Using Debug
This pageapplies toApigee andApigee hybrid.
View Apigee Edge documentation.![]()
This section describes how to create and manage debug sessions, and view the request and response data using the Apigee UI and API.
UseOffline Debug to view and analyze debug sessions that were previously downloaded.
Creating a debug session
The Debug tool is simple to use. You start a debug session, and then make an API call to Apigee, and then view the request and response data in the UI.
Create a debug session using the Apigee UI or API as described in the following sections.
Note: There is a delay of approximately 15 seconds between starting a debug session and its activation across Apigee. This can cause missed API requests in the initial 15-20 seconds of a debug session.Note: The Debug Tool is available in the Apigee UI and some debug actions can be performed using the API. The Apigee UI options are Debug v2 (new) and Debug v1 (released07/01/2022). You can switch between versions of the Debug Tool in the Apigee UI; however, Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.Apigee UI
Debug v2 (new)
To create a debug session:
In the Google Cloud console, go to theProxy development> API Proxies page.
- Select the API proxy that you want to debug. This displays the Proxy EditorOverview pane.
- Click theDebug tab.
- ClickStart debug session. This displays theStart debug session pane.
In theStart debug session pane:
- Select theEnvironment in which you want to run the debug session.
(Optional) From theFilter drop-down list, select a filter to apply to all transactions in the debug session you are creating. The default is
None (All transactions), which includes all transactions in the debug data.For information on using filters, seeUsing filters in a debug session. For information about the built-in filters, seeUsing predefined filters.
- ClickStart.
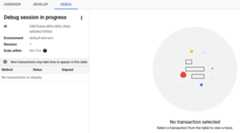
The Apigee UI now displays theDebug session in progress pane.


The debug session records requests for 10 minutes or until 15 requests have been captured. You can adjust the 10-minute limit if you create the debug session using the API. TheEnds within field displays the amount of time remaining in the session.
You won't see any information displayed in the Debug pane until you send a request to the proxy you are debugging in the selected environment for the debug session.
After you send the request, it is displayed in theTransactions list pane. TheTransactions list updates every five seconds.

To view or copy transaction output:
- In theTransactions list, clickView transaction output. TheTransaction output pane displays.
- Click an individual transaction, or clickAll transactions.
- ClickCopy to copy the transaction output to the clipboard.
- ClickClose.
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To create a debug session in the new Proxy Editor:
- Sign in to theGoogle Cloud console.
SelectProxy development > API Proxies.
Select the API proxy that you want to debug. This displays the Proxy EditorOverview view.
- Click theDebug tab at the top-left of the window.
- Click theStart Debug Session at the top right of theDebug pane. This displays theStart debug session dialog.

In the dialog:
- Select theEnvironment in which you want to run the debug session.
- (Optional) From theFilter drop-down list, select a filter to apply to all transactions in the debug session you are creating. The default is
None (All transactions), which includes all transactions in the debug data.For information on using filters, seeUsing filters in a debug session. For information about the built-in filters, seeUsing predefined filters.
- ClickStart.
The Apigee UI now displays theDebug session in progress view.
The debug session records requests for 10 minutes or until 15 requests have been captured. You can adjust the 10-minute limit if you create the debug session using the API. TheEnds within field displays the amount of time remaining in the session.
You won't see any information displayed in the Debug pane until you send a request to the proxy you are debugging in the selected environment. environment for the debug session.
After you send the request, it is displayed at the bottom of the left-hand pane.

