Apigee hybrid example with Kubernetes
This pageapplies toApigee andApigee hybrid.
View Apigee Edge documentation.![]()
This example demonstrates how to use Apigee Adapter for Envoy with an Apigee hybrid deployment.
Prerequisites
| Before you begin: |
|---|
Overview
This example explains how to use Apigee Adapter for Envoy with Apigee hybrid. In this example, you will deploy a simple HTTP service in the same Kubernetes cluster where Apigee hybrid is deployed. Then, you will configure the Apigee Adapter for Envoy to manage API calls to this service with Apigee.
The following figure shows the basic architecture for the Apigee hybrid integration:
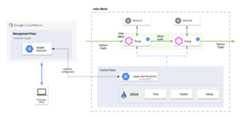
An Envoy proxy is deployed with the target HTTP service as an Istio sidecar in the Istio service mesh. The sidecar handles API traffic to and from the target service, and communicates with the Remote Service. The Remote Service also communicates with the hybrid management plane to retrieve API product and proxy information.
Check your gcloud configuration
- Check that your
gcloudconfiguration is set to the Google Cloud project associated with your hybrid organization.To list the current settings:
gcloud config list
If necessary, set the correct Google Cloud project ID with this command:
gcloud config set projectproject-id
- You must be authenticated with Google Cloud SDK (gcloud) for your Google Cloud project:
gcloud auth login
Provision Apigee hybrid
In this step, you will use the Remote Service CLI to provision hybrid with theremote-service API proxy. The provisioning command also sets up a certificate on Apigee, and generates credentials the remote service will use to securely connect back to Apigee.
- Go to the
$CLI_HOMEdirectory:cd $CLI_HOME
- If you are not an owner of the Google Cloud project associated with the Apigee hybrid organization, be sure that your Google Cloud user account includes either theApigee Organization Admin role, or both theAPI Creator and theDeployer roles.
- Execute this command to get an access token:
TOKEN=$(gcloud auth print-access-token);echo $TOKEN
- (Optional) By default, the adapter looks for default service account credentials in your Google Cloud project for permission to send analytics data to Apigee. If you don't want to use thedefault service account credentials, you can create a service account and reference its key in the provisioning command. The service account must have the
apigee.analyticsAgentrole. For instructions, seeCreating and managing service accounts. - Create the following environment variables. These variables will be used as parameters to the provisioning script:
exportORG=organization_nameexportENV=environment_nameexportRUNTIME=host_alias_urlexportNAMESPACE=hybrid_runtime_namespaceexportAX_SERVICE_ACCOUNT=analytics_service_account## OptionalWhere:
Variable Description organization_name The name of the Apigee organization for you Apigee hybrid installation. environment_name The name of an environment in your Apigee hybrid organization. host_alias_url A URL that includes the hostAliasfor a virtual host defined in your hybrid configuration. The URL must start withhttps://. For example:https://apitest.apigee-hybrid-docs.nethybrid_runtime_namepace The namespace in which the Hybrid runtimecomponents are deployed. Note: The default namespace for a hybrid deployment is apigee.analytics_service_account (Optional) The path to a Google Cloud service account key JSON file that has the Apigee Analytics Agentrole. For a detailed description of this parameter, seeProvision command. - Execute the following command to provision the remote service proxy to Apigee hybrid:NOTE: If your hybrid runtime installation is configured using self-signed TLS certificates for the virtualhost, you must use the
--insecureflag with theprovisioncommand shown below.NOTE:The command output is redirected to a config file that you will use in a later step.IF YOU ARE UPGRADING:If you are upgradingan existing Apigee Adapter for Envoy, you must add the--force-proxy-installflag to theprovisioncommand. This flag forces the Apigee proxy to be replaced with the latest proxy.If you arenot upgrading, use this command to provision Apigee:
./apigee-remote-service-cli provision --organization $ORG --environment $ENV \ --runtime $RUNTIME --namespace $NAMESPACE --analytics-sa $AX_SERVICE_ACCOUNT --token $TOKEN > config.yaml
If you are upgrading, use this command with the
--force-proxy-installflag to provision Apigee:./apigee-remote-service-cli provision --force-proxy-install --organization $ORG --environment $ENV \ --runtime $RUNTIME --namespace $NAMESPACE --analytics-sa $AX_SERVICE_ACCOUNT --token $TOKEN > config.yaml
