Create a private instance with VPC peering
This page describes how to create a Cloud Data Fusion instance with aninternal IP address. You create the instance in aVPC network or aShared VPC network.
Note: In Cloud Data Fusion 6.10.0 and later, we recommend creating private instances withPrivate Service Connect, not with VPC network peering.A private Cloud Data Fusion instance has the following benefits:
Connections to the instance are established over aprivate VPC network in your Google Cloud project.Traffic over the network doesn't go through the public internet.
The instance can connect to your on-premises resources, such as relationaldatabases because your on-premises network connects to theGoogle Cloud private VPC network throughCloud VPN orCloud Interconnect.You can securely access your on-premises resources, such as databases, overthe private network without opening up access to Google Cloud.
Objectives
- Set up the VPC network or the Shared VPC network.
- Allocate an IP range that will be used to deploy the Cloud Data Fusioninstance in the tenant project.
- Create the Cloud Data Fusion private instance.
- Set up the VPC network peering between the VPC thatcontains the Cloud Data Fusion instance and the VPC thatcontains the associated tenant project.
- For Shared VPC networks, set up Identity and Access Management (IAM)permissions.
- If your private instance uses Cloud Data Fusion version 6.2.0 orearlier, create a firewall rule.
- Let different Google Cloud services communicate internally with eachother by enabling Private Google Access on theDataproc subnet.
Before you begin
- To learn about Cloud Data Fusion's deployment architecture, seeNetworking.
Set up the VPC network
If you haven't already done so,create a VPC networkor aShared VPC network.
To set up your VPC network, you must allocate an IP addressrange.
Allocate an IP range
VPC network
If you're not using a Shared VPC network,Cloud Data Fusion allocates an IP range by default when you create aninstance.
Note: If you're not using a Shared VPC network, skip thissection and go toCreate a private instance.Shared VPC network
Note: Follow these steps only if you're using a Shared VPC network.To use a Shared VPC you must allocate an IPrange for your Cloud Data Fusion instance.
To allocate an IP range for your Cloud Data Fusion instance, follow these steps:
In the Google Cloud console, go to theVPC networkspage.
In theName column, click the VPC network in whichyou want to create a private Cloud Data Fusion instance.
TheVPC network details page opens.
ClickPrivate service connection. If prompted, enable theService Networking API by clickingEnable API.
ClickAllocate IP range.
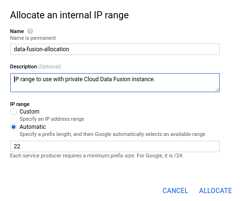
Give your IP range a name.
ForIP range, clickAutomatic.
Note: For custom ranges, Cloud Data Fusion supportsvalid private IPv4 address ranges, including non-RFC 1918 IP ranges. It doesn't support privately used external IP address ranges. This range allocation doesn't have to consume IPs from any of your subnets, but it must not overlap with any range allocations that you make in the future.Specify a prefix size of
Note: The IP range22./22is required per Cloud Data Fusion instance and cannot be shared by multiple instances. The IP range belongs to Google Cloud and is where the underlying instance components and infrastructure are hosted.ClickAllocate.
Create a private instance
Create the private Cloud Data Fusion instance in a VPCnetwork or a Shared VPC network.
Caution: After you create a Cloud Data Fusion instance, you cannot change its edition.VPC network
To create the instance in a VPC network, use either theGoogle Cloud console or cURL.
If you use the Google Cloud console to create your private instance,Cloud Data Fusion allocates the/22 IP address range by default. Tochoose a different IP range, you must use the cURL command.
Console
Go to theCreate Data Fusion instance page.
Enter an instance name and description for your instance.
Select theRegion in which to create the instance.
Select a Cloud Data FusionVersion andEdition.
Specify theDataproc service account to use for running your Cloud Data Fusion pipeline inDataproc. The default Compute Engineaccount is pre-selected.
Note: You must grant appropriate Identity and Access Management roles for your needs tothe service account. For more information, seeGranting service account user permission.Expand theAdvanced Options menu and clickEnable Private IP.
