Use Dataproc, BigQuery, and Apache Spark ML for Machine Learning
TheBigQuery Connector forApache Spark allows Data Scientists to blend the power ofBigQuery'sseamlessly scalable SQL engine withApache Spark’s Machine Learning capabilities. In this tutorial, we show how to use Dataproc, BigQueryand Apache Spark ML to perform machine learning on adataset.
Objectives
Use linear regression to build a model of birth weight as a function offive factors:- gestation weeks
- mother's age
- father's age
- mother's weight gain during pregnancy
- Apgar score
Use the following tools:
- BigQuery, to prepare the linear regression input table, which iswritten to your Google Cloud project
- Python, to query and manage data in BigQuery
- Apache Spark, to access the resulting linear regression table
- Spark ML, to build and evaluate the model
- Dataproc PySpark job, to invoke Spark ML functions
Costs
In this document, you use the following billable components of Google Cloud:
- Compute Engine
- Dataproc
- BigQuery
To generate a cost estimate based on your projected usage, use thepricing calculator.
Before you begin
A Dataproc cluster has the Spark components, including Spark ML, installed.To set up a Dataproc cluster and run the code in this example, you willneed to do (or have done) the following:
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, Compute Engine APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Enable the Dataproc, BigQuery, Compute Engine APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.Install the Google Cloud CLI.
If you're using an external identity provider (IdP), you must first sign in to the gcloud CLI with your federated identity.
Toinitialize the gcloud CLI, run the following command:
gcloudinit
- Create aDataproc cluster in your project. Your cluster should be running aDataproc version with Spark 2.0 or higher, (includes machine learning libraries).
Create a subset of BigQuery natality data
In this section, you create a dataset in your project, then create a tablein the dataset to which you copy a subset of birth rate data from thepublicly availablenatalityBigQuery dataset. Later in this tutorial you will use thesubset data in this table to predict birth weight as a function of maternal age,paternal age, and gestation weeks.
You can create the data subset using the Google Cloud console or runninga Python script on your local machine.
Console
Create a dataset in your project.
- Go to the BigQuery Web UI.
- In the left navigation panel, click your project name, then clickCREATE DATASET.
- In theCreate dataset dialog:
- ForDataset ID, enter "natality_regression".
- ForData location, you can choose alocationfor the dataset. The default value location is
US multi-region.After a dataset is created, the location cannot be changed. - ForDefault table expiration, choose one of the following options:
- Never (default): You must delete the table manually.
- Number of days: The table will be deletedafter the specified number days from its creation time.
- ForEncryption, choose one of the following options:
- Google-owned and Google-managed encryption key (default).
- Customer-managed key: SeeProtecting data with Cloud KMS keys.
- ClickCreate dataset.You cannot add a description or a label when you create a dataset usingthe Web UI. After the dataset is created, you canadd a description,andadd a label.
Run a query against the public natality dataset, then save the query results in a new table in your dataset.
- Copy and paste the following query into the Query Editor, thenclick Run.
CREATE OR REPLACE TABLE natality_regression.regression_input asSELECTweight_pounds,mother_age,father_age,gestation_weeks,weight_gain_pounds,apgar_5minFROM`bigquery-public-data.samples.natality`WHEREweight_pounds IS NOT NULLAND mother_age IS NOT NULLAND father_age IS NOT NULLAND gestation_weeks IS NOT NULLAND weight_gain_pounds IS NOT NULLAND apgar_5min IS NOT NULL
- After the query completes (in approximately one minute), the resultsare saved as "regression_input" BigQuery tablein the
natality_regressiondataset in your project.
- Copy and paste the following query into the Query Editor, thenclick Run.
Python
Before trying this sample, follow thePython setup instructions in theDataproc quickstart using client libraries. For more information, see theDataprocPython API reference documentation.
To authenticate to Dataproc, set up Application Default Credentials. For more information, seeSet up authentication for a local development environment.
