Use custom holidays in an ARIMA_PLUS time-series forecasting model
This tutorial shows you how to do the following tasks:
- Create an
ARIMA_PLUStime-series forecasting modelthat uses only built-in holidays. - Create an
ARIMA_PLUStime-series forecasting model that uses customholidays in addition to built-in holidays. - Visualize the forecasted results from these models.
- Inspect a model to see which holidays it models.
- Evaluate the effects of the custom holidays on the forecasted results.
- Compare the performance of the model that uses only built-in holidays to theperformance of the model that uses custom holidays in addition tobuilt-in holidays.
This tutorial uses thebigquery-public-data.wikipedia.pageviews_*public tables.
Required permissions
To create the dataset, you need the
bigquery.datasets.createIAM permission.To create the model, you need the following permissions:
bigquery.jobs.createbigquery.models.createbigquery.models.getDatabigquery.models.updateData
To run inference, you need the following permissions:
bigquery.models.getDatabigquery.jobs.create
For more information about IAM roles and permissions inBigQuery, seeIntroduction to IAM.
Costs
In this document, you use the following billable components of Google Cloud:
- BigQuery: You incur costs for the data you process in BigQuery.
To generate a cost estimate based on your projected usage, use thepricing calculator.
For more information, seeBigQuery pricing.
Before you begin
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the BigQuery API.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Roles required to select or create a project
- Select a project: Selecting a project doesn't require a specific IAM role—you can select any project that you've been granted a role on.
- Create a project: To create a project, you need the Project Creator role (
roles/resourcemanager.projectCreator), which contains theresourcemanager.projects.createpermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Verify that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
Enable the BigQuery API.
Roles required to enable APIs
To enable APIs, you need the Service Usage Admin IAM role (
roles/serviceusage.serviceUsageAdmin), which contains theserviceusage.services.enablepermission.Learn how to grant roles.
Create a dataset
Create a BigQuery dataset to store your ML model.
Console
In the Google Cloud console, go to theBigQuery page.
In theExplorer pane, click your project name.
ClickView actions > Create dataset
On theCreate dataset page, do the following:
ForDataset ID, enter
bqml_tutorial.ForLocation type, selectMulti-region, and then selectUS (multiple regions in United States).
Leave the remaining default settings as they are, and clickCreate dataset.
bq
To create a new dataset, use thebq mk commandwith the--location flag. For a full list of possible parameters, see thebq mk --dataset commandreference.
Create a dataset named
bqml_tutorialwith the data location set toUSand a description ofBigQuery ML tutorial dataset:bq --location=US mk -d \ --description "BigQuery ML tutorial dataset." \ bqml_tutorial
Instead of using the
--datasetflag, the command uses the-dshortcut.If you omit-dand--dataset, the command defaults to creating adataset.Confirm that the dataset was created:
bqls
API
Call thedatasets.insertmethod with a defineddataset resource.
{"datasetReference":{"datasetId":"bqml_tutorial"}}
BigQuery DataFrames
Before trying this sample, follow the BigQuery DataFrames setup instructions in theBigQuery quickstart using BigQuery DataFrames. For more information, see theBigQuery DataFrames reference documentation.
To authenticate to BigQuery, set up Application Default Credentials. For more information, seeSet up ADC for a local development environment.
importgoogle.cloud.bigquerybqclient=google.cloud.bigquery.Client()bqclient.create_dataset("bqml_tutorial",exists_ok=True)Prepare the time-series data
Aggregate the Wikipedia page view data for theGoogle I/O page into a singletable, grouped by day:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
CREATEORREPLACETABLE`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`ASSELECTDATETIME_TRUNC(datehour,DAY)ASdate,SUM(views)ASviewsFROM`bigquery-public-data.wikipedia.pageviews_*`WHEREdatehour>='2017-01-01'ANDdatehour<'2023-01-01'ANDtitle='Google_I/O'GROUPBYDATETIME_TRUNC(datehour,DAY)
Create a time-series forecasting model that uses built-in holidays
Create a model that forecasts daily page views for the Wikipedia"Google I/O" page, based on pageview data before 2022 and taking built-in holidays into account:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
CREATEORREPLACEMODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio`OPTIONS(model_type='ARIMA_PLUS',holiday_region='US',time_series_timestamp_col='date',time_series_data_col='views',data_frequency='DAILY',horizon=365)ASSELECT*FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`WHEREdate<'2022-01-01';
Visualize the forecasted results
After you create the model using built-in holidays, join the original data fromthebqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views table with the forecasted value from theML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST function,and then visualize it byusing Looker Studio:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
SELECToriginal.date,original.viewsASoriginal_views,explain_forecast.time_series_adjusted_dataASadjusted_views_without_custom_holiday,FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`originalINNERJOIN(SELECT*FROMML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST(MODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio`,STRUCT(365AShorizon)))explain_forecastONTIMESTAMP(original.date)=explain_forecast.time_series_timestampORDERBYoriginal.date;
In theQuery results pane, clickOpen in>Looker Studio. Looker Studioopens in a new tab.
In the Looker Studio tab, clickAdd a chart, and thenclick the time series chart:
Place the chart on the report.
On theSetup tab of theChart pane, clickAdd metric and selectadjusted_views_without_custom_holiday:
The chart looks similar to the following:
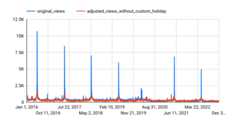
You can see that the forecasting model captures the general trend prettywell. However, it isn't capturing the increased traffic related to previousGoogle I/O events, and it isn't able to generate an accurate forecast for
- The next sections show you how to deal with some of theselimitations.
Create a time-series forecasting model that uses built-in holidays and custom holidays
As you can see inGoogle I/O history,the Google I/O event occurred on different dates between 2017 and 2022. To takethis variation into account, create a model that forecasts page views for theWikipedia "Google_I/O" page through 2022, based on page view data from before2022, and using custom holidays to represent the Google I/O event each year.In this model, you also adjust the holiday effect window to cover three daysaround the event date, to better capture some potential page traffic beforeand after the event.
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
CREATEORREPLACEMODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio_with_custom_holiday`OPTIONS(model_type='ARIMA_PLUS',holiday_region='US',time_series_timestamp_col='date',time_series_data_col='views',data_frequency='DAILY',horizon=365)AS(training_dataAS(SELECT*FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`WHEREdate<'2022-01-01'),custom_holidayAS(SELECT'US'ASregion,'GoogleIO'ASholiday_name,primary_date,1ASpreholiday_days,2ASpostholiday_daysFROMUNNEST([DATE('2017-05-17'),DATE('2018-05-08'),DATE('2019-05-07'),-- cancelled in 2020 due to pandemicDATE('2021-05-18'),DATE('2022-05-11')])ASprimary_date));
Visualize the forecasted results
After you create the model using custom holidays, join the original data fromthebqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views table with the forecasted value from theML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST function,and then visualize it byusing Looker Studio:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
SELECToriginal.date,original.viewsASoriginal_views,explain_forecast.time_series_adjusted_dataASadjusted_views_with_custom_holiday,FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`originalINNERJOIN(SELECT*FROMML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST(MODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio_with_custom_holiday`,STRUCT(365AShorizon)))explain_forecastONTIMESTAMP(original.date)=explain_forecast.time_series_timestampORDERBYoriginal.date;
In theQuery results pane, clickExplore data,and then clickExplore with Looker Studio. Looker Studioopens in a new tab.
In the Looker Studio tab, clickAdd a chart, click thetime series chart, and place the chart on the report.
On theSetup tab of theChart pane, clickAdd metric and selectadjusted_views_with_custom_holiday.
The chart looks similar to the following:

