}# Define a DAG (directed acyclic graph) of tasks.# Any task you create within the context manager is automatically added to the# DAG object.withmodels.DAG(# The id you will see in the DAG airflow page"dataproc_workflow_dag",default_args=default_args,# The interval with which to schedule the DAGschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),# Override to match your needs)asdag:start_template_job=dataproc_operator.DataprocWorkflowTemplateInstantiateOperator(# The task id of your jobtask_id="dataproc_workflow_dag",# The template id of your workflowtemplate_id="sparkpi",project_id=project_id,# The region for the template# For more info on regions where Dataflow is available see:# https://cloud.google.com/dataflow/docs/resources/locationsregion="us-central1",) - Upload yourDAG to your environment folder in Cloud Storage. After the upload has been completed successfully, click theDAGs Folder link on the Cloud Composer Environment's page.
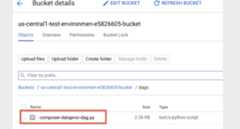
View a task's status
Airflow UI
- Open theAirflow web interface.
- On the DAGs page, click the DAG name (for example,
dataproc_workflow_dag). - On the DAGs Details page, clickGraph View.
- Check status:
- Failed: The task has a red box around it. You can also hold the pointer over task and look forState: Failed.
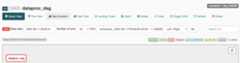
- Success: The task has a green box around it. You can also hold the pointer over the task and check forState: Success.
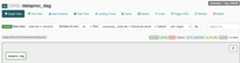
- Failed: The task has a red box around it. You can also hold the pointer over task and look forState: Failed.
Console
Click the Workflows tab to see workflow status.

gcloud command
gcloud dataproc operations list \ --region=us-central1 \ --filter="labels.goog-dataproc-workflow-template-id=sparkpi"
Clean up
To avoid incurring charges to your Google Cloud account, you can delete theresources used in this tutorial:
What's next
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