SeeSetting Up a Python Development Environment for instructions on installing Python and the Google Cloud Client Library forPython (needed to run the code). Installing and using a Python
virtualenvis recommended.Copy and paste the
Setting up to run the application code locally:natality_tutorial.pycode, below,into apythonshell on your local machine.Press the<return>key in the shell to run the code to create a"natality_regression" BigQuery dataset in your defaultGoogle Cloud project with a"regression_input" table that is populated with a subset of the publicnatalitydata.- Run
gcloud config list projectto see the name of yourdefault project. - Run
gcloud config set projectproject-nameto change thedefault project. - Run
gcloud auth application-default loginto setapplication credentials to your user account.
"""Create a Google BigQuery linear regression input table.In the code below, the following actions are taken:* A new dataset is created "natality_regression."* A query is run against the public dataset, bigquery-public-data.samples.natality, selecting only the data of interest to the regression, the output of which is stored in a new "regression_input" table.* The output table is moved over the wire to the user's default project via the built-in BigQuery Connector for Spark that bridges BigQuery and Cloud Dataproc."""fromgoogle.cloudimportbigquery# Create a new Google BigQuery client using Google Cloud Platform project# defaults.client=bigquery.Client()# Prepare a reference to a new dataset for storing the query results.dataset_id="natality_regression"dataset_id_full=f"{client.project}.{dataset_id}"dataset=bigquery.Dataset(dataset_id_full)# Create the new BigQuery dataset.dataset=client.create_dataset(dataset)# Configure the query job.job_config=bigquery.QueryJobConfig()# Set the destination table to where you want to store query results.# As of google-cloud-bigquery 1.11.0, a fully qualified table ID can be# used in place of a TableReference.job_config.destination=f"{dataset_id_full}.regression_input"# Set up a query in Standard SQL, which is the default for the BigQuery# Python client library.# The query selects the fields of interest.query=""" SELECT weight_pounds, mother_age, father_age, gestation_weeks, weight_gain_pounds, apgar_5min FROM `bigquery-public-data.samples.natality` WHERE weight_pounds IS NOT NULL AND mother_age IS NOT NULL AND father_age IS NOT NULL AND gestation_weeks IS NOT NULL AND weight_gain_pounds IS NOT NULL AND apgar_5min IS NOT NULL"""# Run the query.client.query_and_wait(query,job_config=job_config)# Waits for the query to finish- Run
Confirm the creation of the
natality_regressiondataset andtheregression_inputtable.
Run a linear regression
In this section, you'll run a PySpark linear regression by submittingthe job to the Dataproc service using the Google Cloud consoleor by running thegcloud command from a local terminal.
Console
Copy and paste the following code into a new
natality_sparkml.pyfile on your local machine."""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML.In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML"""frompyspark.contextimportSparkContextfrompyspark.ml.linalgimportVectorsfrompyspark.ml.regressionimportLinearRegressionfrompyspark.sql.sessionimportSparkSession# The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear# regression as well as the Vectors types.# Define a function that collects the features of interest# (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector.# Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that# row.defvector_from_inputs(r):return(r["weight_pounds"],Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]),float(r["father_age"]),float(r["gestation_weeks"]),float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]),float(r["apgar_5min"])))sc=SparkContext()spark=SparkSession(sc)# Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe.natality_data=spark.read.format("bigquery").option("table","natality_regression.regression_input").load()# Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data.natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality")# As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist.sql_query="""SELECT *from natalitywhere weight_pounds is not nulland mother_age is not nulland father_age is not nulland gestation_weeks is not null"""clean_data=spark.sql(sql_query)# Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function.training_data=clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label","features"])training_data.cache()# Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data.lr=LinearRegression(maxIter=5,regParam=0.2,solver="normal")model=lr.fit(training_data)# Print the model summary.print("Coefficients:"+str(model.coefficients))print("Intercept:"+str(model.intercept))print("R^2:"+str(model.summary.r2))model.summary.residuals.show()
Copy the local
natality_sparkml.pyfile to a Cloud Storagebucket in your project.gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
Run the regression from the DataprocSubmit a job page.
