Integrate Apigee with your SIEM solution
This pageapplies toApigee andApigee hybrid.
Many organizations seek to integrate Apigee with their Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions. This integration enables the valuable correlation of Apigee data with other network and security product logs, facilitating advanced threat detection, comprehensive logging, and compliance reporting. This document explores various integration approaches, catering to scenarios both with and without theAdvanced API Security add-on.
Audience
The audience for this document includes:
- API administrators responsible for ensuring API security, managing platform configurations, supporting operational efficiency, and adhering to security compliance requirements.
- Security analysts focused on proactively detecting and investigating API-related security incidents to minimize risk and safeguard sensitive data.
Configuration options
Apigee offers two primary methods for sending log information to a SIEM:
| Option | Description | Google Cloud platform logs | Provides a foundational level of API log data, including service-specific logs helpful for debugging and troubleshooting. |
|---|---|
| Apigee Message Logging policy | TheMessage Logging policy offers greater flexibility and control, allowing you to send a wide range of Apigee log data, including specific flow variables, to your SIEM. |
Integrating Apigee with your SIEM
Apigee's adaptability ensures smooth integration with your chosen SIEM solution. The general integration steps are:
Note: If you use Google Security Operations SIEM, seeIntegrate Apigee with Google SecOps for more information. See alsoGoogle Security Operations SIEM overview.- Choose your integration method. Select either Google Cloud platform logs or the ApigeeMessage Logging policy based on your data requirements and SIEM capabilities.
- Establish Data Forwarding. To establish data forwarding, configure Apigee to send the desired log data to your SIEM. The basic steps for this configuration are as follows. The exact steps depend on your SIEM system's setup and configuration details:
- Set up a connection or integration between Apigee and your SIEM.
- Specify in your SIEM configuration which Apigee logs or events to forward to your SIEM.
- Grant necessary permissions within your SIEM to receive and process the Apigee data.
- Align Data Structures. Map the Apigee log fields andflow variables (like
client.ip,request.uri, etc.) to the corresponding fields in your SIEM's data model. This alignment ensures that the SIEM can correctly interpret and categorize the Apigee data for effective analysis and correlation with other security events.
Log Advanced API security data
If you wish to log data that was identified by Advanced APIsecurityAbuse detection, you can useActions with the Apigee Message Loggingpolicy.
Follow these steps:
- UseAdvanced API Security actions to flag a rule you want to log.
- Use the header added by the action to trigger the Message Logging policy to log the flagged request. For example, the following image shows the header
apisecconfigured with the valueabusein the actions UI: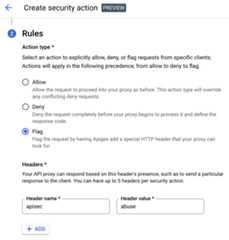
Following this example, you could configure the Message Logging policy to trigger when it sees the header:
<PostFlow name="PostFlow"> <Request> <Step> <Condition>request.header.apisec="abuse"</Condition> <Name>LogMessagePolicy</Name> </Step> </Request></PostFlow>
Example: Use the Apigee Message Logging policy
This example shows how to configure the ApigeeMessage Logging policy to send Apigee log data to a SIEM. With this option, you specify in the Message Logging policy which Apigeeflow variables you wish to send to the SIEM. This option lets you send a richer set of log details to the SIEM than you get with the Cloud platform log option.
Note:To use this option, you must be familiar with configuring and usingApigee policies.- Enable ingestion of Apigee data into the SIEM.
- Create aMessage Logging policy with the following XML body. For help, seeAttaching and configuring policies in the UI.Note: Only the flow variables specified in the policy will be sent to the SIEM. If you do not wish to log certain variables, remove them from the policy body.
<?xmlversion="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"standalone="yes"?><MessageLoggingcontinueOnError="false"enabled="true"name="ML-SIEM-Integration"><CloudLogging><LogName>projects/{organization.name}/logs/Apigee-SIEM-Integration-{environment.name}</LogName><MessagecontentType="application/json"defaultVariableValue="unknown">{"apigee.metrics.policy.{policy_name}.timeTaken":"{apigee.metrics.policy.{policy_name}.timeTaken}","client.country":"{client.country}","client.host":"{client.host}","client.ip":"{client.ip}","client.locality":"{client.locality}","client.port":"{client.port}","client.state":"{client.state}","organization.name":"{organization.name}","proxy.client.ip":"{proxy.client.ip}","proxy.name":"{proxy.name}","proxy.pathsuffix":"{proxy.pathsuffix}","proxy.url":"{proxy.url}","request.uri":"{request.uri}","request.verb":"{request.verb}","response.content":"{response.content}","response.reason.phrase":"{response.reason.phrase}","response.status.code":"{response.status.code}","system.region.name":"{system.region.name}","system.timestamp":"{system.timestamp}","system.uuid":"{system.uuid}","target.country":"{target.country}","target.host":"{target.host}","target.ip":"{target.ip}","target.locality":"{target.locality}","target.organization":"{target.organization}","target.port":"{target.port}","target.scheme":"{target.scheme}","target.state":"{target.state}","target.url":"{target.url}"}</Message></CloudLogging></MessageLogging>
- Attach the policy to the Proxy Endpoint Post Flow. SeeAttaching and configuring policies in the UI.
As the API proxy processes traffic, the logging policy will capture the specified fields from the requests and responses and write them out to the log file for analysis and debugging.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.
