Run a Hadoop wordcount job on a Dataproc cluster
Cloud Composer 3 | Cloud Composer 2 | Cloud Composer 1
This tutorial shows how to use Cloud Composer to create anApache Airflow DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph)that runs an Apache Hadoop wordcount job on a Dataproccluster.
Objectives
- Access your Cloud Composer environment and use theAirflow UI.
- Create and view Airflow environment variables.
- Create and run aDAG that includes the following tasks:
- Creates aDataproc cluster.
- Runs anApache Hadoop word-count job on the cluster.
- Outputs the word-count results to aCloud Storage bucket.
- Deletes the cluster.
Costs
In this document, you use the following billable components of Google Cloud:
- Cloud Composer
- Dataproc
- Cloud Storage
To generate a cost estimate based on your projected usage, use thepricing calculator.
Before you begin
Make sure that the following APIs are enabled in your project:
Console
Enable the Dataproc, Cloud Storage APIs.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.gcloud
Enable the Dataproc, Cloud Storage APIs:
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.gcloudservicesenabledataproc.googleapis.com
storage-component.googleapis.com In your project,create a Cloud Storage bucketof any storage class and region to store the results of the Hadoopword-count job.
Note: For data residency requirements or performance benefits, create thestorage bucket in the same region you plan to create your environment in.Note the path of the bucket that you created, for example
gs://example-bucket. You'll define an Airflow variable for this path anduse the variable in the example DAG later in this tutorial.Create a Cloud Composer environment with defaultparameters. Wait until environment creation is completed. When done, thegreen check mark displays to the left of the environment name.
Note the region where you created your environment, for example
us-central. You'll define an Airflow variable for this regionand use it in the example DAG to run a Dataproc clusterin the same region.
Set Airflow variables
Set the Airflow variables to use later in the example DAG. For example, youcan set Airflow variables in theAirflow UI.
| Airflow variable | Value |
|---|---|
gcp_project | Theproject ID of the projectyou're using for this tutorial, such asexample-project. |
gcs_bucket | The URI Cloud Storage bucket you created for this tutorial,such asgs://example-bucket |
gce_region | The region where you created your environment, such asus-central1.This is the region where your Dataproc clusterwill be created. |
View the example workflow
An Airflow DAG is a collection of organized tasks that you want to scheduleand run. DAGs are defined in standard Python files. The code shown inhadoop_tutorial.py is the workflow code.
Airflow 2
"""Example Airflow DAG that creates a Cloud Dataproc cluster, runs the Hadoopwordcount example, and deletes the cluster.This DAG relies on three Airflow variableshttps://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/concepts/variables.html* gcp_project - Google Cloud Project to use for the Cloud Dataproc cluster.* gce_region - Google Compute Engine region where Cloud Dataproc cluster should be created.* gcs_bucket - Google Cloud Storage bucket to use for result of Hadoop job. See https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/creating-buckets for creating a bucket."""importdatetimeimportosfromairflowimportmodelsfromairflow.providers.google.cloud.operatorsimportdataprocfromairflow.utilsimporttrigger_rule# Output file for Cloud Dataproc job.# If you are running Airflow in more than one time zone# see https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/timezone.html# for best practicesoutput_file=(os.path.join("{{ var.value.gcs_bucket }}","wordcount",datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"),)+os.sep)# Path to Hadoop wordcount example available on every Dataproc cluster.WORDCOUNT_JAR="file:///usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples.jar"# Arguments to pass to Cloud Dataproc job.input_file="gs://pub/shakespeare/rose.txt"wordcount_args=["wordcount",input_file,output_file]HADOOP_JOB={"reference":{"project_id":"{{ var.value.gcp_project }}"},"placement":{"cluster_name":"composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}"},"hadoop_job":{"main_jar_file_uri":WORDCOUNT_JAR,"args":wordcount_args,},}CLUSTER_CONFIG={"master_config":{"num_instances":1,"machine_type_uri":"n1-standard-2"},"worker_config":{"num_instances":2,"machine_type_uri":"n1-standard-2"},}yesterday=datetime.datetime.combine(datetime.datetime.today()-datetime.timedelta(1),datetime.datetime.min.time())default_dag_args={# Setting start date as yesterday starts the DAG immediately when it is# detected in the Cloud Storage bucket."start_date":yesterday,# To email on failure or retry set 'email' arg to your email and enable# emailing here."email_on_failure":False,"email_on_retry":False,# If a task fails, retry it once after waiting at least 5 minutes"retries":1,"retry_delay":datetime.timedelta(minutes=5),"project_id":"{{ var.value.gcp_project }}","region":"{{ var.value.gce_region }}",}withmodels.DAG("composer_hadoop_tutorial",# Continue to run DAG once per dayschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),default_args=default_dag_args,)asdag:# Create a Cloud Dataproc cluster.create_dataproc_cluster=dataproc.DataprocCreateClusterOperator(task_id="create_dataproc_cluster",# Give the cluster a unique name by appending the date scheduled.