In theMain python file field, insert the
gs://URI ofthe Cloud Storage bucket where your copy of thenatality_sparkml.pyfile is located.Select
PySparkas theJob type.Insert
gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-latest_2.12.jarin theJar files field. This makes the spark-bigquery-connector availableto the PySpark application at runtime to allow it to read BigQuerydata into a Spark DataFrame. The 2.12 jar is compatible with Dataproc clusters created withthe 1.5 or later image. If your Dataproc cluster was created with the1.3 or 1.4 image, specify the 2.11 jar instead(gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-latest_2.11.jar).Fill in theJob ID,Region, andCluster fields.
ClickSubmit to run the job on your cluster.
When the job completes, the linear regression output model summary appears inthe Dataproc Job details window.Model Summary Terminology: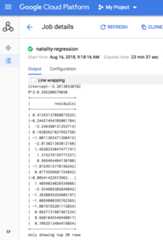
gcloud
Copy and paste the following code into a new
natality_sparkml.pyfile on your local machine."""Run a linear regression using Apache Spark ML.In the following PySpark (Spark Python API) code, we take the following actions: * Load a previously created linear regression (BigQuery) input table into our Cloud Dataproc Spark cluster as an RDD (Resilient Distributed Dataset) * Transform the RDD into a Spark Dataframe * Vectorize the features on which the model will be trained * Compute a linear regression using Spark ML"""frompyspark.contextimportSparkContextfrompyspark.ml.linalgimportVectorsfrompyspark.ml.regressionimportLinearRegressionfrompyspark.sql.sessionimportSparkSession# The imports, above, allow us to access SparkML features specific to linear# regression as well as the Vectors types.# Define a function that collects the features of interest# (mother_age, father_age, and gestation_weeks) into a vector.# Package the vector in a tuple containing the label (`weight_pounds`) for that# row.defvector_from_inputs(r):return(r["weight_pounds"],Vectors.dense(float(r["mother_age"]),float(r["father_age"]),float(r["gestation_weeks"]),float(r["weight_gain_pounds"]),float(r["apgar_5min"])))sc=SparkContext()spark=SparkSession(sc)# Read the data from BigQuery as a Spark Dataframe.natality_data=spark.read.format("bigquery").option("table","natality_regression.regression_input").load()# Create a view so that Spark SQL queries can be run against the data.natality_data.createOrReplaceTempView("natality")# As a precaution, run a query in Spark SQL to ensure no NULL values exist.sql_query="""SELECT *from natalitywhere weight_pounds is not nulland mother_age is not nulland father_age is not nulland gestation_weeks is not null"""clean_data=spark.sql(sql_query)# Create an input DataFrame for Spark ML using the above function.training_data=clean_data.rdd.map(vector_from_inputs).toDF(["label","features"])training_data.cache()# Construct a new LinearRegression object and fit the training data.lr=LinearRegression(maxIter=5,regParam=0.2,solver="normal")model=lr.fit(training_data)# Print the model summary.print("Coefficients:"+str(model.coefficients))print("Intercept:"+str(model.intercept))print("R^2:"+str(model.summary.r2))model.summary.residuals.show()
Copy the local
natality_sparkml.pyfile to a Cloud Storagebucket in your project.gcloud storage cp natality_sparkml.py gs://bucket-name
Submit the Pyspark job to the Dataproc service by running the
gcloudcommand, shown below, from a terminal window on your local machine.- The--jars flag value makes the spark-bigquery-connector availableto the PySpark jobv at runtime to allow it to readBigQuery data into a Spark DataFrame.
gcloud dataproc jobs submit pyspark \ gs://your-bucket/natality_sparkml.py \ --cluster=cluster-name \ --region=region \ --jars=gs://spark-lib/bigquery/spark-bigquery-with-dependencies_SCALA_VERSION-CONNECTOR_VERSION.jar
- The--jars flag value makes the spark-bigquery-connector availableto the PySpark jobv at runtime to allow it to readBigQuery data into a Spark DataFrame.
Clean up
After you finish the tutorial, you can clean up the resources that you created so that they stop using quota and incurring charges. The following sections describe how to delete or turn off these resources.
Delete the project
The easiest way to eliminate billing is to delete the project that you created for the tutorial.
To delete the project:
Delete the Dataproc cluster
SeeDelete a cluster.
What's next
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