Note: During an active debug session, you can start another session in the Apigee UI. To do so, simply clickStart Debug Session again.
API
To create a debug session using the API, issue aPOST request to the following resource:
https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/$ORG/environments/$ENV/apis/$API/revisions/$REV/debugsessions
Optionally, you can:
- Set the length of a debug session (in seconds) by passing the
timeoutproperty as a query parameter or in the request body. If both are specified, thetimeoutvalue specified in the request body takes precedence. - Filter data in a debug session by passing the
filterproperty in the request body.
The following example demonstrates how to create a debug session using the API.
curl "https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/ORG/environments/ENV/apis/PROXY/revisions/REV/debugsessions" \ -X POST \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where$TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token, as described inObtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token. For information about thecurl options used in this example, seeUsing curl. For a description of environment variables you can use, seeSettingenvironment variables for Apigee API requests.
The following provides an example of the response:
{ "name":"56382416-c4ed-4242-6381-591bbf2788cf", "validity":300, "count":10, "tracesize":5120, "timeout":"600" }Subsequent requests to your API proxy (until the session duration or maximum number of requests is reached) will be evaluated and potentially stored in the debug session data.
For more information, see theCreate debug session API.
Setting the length of a debug session using the API
To set the length of a debug session using the API, include the following as a payload in your debug session creation request:
{ "timeout":"debug_session_length_in_seconds" }The following example creates a debug session that is just 42 seconds long:
curl https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/ORG/environments/ENV/apis/PROXY/revisions/REV/debugsessions" -X "POST" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \ -d ' { "timeout":"42" } 'You can set a session'stimeout in debug session creation requests only; you cannot change a session's duration after you create the session.
The default value oftimeout is 300 (5 minutes). The maximum value is 600 seconds (10 minutes).
Copy the proxy URL
The proxy URL is used to send requests to your API proxy.
Debug v2 (new)
To find and copy the proxy URL:
- In theDebug session pane,URL field, clickCopy.
- If aDebug session is not open:
In the Google Cloud console, go to theManagement> Environments> Environment Groups page.
- The URL is theHostname for the respective environment you'd like to run your debug session with. Select it and then copy it.
To select a different proxy URL:
- In theDebug session pane,URL field, clickEdit.
- Make any desired changes and then clickUpdate.
- If aDebug session is not open:
- Find the proxy URL.
- ClickMore, and then clickEdit.
- Make any desired changes and then clickUpdate.
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To find and copy the proxy URL:
- In the Google Cloud console, go toManagement > Environments > Environment Groups
- The URL is theHostname for the respective environment you'd like to run your debug session with. Select it and then copy it.
To edit the proxy URL:
- Find the proxy URL.
- ClickMore, and then clickEdit.
- Make any desired changes and then clickUpdate.
Starting another debug session in the UI
You can create any number of debug sessions in the UI.
During an active debug session, youcan start another session in the Apigee UI. To do this, clickClose in theDebug session pane:

The UI returns to theStart a debug session panel, where you can start a newdebug session.
When does a debug session end?
You cannot simplystop an active debug session. You can, however, delete an active session's data, as described inDeleting debug session data.
When you create a debug session, two properties determine when it ends:
- timeout: The length of time for which you collect data during a session.The default length depends on how you started the session (through the UI or API). Themaximum value is 600 seconds (or 10 minutes).Tip: You cannot configure the timeout when you createa new debug session with the Apigee UI. Youcan, however, set the timeout whenyoucreate a new debug session using the API.
- count: The maximum number of requests that are recorded in a singlesessionper Message Processor. Because the number of Message Processors in mostclusters is variable, the effects of the count can be unpredictable. Apigee does notrecommend customizing this setting.
When either the timeout or the count is reached, the debug session for that Message Processorends.
The following terms are used to describe the state of a debug session:
- active session is a debug session that has not yet reached its timeout or exceededits count. An active session is still recording request data for requests that are not filteredout.
- completed session is a debug session that has either reached its timeout or exceededits count; a completed session no longer records data about new requests and its data isdeleted within 24 hours of the time at which the session ended.
How to read a debug session
This section provides an overview of a debug session.
See also:
Debug v2 (new)
The Debug Tool has two main parts, the transaction pane and the phase details:
- The transaction pane usesicons to mark each notable step that occurs during an API proxy transaction, including policy execution, conditional steps, and transitions. Hover over anyicon to see summary information. The request flow steps appear along the top of the transaction map and response flow steps along the bottom.
- Thephase details pane lists information about the proxy's internal processing, including variables that were set or read, request and response headers, and much more. Click any icon to see thephase details for that step.
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.This version of the debug tool utilizes a Gantt chart to display the steps in the request and response.
Transaction pane
The transaction pane shows the steps in the request and response.
Debug v2 (new)
Here's a sample debug tool transaction pane with the main proxy processing segments labeled:


Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To view the details of a transaction (request and response) in the Debug view, click the row for the transaction to display aGantt chart in the right-hand pane that shows the steps in the request and response.

