Apigee networking options
You can choose one of two distinct networking options when you provision a new Apigee organization:Non-VPC Peering orVPC peering. These two options are summarized below.
- The Non-VPC Peering option usesPrivate Service Connect (PSC) to route traffic from clients to Apigee (northbound traffic) and from Apigee to target services hosted in your Google Cloud projects (southbound traffic). In this model, you do not need to provide dedicated IP ranges in your network during Apigee provisioning. See alsoSouthbound networking patterns andNorthbound networking with Private Service Connect.
- The VPC-peering option usesprivate service access to create a private connection between your VPC network and a network owned by Apigee. This model employsVPC network peering to connect your network with Apigee's. The peering model requires you to allocate dedicated IP ranges in your network when you provision a new instance of Apigee. Additionally, you can also leveragePrivate Service Connect (PSC) to route traffic from clients to Apigee (northbound traffic) and from Apigee to target services hosted in your Google Cloud projects (southbound traffic) along with VPC peering.
Non-VPC Peering option
Note:The non-VPC peering option is available using the CLI provisioning steps only. Non-VPC peering through the Cloud console is not available at this time. You can use the CLI to provision Apigee with non-VPC peering forsubscription,Pay-as-you-go, andeval organizations.We also support usingTerraform to provision Apigee without VPC peering. TheApigee terraform modules repository on GitHub. provides end-to-end sample modules and reusable terraform modules for Apigee.
This option does not require VPC peering. With this approach, you are not required to provide networks and IP ranges during the Apigee provisioning process. Instead, you usePrivate Service Connect (PSC) for routing northbound traffic (from clients to Apigee) and southbound traffic (from Apigee to to target services running in your Google Cloud projects).
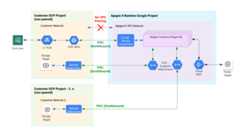
PSC enables private connection between a service producer (Apigee) and a service consumer (one or more other Cloud projects that you control). With non-VPC peering provisioning, requests pass through either a global external load balancer or a regional external load balancer to a single point of attachment, called aservice attachment (Figure 1) using PSC.
The non-VPC provisioning steps are described inProvision without VPC peering

VPC peering option
Traditionally, Apigee has employedVPC network peering to enable communication between a virtual private cloud (VPC) network managed by you and a VPC network managed by Apigee. This configuration allows bi-directional communication between the two VPC networks and allows Apigee API proxies to call target services deployed in your VPC. If target applications are in the peered network, Apigee can access their IP addresses and route API proxy traffic to them. See alsoApigee architecture overview.
To create an Apigee instance, you are required to allocate a pair of IP Address Ranges (a /22 and /28 CIDR range) to Apigee and perform the VPC peering between your network and Apigee's network. Each Apigee instance requires a non-overlapping CIDR range of /22 and /28. The Apigee runtime plane is assigned IP addresses from within this CIDR range. As a result, it's important that the range is reserved for Apigee and not used by other applications in your VPC network.
Apigee supports peering with only one network; however, many enterprises have multiple networks where applications and services are deployed. In these cases, you can use PSC to privately connect Apigee to target services running across VPC networks in addition to the peered network (Figure 2). See Southbound networking patterns for more information.


The steps for provisioning Apigee with VPC peering are covered inProvision with VPC peering.
How to choose a networking option
The following table describes the features/approaches available with each networking option:
| Feature availability | VPC peering-based provisioning | Non-VPC peering-based provisioning |
| Network requirements | ||
| Requires network information for Apigee organization creation | Yes | No |
| Requires IP range allocation for Apigee instance creation | Yes (/22 & /28 CIDR ranges for each region) | No |
Northbound routing | ||
| PSC-based routing | Yes | Yes |
| MIG-based routing | Yes | No |
| Global load balancing | Yes | Yes |
| Global load balancing (Classic) | Yes | No |
| Regional load balancing | Yes | Yes |
| Active health check for multi-region failover routing | Yes (withMIG-based routing) | No (withPSC NEGs) Yes (withMIG-based routing) |
Southbound routing | ||
| Southbound routing options | Can use VPC peering or PSC | PSC Only |
Other features | ||
| DNS peering (SeeConnecting with private DNS peering zones) | Yes | Yes |
| VPC Service Controls | Yes | No |
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2026-02-19 UTC.