# See https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/macros-ref.htmlcluster_name="composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}",cluster_config=CLUSTER_CONFIG,region="{{ var.value.gce_region }}",)# Run the Hadoop wordcount example installed on the Cloud Dataproc cluster# master node.run_dataproc_hadoop=dataproc.DataprocSubmitJobOperator(task_id="run_dataproc_hadoop",job=HADOOP_JOB)# Delete Cloud Dataproc cluster.delete_dataproc_cluster=dataproc.DataprocDeleteClusterOperator(task_id="delete_dataproc_cluster",cluster_name="composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}",region="{{ var.value.gce_region }}",# Setting trigger_rule to ALL_DONE causes the cluster to be deleted# even if the Dataproc job fails.trigger_rule=trigger_rule.TriggerRule.ALL_DONE,)# Define DAG dependencies.create_dataproc_cluster >>run_dataproc_hadoop >>delete_dataproc_clusterAirflow 1
"""Example Airflow DAG that creates a Cloud Dataproc cluster, runs the Hadoopwordcount example, and deletes the cluster.This DAG relies on three Airflow variableshttps://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/concepts/variables.html* gcp_project - Google Cloud Project to use for the Cloud Dataproc cluster.* gce_region - Google Compute Engine region where Cloud Dataproc cluster should be created.* gcs_bucket - Google Cloud Storage bucket to use for result of Hadoop job. See https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/creating-buckets for creating a bucket."""importdatetimeimportosfromairflowimportmodelsfromairflow.contrib.operatorsimportdataproc_operatorfromairflow.utilsimporttrigger_rule# Output file for Cloud Dataproc job.# If you are running Airflow in more than one time zone# see https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/timezone.html# for best practicesoutput_file=(os.path.join("{{ var.value.gcs_bucket }}","wordcount",datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S"),)+os.sep)# Path to Hadoop wordcount example available on every Dataproc cluster.WORDCOUNT_JAR="file:///usr/lib/hadoop-mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples.jar"# Arguments to pass to Cloud Dataproc job.input_file="gs://pub/shakespeare/rose.txt"wordcount_args=["wordcount",input_file,output_file]yesterday=datetime.datetime.combine(datetime.datetime.today()-datetime.timedelta(1),datetime.datetime.min.time())default_dag_args={# Setting start date as yesterday starts the DAG immediately when it is# detected in the Cloud Storage bucket."start_date":yesterday,# To email on failure or retry set 'email' arg to your email and enable# emailing here."email_on_failure":False,"email_on_retry":False,# If a task fails, retry it once after waiting at least 5 minutes"retries":1,"retry_delay":datetime.timedelta(minutes=5),"project_id":"{{ var.value.gcp_project }}",}withmodels.DAG("composer_hadoop_tutorial",# Continue to run DAG once per dayschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),default_args=default_dag_args,)asdag:# Create a Cloud Dataproc cluster.create_dataproc_cluster=dataproc_operator.DataprocClusterCreateOperator(task_id="create_dataproc_cluster",# Give the cluster a unique name by appending the date scheduled.# See https://airflow.apache.org/docs/apache-airflow/stable/macros-ref.htmlcluster_name="composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}",num_workers=2,region="{{ var.value.gce_region }}",master_machine_type="n1-standard-2",worker_machine_type="n1-standard-2",)# Run the Hadoop wordcount example installed on the Cloud Dataproc cluster# master node.run_dataproc_hadoop=dataproc_operator.DataProcHadoopOperator(task_id="run_dataproc_hadoop",main_jar=WORDCOUNT_JAR,region="{{ var.value.gce_region }}",cluster_name="composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}",arguments=wordcount_args,)# Delete Cloud Dataproc cluster.delete_dataproc_cluster=dataproc_operator.DataprocClusterDeleteOperator(task_id="delete_dataproc_cluster",cluster_name="composer-hadoop-tutorial-cluster-{{ ds_nodash }}",region="{{ var.value.gce_region }}",# Setting trigger_rule to ALL_DONE causes the cluster to be deleted# even if the Dataproc job fails.trigger_rule=trigger_rule.TriggerRule.ALL_DONE,)# Define DAG dependencies.create_dataproc_cluster >>run_dataproc_hadoop >>delete_dataproc_clusterOperators
To orchestrate the three tasks in the example workflow, the DAG imports thefollowing three Airflow operators:
DataprocClusterCreateOperator: Creates a Dataproc cluster.DataProcHadoopOperator: Submits a Hadoop wordcount job and writes resultsto a Cloud Storage bucket.DataprocClusterDeleteOperator: Deletes the cluster to avoid incurringongoing Compute Engine charges.