The horizontal axis of the diagram denotes the times at which each step occurred, measured in milliseconds. Each step is represented by a rectangle that extends from the start time to the end time of the step.
You can step through a debug session using theBack andNext buttons at the bottom right of the debug pane. Click:
- Back to move the selected row to the previous step in the chart.
- Next to move the selected row to the next step in the chart.
In the example shown above, the chart displays two policies that are executed in the response:
- ResponsePayload
- Add CORS
You can click on either of these steps to view its details. For example, if you clicked theAdd CORS policy, you would see details like the ones shown below displayed next to the Gantt chart.

If you then decided to change something in the policy configuration, you could then clickDevelop to switch to theDevelop view, where you would see the same two policies in the Response PostFlow.

Transaction pane legend
The following describes the icons in the transaction pane:
Debug v2 (new)
This section describes the icons in the transaction pane:
Policy icons
Each type of policy has a unique icon. These icons let you see where policies are executed in the proper order and if they are successful or not. You can click a policy icon to see the results of its execution and if they are expected or not. For example, you can see if the message was transformed properly or if it is being cached.
Standard policies augment your APIs to control traffic, enhance performance, enforce security, and increase the utility of your APIs, without requiring you to write code or modify backend services.
Extensible policies let you add custom logic to your API proxies. You can use these policies to add functionality that is not provided by the standard policies.
See Policy reference overview for more information about policies and categories.
To filter the table:
- Select one policy type and/or one policy category.
- Click theName column header to sort the table by policy name.
- Type a keyword to search for a policy name.
| Icon | Name | Type | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| manage_search | ParseDialogflowRequest policy | Extensible | Dialog flow |
| chat_add_on | SetDialogflowResponse policy | Extensible | Dialog flow |
| stacked_line_chart | DataCapture policy | Extensible | Extension |
| display_external_input | ExternalCallout policy | Standard | Extension |
| flowsheet | FlowCallout policy | Extensible | Extension |
| automation | IntegrationCallout policy | Extensible | Extension |
| JavaCallout policy | Extensible | Extension | |
| JavaScript policy | Extensible | Extension | |
| add_notes | MessageLogging policy | Extensible | Extension |
| chat_paste_go | PublishMessage policy | Standard | Extension |
| PythonScript policy | Extensible | Extension | |
| integration_instructions | ServiceCallout policy | Extensible | Extension |
| automation | SetIntegrationRequest policy | Extensible | Extension |
| waterfall_chart | TraceCapture policy | Extensible | Extension |
| cloud_done | AccessEntity policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| account_tree | AsseretCondition policy | Standard | Mediation |
| edit_square | AssignMessage policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| login | ExtractVariables policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| GraphQL policy | Standard | Mediation | |
| sync_alt | HTTPModifier policy | Standard | Mediation |
| sync_alt | JSONtoXML policy | Standard | Mediation |
| account_tree | KeyValueMapOperations policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| sync_alt | MonetizationLimitsCheck policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| cloud_done | OASValidation policy | Standard | Mediation |
| report | RaiseFault policy | Standard | Mediation |
| sync_alt | ReadPropertySet policy | Standard | Mediation |
| cloud_done | SOAPMessageValidation policy | Standard | Mediation |
| sync_alt | XMLtoJSON policy | Standard | Mediation |
| cloud_done | XSLTransform policy | Extensible | Mediation |
| lock | AccessControl policy | Standard | Security |
| security | BasicAuthentication policy | Extensible | Security |
| connect_without_contact | CORS policy | Standard | Security |
| lock | DecodeJWS policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | DecodeJWT policy | Standard | Security |
| passkey | DeleteOAuthV2Info policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | GenerateSamlAssertion policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | GenerateJWS policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | GenerateJWT policy | Extensible | Security |
| passkey | GetOAuthV2Info policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | HMAC policy | Standard | Security |
| security | JSONThreatProtection policy | Extensible | Security |
| passkey | OAuthV2 policy | Extensible | Security |
| security | RegularExpressionProtection policy | Extensible | Security |
| passkey | RevokeOAuthV2 policy | Extensible | Security |
| passkey | SetOAuthV2Info policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | ValidateSamlAssertion policy | Extensible | Security |
| key | VerifyAPIKey policy | Extensible | Security |
| passkey | VerifyIAM policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | VerifyJWS policy | Extensible | Security |
| lock | VerifyJWT policy | Standard | Security |
| security | XMLThreatProtection policy | Extensible | Security |