- Check the contents of the
config.yamlfile. It should look something like this:#Configurationforapigee-remote-service-envoy(platform:GoogleCloud)#generatedbyapigee-remote-service-cliprovisionon2020-11-2002:49:28apiVersion:v1kind:ConfigMapmetadata:name:apigee-remote-service-envoynamespace:apigeedata:config.yaml:|tenant:remote_service_api:https://apitest.example.com/remote-serviceorg_name:hybrid-gkeenv_name:testanalytics:collection_interval:10sauth:jwt_provider_key:https://apitest.example.com/remote-token/token---apiVersion:v1kind:Secretmetadata:name:hybrid-gke-new-test-policy-secretnamespace:apigeetype:Opaquedata:remote-service.crt:eyJrZXlzIjpbeyJrdHkiOiJSU0EiLCJhbGci...remote-service.key:LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBSU0EgUFJJVkFURS...remote-service.properties:a2lkPTIwMjAtMDctMDZ...---apiVersion:v1kind:Secretmetadata:name:hybrid-gke-new-test-analytics-secretnamespace:apigeetype:Opaquedata:client_secret.json:ewogICJ0eXBlIjogInNlcnZ...---apiVersion:v1kind:ServiceAccountmetadata:name:apigee-remote-service-envoynamespace:apigee
- Apply the service configuration (the file output by the provisioning command) to the cluster where Apigee hybrid was installed inStep 1: Create a cluster.
kubectl apply -f $CLI_HOME/config.yaml
- Verify your proxy and certificate. The following should return valid JSON:
curl -i $RUNTIME/remote-token/certs
The output looks something like this:
{ "keys": [ { "alg": "RS256", "e": "AQAB", "kid": "2020-05-11T11:32:26-06:00", "kty": "RSA", "n": "0v-nbTQyAmtVZ-wZRP0ZPIbrVaX91YO9JZ9xCQPb4mOdOSS7yKfTDJGg0KM130sGVYBvR76alN8 fhrrSDEG5VXG8YYMqPXarwRC7MRJWocCQ_ECYrjDD0_Q018M2HyXZYSd8fhAogi9mVUYsEmCKqJH53Dh1 jqsHOQzBLKsX0iDO9hEZNFtjbX0UCbSxsUlmBCub7Uj2S-PahA6DEQOMhQjZM7bBMtkTMpFmaJ_RZTmow BHP57qMna17R8wHD4kUsO2u_-3HHs5PSj1NrEYoVU2dwLQw0GlkB__ZWeFgXTqot81vb-PmoM9YxwoZrm TcHdljugWy_s7xROPzTod0uw" } ]}
Create sample configuration files
Use theapigee-remote-service-cli samples create command to generate sample configuration files.
For this example, you need these generated files:
httpbin.yaml- A deployment configuration for an HTTP service.apigee-envoy-adapter.yaml- A deployment configuration for the Remote Service for Envoy.envoyfilter-sidecar.yaml- A configuration that installs an EnvoyFilter. to the default namespace.
To generate the samples:
- Go to the
$CLI_HOMEdirectory. Execute this command to generate the files:
./apigee-remote-service-cli samples create -c ./config.yaml --template istio-1.12
./apigee-remote-service-cli samples templatesThe following files are output the
./samplesdirectory:ls samplesapigee-envoy-adapter.yaml envoyfilter-sidecar.yaml httpbin.yaml request-authentication.yaml
For more information, seeSamples command.
Deploy a test service to the cluster
In this step, you will deploy a simple HTTP request/response test service to the same cluster where Apigee hybrid is deployed.
- Enable Istio injection in the
defaultnamespace of the cluster. In a later step, you will deploy an Envoy sidecar to this same cluster. Enabling Istio injection makes the sidecar deployment possible. This example uses thedefaultnamespace, and all subsequent instructions assume this is the case.If you are using open source Istio:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled --overwrite
If you are using ASM:
kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabled istio.io/rev=REVISION --overwrite
- Apply the simple
httpbinservice to the cluster in the default namespace:kubectl apply -f $CLI_HOME/samples/httpbin.yaml
- Now, test the service. Start a
curlservice running in the cluster and open a terminal:kubectl run -it curl --image=curlimages/curl --restart=Never -- sh
- Test the service by calling it from inside the cluster:
curl -i httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local/headers
On success, you will see a 200 status, and the service returns a list of headers. For example:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKserver: envoydate: Tue, 12 May 2020 17:09:01 GMTcontent-type: application/jsoncontent-length: 328access-control-allow-origin: *access-control-allow-credentials: truex-envoy-upstream-service-time: 7{ "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Content-Length": "0", "Host": "httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local", "User-Agent": "curl/7.70.0-DEV", "X-B3-Parentspanid": "69f88bc3e322e157", "X-B3-Sampled": "0", "X-B3-Spanid": "8dd725f30e393d8b", "X-B3-Traceid": "38093cd817ad30a569f88bc3e322e157" }}curlclient running and the shell open. You will use it in a later step.