As you can see, the custom holidays boosted the performanceof the forecasting model. It now effectively captures the increase of pageviews caused by Google I/O.
Inspect holiday information
Inspect the list of holidays that were taken into account during modelingby using theML.HOLIDAY_INFO function:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
SELECT*FROMML.HOLIDAY_INFO(MODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio_with_custom_holiday`);
The results show both Google I/O and the built-in holidays in the listof holidays:

Evaluate the effects of the custom holidays
Evaluate the effects of the custom holidays on the forecasted results byusing theML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST function:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
SELECTtime_series_timestamp,holiday_effect_GoogleIO,holiday_effect_US_Juneteenth,holiday_effect_Christmas,holiday_effect_NewYearFROMML.EXPLAIN_FORECAST(model`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio_with_custom_holiday`,STRUCT(365AShorizon))WHEREholiday_effect!=0;
The results show that Google I/O contributes a large amount of holidayeffect to the forecasted results:

Compare model performance
Use theML.EVALUATE functionto compare the performance of the first model created without custom holidaysand the second model created with custom holidays. To see how the secondmodel performs when it comes to forecasting a future custom holiday, set thetime range to the week of Google I/O in 2022:
Go to theBigQuery page.
In the SQL editor pane, run the following SQL statement:
SELECT"original"ASmodel_type,*FROMml.evaluate(MODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio`,(SELECT*FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`WHEREdate>='2022-05-08'ANDdate<'2022-05-12'),STRUCT(365AShorizon,TRUEASperform_aggregation))UNIONALLSELECT"with_custom_holiday"ASmodel_type,*FROMml.evaluate(MODEL`bqml_tutorial.forecast_googleio_with_custom_holiday`,(SELECT*FROM`bqml_tutorial.googleio_page_views`WHEREdate>='2022-05-08'ANDdate<'2022-05-12'),STRUCT(365AShorizon,TRUEASperform_aggregation));
The results show that the second model offers a significant performanceimprovement:

Clean up
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-15 UTC.