In theNetwork field, choose a network in which to create theinstance.
ClickCreate. It takes up to 30 minutes for the instance creationprocess to complete.
Note: While Cloud Data Fusion creates your instance, a progresswheel displays next to the instance name on theInstances page.After completion, it turns into a green check mark and indicatesthat you can start using the instance.
cURL
For your convenience, you can export the following variables, or you candirectly substitute these values into the following commands:
exportPROJECT=PROJECT_IDexportLOCATION=REGIONexportDATA_FUSION_API_NAME=datafusion.googleapis.comTo create the instance, call itscreate()method:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://$DATA_FUSION_API_NAME/v1/projects/$PROJECT/locations/$LOCATION/instances?instance_id=INSTANCE_ID -X POST -d '{"description": "Private CDF instance created through REST.", "type": "ENTERPRISE", "privateInstance": true, "networkConfig": {"network": "NETWORK_NAME", "ipAllocation": "IP_RANGE"}}'Replace the following:
INSTANCE_ID: The ID string your new instance should get.NETWORK_NAME: The name of theVPC network where you want to create your privateinstance.IP_RANGE: TheIPrange that you allocated. To find the IP range in theGoogle Cloud console, go toVPC network details>Private service connection>Internal IP range .
Shared VPC network
To create your instance in a Shared VPC network, use cURL, not theGoogle Cloud console.
cURL
For your convenience, you can export the following variables.Alternatively, you can directly substitute these values in the followingcommands:
export PROJECT=PROJECT_IDexport LOCATION=REGIONexport DATA_FUSION_API_NAME=datafusion.googleapis.com
To create the instance, call itscreate()method:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://$DATA_FUSION_API_NAME/v1/projects/$PROJECT/locations/$LOCATION/instances?instanceId=INSTANCE_ID -X POST -d '{"description": "Private CDF instance created through REST.", "type": "ENTERPRISE", "privateInstance": true, "networkConfig": {"network": "projects/SHARED_VPC_HOST_PROJECT_ID/global/networks/NETWORK_NAME", "ipAllocation": "IP_RANGE"}}'Replace the following:
INSTANCE_ID: The ID string your new instance should get.SHARED_VPC_HOST_PROJECT_ID: The ID of theproject that'shosting the Shared VPC network.NETWORK_NAME: The name of theVPC network in which you want to create the privateinstance.IP_RANGE: TheIP range that you allocated.To find the IP range in the Google Cloud console, go to theVPC network details page>Private service connection>Internal IP range.
Set up VPC network peering
Key Point: Your Cloud Data Fusion instance is created in its ownVPC and you might need to set up VPC network peering toconnect with the source and sink that you use in your pipeline.Cloud Data Fusion services that you use in yourdesign environment(for example: Wrangler, Connection Manager, and Schema Validation) initiatenetwork connections from the tenant project VPC to the sourcesystems. Cloud Data Fusion usesVPC network peering to establish networkconnectivity to the VPC or Shared VPC that contains yourinstance. The VPC network peering lets Cloud Data Fusion accessresources in your network through internal IP addresses using your ownVPC and its controls. To connect with a resource in anothernetwork, see thesteps for connection use cases.
The following section describes how tocreate a peering configurationbetween your network and the Cloud Data Fusiontenant projectnetwork.
Get the tenant project ID
To create a peering configuration, you need thetenant project ID.
Go to the Cloud Data FusionInstances page.
In theInstance Name column, select the instance.
On theInstance details page, copy theTenant project ID, which isrequired when you create a peering connection in the following steps.
Create a peering connection
Go to theVPC network peering page.
ClickCreate connection>Continue.
On theCreate peering connection page that opens, do the following:
- Enter aName for your peering connection.
- ForYour VPC network, select the network that contains yourCloud Data Fusion instance.
- ForPeered VPC network, selectIn another project.
- ForProject ID, enter thetenant project ID you found previously inthis tutorial.
ForVPC network name, select a network or enterINSTANCE_REGION-INSTANCE_ID.