Run the Remote Service for Envoy
In this step, you start the Remote Service for Envoy client. This service provides the endpoints to the Istio sidecars that are installed on target services. You will also install a sidecar with thehttpbin service.
- Apply the Apigee Remote Service to the service mesh:
kubectl apply -f $CLI_HOME/samples/apigee-envoy-adapter.yaml
- Apply the
EnvoyFilterto the Istio sidecars in the default namespace. TheEnvoyFilterenables thehttpbinsidecar to communicate with the Apigee Remote Service.kubectl apply -f $CLI_HOME/samples/envoyfilter-sidecar.yaml
Test the installation
- Now, go back to the curl shell you opened in the step Deploy a test service to the cluster and call the
httpbinservice:curl -i httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local/headers
The service is now being managed by Apigee, and because you did not supply an API key, the server returns the following error.
curl -i httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local/headersHTTP/1.1 403 Forbiddendate: Tue, 12 May 2020 17:51:36 GMTserver: envoycontent-length: 0x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 11
- Configure an API product and get an API key as explained inHow to obtain an API key.
- Make an API call using the key:
exportAPIKEY=YOUR_API_KEYcurl-ihttpbin.default.svc.cluster.local/headers-H"x-api-key: $APIKEY"The call should succeed with a 200 status and returning a list of headers in the response. For example:
curl -i httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local/headers -H "x-api-key: kyOTalNNLMPfOSy6rnVeclmVSL6pA2zS"HTTP/1.1 200 OKserver: envoydate: Tue, 12 May 2020 17:55:34 GMTcontent-type: application/jsoncontent-length: 828access-control-allow-origin: *access-control-allow-credentials: truex-envoy-upstream-service-time: 301{ "headers": { "Accept": "*/*", "Content-Length": "0", "Host": "httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local", "User-Agent": "curl/7.70.0-DEV", "X-Api-Key": "kyOTalNNLMPfOSy6rnVeclmVSL6pA2zS", "X-Apigee-Accesstoken": "", "X-Apigee-Api": "httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local", "X-Apigee-Apiproducts": "httpbin", "X-Apigee-Application": "httpbin", "X-Apigee-Authorized": "true", "X-Apigee-Clientid": "kyOTalNNLMPfOSy6rnVeclmVSL6pA2zS", "X-Apigee-Developeremail": "jdoe@example.com", "X-Apigee-Environment": "envoy", "X-Apigee-Organization": "acme-org", "X-Apigee-Scope": "", "X-B3-Parentspanid": "1476f9a2329bbdfa", "X-B3-Sampled": "0", "X-B3-Spanid": "1ad5c19bfb4bc96f", "X-B3-Traceid": "6f329a34e8ca07811476f9a2329bbdfa" }}
Next steps
API traffic to thehttpbin service is now managed by Apigee. Here are some features you can explore and try:
- Access Apigee Analytics in the Edge UI. Go toAnalyze > API Metrics > API Proxy Performance.
- Use the CLI to manage, create tokens, and control bindings. For CLI details, see theReference.
Uninstall Apigee Adapter for Envoy
To remove an Apigee Envoy adapter installation:
- Wherever you chose to have envoy adapter run (natively or on Docker), remove it.
- Delete theremote-service andremote-token proxies from your Apigee environment(s). SeeDeleting an API proxy.
- Remove any unused API products oroperations used by the Envoy adapter use cases. SeeDeleting an API product.
Also, you can execute the following commands:
kubectl delete -f $CLI_HOME/samples/envoyfilter-sidecar.yaml kubectl delete -f $CLI_HOME/samples/apigee-envoy-adapter.yaml kubectl delete -f $CLI_HOME/samples/httpbin.yaml kubectl delete -f $CLI_HOME/config.yaml
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.