Dependencies
You organize tasks that you want to run in a way that reflects theirrelationships and dependencies. The tasks in this DAG run sequentially.
Airflow 2
# Define DAG dependencies.create_dataproc_cluster >>run_dataproc_hadoop >>delete_dataproc_clusterAirflow 1
# Define DAG dependencies.create_dataproc_cluster >>run_dataproc_hadoop >>delete_dataproc_clusterScheduling
The name of the DAG iscomposer_hadoop_tutorial, and the DAG runs once eachday. Because thestart_date that is passed in todefault_dag_args isset toyesterday, Cloud Composer schedules the workflowto start immediately after the DAG is uploaded to the environment's bucket.
Airflow 2
withmodels.DAG("composer_hadoop_tutorial",# Continue to run DAG once per dayschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),default_args=default_dag_args,)asdag:Airflow 1
withmodels.DAG("composer_hadoop_tutorial",# Continue to run DAG once per dayschedule_interval=datetime.timedelta(days=1),default_args=default_dag_args,)asdag:Upload the DAG to the environment's bucket
Cloud Composer stores DAGs in the/dags folder in yourenvironment's bucket.
To upload the DAG:
On your local machine, save
hadoop_tutorial.py.In the Google Cloud console, go to theEnvironments page.
In the list of environments, in theDAGs folder column for yourenvironment, click theDAGs link.
ClickUpload files.
Select
hadoop_tutorial.pyon your local machine and clickOpen.
Cloud Composer adds the DAG to Airflow and schedules the DAGautomatically. DAG changes occur within 3-5 minutes.
Explore DAG runs
View task status
When you upload your DAG file to thedags/ folder in Cloud Storage,Cloud Composer parses the file. When completed successfully, the nameof the workflow appears in the DAG listing, and the workflow is queued to runimmediately.
To see task status, go to the Airflow web interface and clickDAGsin the toolbar.
To open the DAG details page, click
composer_hadoop_tutorial. Thispage includes a graphical representation of workflow tasks anddependencies.
To see each task's status, clickGraph View and thenmouseover the graphic for each task.
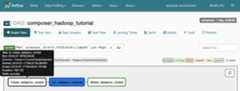
Queue the workflow again
To run the workflow again from theGraph View:
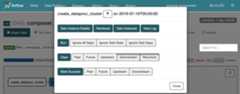
- In the Airflow UI Graph View, click the
create_dataproc_clustergraphic. - To reset the three tasks, clickClear and then clickOK to confirm.
- Click
create_dataproc_clusteragain in Graph View. - To queue the workflow again, clickRun.
View task results
You can also check the status and results of thecomposer_hadoop_tutorialworkflow by going to the following Google Cloud console pages:
Dataproc Clusters: to monitor cluster creation anddeletion. Note that the cluster created by the workflow is ephemeral: itonly exists for the duration of the workflow and is deleted as part of thelast workflow task.
Dataproc Jobs: to view or monitor the Apache Hadoopwordcount job. Click the Job ID to see job log output.
Cloud Storage Browser: to see the results of the wordcount inthe
wordcountfolder in the Cloud Storage bucket you createdfor this tutorial.
Cleanup
Delete theresources used in this tutorial:
Delete the Cloud Composer environment, includingmanually deleting the environment's bucket.
Delete the Cloud Storage bucket thatstores the results of the Hadoop word-count job.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