Replace the following:
- INSTANCE_REGION: the region in which you created yourCloud Data Fusion instance.
- INSTANCE_ID: the ID of your Cloud Data Fusion instance.
-INSTANCE_ID is created in thetenant project. The private Cloud Data Fusion instance is deployedin that VPC. This network already exists with theconfiguration to peer with your customer project VPC.Select the Internet Protocol version for the peering connection toexchange IPv4 and IPv6 routes between your VPC network andthe peered VPC network. For more information, seeVPC network peering.
SelectExport custom routes so that customroutescan be exported from your VPC network to the tenantVPC network.
Choose whether to allow subnet routes with public IPv4 to be imported orexported into your VPC network.
ClickCreate.
The VPC network peering becomes active shortly after it is created.
Set up IAM permissions
VPC network
Skip this step and go toCreate a firewall rule.
Shared VPC network
If you create your Cloud Data Fusion instance in a Shared VPCnetwork, you must grant theCompute Network User roleto the following service accounts. To give permissions to all subnets, grantthe role to the Shared VPC host project.
To further control access, instead grant the role to a specific subnet, andtheNetwork Viewer role onthe host project.
- Cloud Data Fusion service account:
service-PROJECT_NUMBER@gcp-sa-datafusion.iam.gserviceaccount.com - Dataproc service account:
service-PROJECT_NUMBER@dataproc-accounts.iam.gserviceaccount.com
PROJECT_NUMBER is the number of theGoogle Cloud project that contains your Cloud Data Fusioninstance.
For more information, seeGranting accessto the required service accounts.
Create a firewall rule
Create a firewall rule on your VPC network that allows forincoming SSH connections from the IP range you specified when you created yourprivate Cloud Data Fusion instance.
This step is required for Cloud Data Fusion versions earlier than 6.2.0. Itallows communication between Cloud Data Fusion and Dataprocclusters running pipelines.
You can create the firewall rule byusing the Google Cloud consoleor byusing the gcloud CLI.
Console
gcloud
Run the following command:
gcloud compute firewall-rules createFIREWALL_NAME-allow-ssh --allow=tcp:22 --source-ranges=IP_RANGE --network=NETWORK_NAME --project=PROJECT_ID
Replace the following:
FIREWALL_NAME: The name of the firewall rule tocreate.IP_RANGE: TheIP range youallocated.NETWORK_NAME: The name of the network to whichthe firewall rule is attached. It's the name of the VPCnetwork in which you created the private instance.PROJECT_ID: The ID of the project that'shosting the VPC network.
Steps for connection use cases
The following sections describe connection-related use cases for privateinstances.
Enable Private Google Access
Toaccess resources through internal IP addresses,Cloud Data Fusion must create the Dataproc clusters and runthe data pipelines in a subnet that has Private Google Access. You mustenable Private Google Access for the subnet that contains theDataproc clusters.
- If only one subnet is present in the region where the Dataprocclusters are launched, then the cluster is launched in that subnet.
If there are multiple subnets in a region, you must configureCloud Data Fusion to select the subnet withPrivate Google Access for launching Dataproc clusters.
Caution: If Private Google Access isn't enabled on that subnet, the pipeline run fails. To specify the subnet after you create an instance, edit the compute profile.
To enable Private Google Access for the subnet, seePrivate Google Access configuration.
Optional: Connect to other sources
After you create a private instance in Cloud Data Fusion, you can connectto other sources, such as the following use cases:
- On-premises databases and systems running in other VPC networks
- Other Google Cloud services running in their own network in private mode, such asCloud SQL
- Sources on the public internet
Optional: Enable DNS Peering
EnableDNS Peering in thefollowing cases:
- When Cloud Data Fusion connects to systems through hostnames, and not IPaddresses
- When the target system is deployed behind a load balancer, such as it does insome SAP deployments
What's next
- Learn aboutsecurity concepts in Cloud Data Fusion.
- Learn aboutconnecting to resources in external networks.
- Learn about other key Cloud Data Fusionconcepts and features.
- See Cloud Data Fusionpricing.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