| cached | InvalidateCache policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| cached | LookupCache policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| cached | PopulateCache policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| bar_chart_4_bars | Quota policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| repartition | ResetQuota policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| cached | ResponseCache policy | Extensible | Traffic management |
| emergency_home | SpikeArrest policy | Standard | Traffic management |
Other icons
The following table describes the intent of the other icons you will see in the transaction pane. These icons mark each of the notable processing steps throughout the proxy flow.
To filter the table:
- Select one icon type.
- Click theName column header to sort the table by icon name.
- Type a keyword to search for an icon name.
| Icon | Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| monitor | Client app | Standard transaction | The client app that sends a request to the ProxyEndpoint of the API proxy. |
| circle | Transitional endpoint | Standard transaction | The circle marks transitional endpoints in the proxy flow. They are there when a request comes in from the client, when the request goes to the target, when the response comes back from the target, and when the response goes back to the client. |
| stat_0 | Flow segment | Standard transaction | The diamond indicates the beginning of a flow segment in the API proxy flow. Flow segments are: ProxyEndpoint request, TargetEndpoint request, TargetEndpoint response, and ProxyEndpoint response. A segment includes the PreFlow, Conditional Flows, and PostFlow. See Conditional flows for more information. |
| Conditional flow true | Standard transaction | A conditional flow that evaluates to true (like an Note that some conditions are Apigee-generated. For example, the following is an expression that Apigee uses to check if an error occurred in the ProxyEndpoint:
| |
| Conditional flow false | Standard transaction | A conditional flow that evaluates to false. For an introduction to conditional flows, see Conditional flows. Note that some conditions are Apigee-generated. For example, the following is an expression that Apigee uses to check if an error occurred in the TargetEndpoint:
| |
| Flow info | Standard transaction | Represents contextual information about the API proxy execution, which varies depending on the point in the flow. This includes details about the proxy configuration, the current execution state (e.g., PreFlow, PostFlow, flow hooks), policy execution details, and variables populated during policy execution, to indicate the specific state of the proxy at that point. | |
| done_all | Flow execution | Standard transaction | Marks the beginning or end of a flow's execution, indicating the timeframe of a distinct flow segment, to visually demarcate flow boundaries and indicate the sequence of flow execution. |
| commit | Flow processing | Standard transaction | Indicates active processing within a flow, representing the period during which policies and flow logic are executed. |
| bar_chart | Apigee analytics captured data | Standard transaction | Indicates that Analytics actions have occurred in the background. |
| location_on | Backend service | Standard transaction | Backend service that receives the request. The backend target called by the API proxy. |
| Disabled | Step status | Appears on a policy icon when a policy is disabled. A policy can be disabled with the public API. See API proxy configuration reference. | |
| Error | Step status | Appears on a policy icon when the policy step condition evaluates to false (see Conditions with flow variables), or on the RaiseFault policy icon whenever a RaiseFault policy executes. | |
| Skipped | Step status | Appears on a policy icon when the policy was not executed because the step condition evaluated to false. See Conditions with flow variables) for more information. |
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.This version utilizes a Gantt chart to display the steps in the request and response; there is no legend provided.
Phase details pane
The phase details pane tells you about the state of your proxy at each processing step.
Debug v2 (new)
The phase details pane tells you a lot about the state of your proxy at each processing step. Here are some of the details provided. Click any icon in the debug tool to see details for the selected step, or use the>Next or<Back buttons to move from one step to another.
Warning: Debug captures message content. If your message payloads contain sensitive information, then you should enable data masking. For instructions, see Masking and hiding data.The following table describes the details provided in the phase details pane.
| Phase Detail | Description |
| Variables | Lists the flow variables that were read and assigned a value by a policy, See also Using flow variables. Note:
|
| Request Headers | Lists the HTTP request headers. |
| Request Content | Shows the HTTP request body. |
| Properties | Properties represent the internal state of the API proxy. These are not shown by default. |
| Target Endpoint | Indicates which TargetEndpoint was selected for execution. |
| Response Headers | Lists the HTTP response headers. |
| Response Content | Shows the HTTP response body. |
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.Click on steps in the Gantt chart to see the phase details or step through a debug session using the>Next or<Back buttons.
Timeline
The timeline indicates how long (in milliseconds) that the processing time took to complete. Comparing the elapsed time segments helps you isolate the policies that are taking the longest to execute that are slowing down your API calls.
The Epsilon indicates a time-span smaller than a millisecond.
Debug v2 (new)


Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.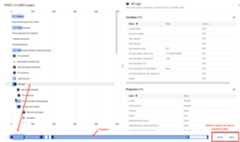

Expanding and collapsing groups
This section describes how to expand and collapse groups in theTransaction pane.
Debug v2 (new)
Transaction steps, for both request and response, are grouped by how they were configured previously on theDevelop tab; by shared flow. For example: pre-proxy, post-proxy, pre-target, and post-target.
Each grouping clearly displays relevant policies, conditions, shared flows, and flow information.
Shared flows are grouped and collapsed by default.
The following actions are available in theTransaction pane:
| Item | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
  | Expand all Collapse all | Expand or collapse all groups. |
| Expand Collapse | Expand or collapse a group. |
See also:
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.Expanding and collapsing groups is not available in this version.
Search
Search allows you to find a word or phrase in the request or response.
Debug v2 (new)
Search allows you to find a word or phrase in the request or response.
Note the following:
- Search is case-insensitive
- Search applies to a single transaction; that is, it does not search across all transactions in the entire debug session.
- Search expands collapsed sections, but does not show information on nodes that are filtered out by View Options selections.
To search:
- Type text in the search box.
PressEnter.
The search results are highlighted in theTransaction pane and in thePhase Details pane.
- Clickkeyboard_arrow_upBack orkeyboard_arrow_downNext to move to the next or previous step.


Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.Search is not available in this version.
Zoom
Zoom allows you to control the view of theTransaction pane.
Debug v2 (new)
Zoom controls the view of theTransaction pane as follows:

| Icon | Description |
|---|---|
| 100% | Current zoom level. Defaults to 100%. |
| fit_screen | Fit to screen |
| zoom_in | Zoom in |
| zoom_out | Zoom out |
| youtube_searched_for | Zoom reset |
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.Zoom is not available in this version.
Debugging with the debug tool
The debug lets you see a lot of internal details about an API proxy. For example:
- You can see at a glance which policies are executing correctly or failing.
- Let's say you noticed through one of the Analytics dashboards that one of your APIs is experiencing an unusual decrease in performance. Now, you can use Debug to help identify where the bottleneck is occurring. Debug gives the time, in milliseconds, that it takes for each processing step to complete. If you find one step is taking too long, you can take corrective action.
- You can check headers that are being sent to the backend, view variables set by policies, and so on.
- By verifying the base path, you can ensure that a policy is routing the message to the correct server.
Filtering data in a debug session
When you create a debug session, you can add a filter to that session so that Apigee returns only the data you want. A filter is a conditional statement that Apigee evaluates against request and response messages to determine if its debug data should be included in the debug session. For example, you can filter out all requests with an HTTPresponse code that is less than 599 or compare values in the request against custom variables.
Note the following:
- Requests that are not included in a debug session because they are filtered out do not counttowards themaximum number oftransactions in the debug session.
- Apigee does not support adding filters in the query string.
- You cannot add a filter to a debug session once the session has started. To add a filter, youmust create a debug session.
Using filters
Use a filter when creating a debug session using the Apigee UI or API, as described in the following sections.
Apigee UI
When youcreate a debug session in the UI, in theFilters drop-down list you can choose apredefined filter to apply in theStart a debug session panel or chooseCustom Filter and build your own with thefilter syntax.
API
To create a debug session with a filter using the API, include the following as a payload in your debug session creation request:
{ "filter":"filter_body"}For information on constructing filters, seeFilter syntax.
The following example creates a debug session that includes only transactions in which headerA equals42 and headerB equals43, or the fault code isExpectedEOF:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" -X "POST" https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/ORG/environments/ENV/apis/PROXY/revisions/REV/debugsessions -d ' { "filter":"(request.header.A == '42' && request.header.B == '43') || fault.code == 'jsonparser.ExpectedEOF'" } 'You can define a filter in debug session creation requests only; you cannot add a filter to anexisting debug session, and you cannot remove a filter from an active debug session.
Filter syntax
Filters support the same syntax that is used by Apigee conditions, as described inConditions reference. This includes:
- Grouping
- Logical AND (
&&) and OR (|") - Path expressions
- Operators andOperands
- Literals (
null,true, andfalse)
In addition, filters can access all flow variables that are described in theFlow variables reference as well as custom variables. The following examples show just some ofthe possible flow variables that you can use in filters:
# Response codes: response.status.code <= 599 response.status.code >=301 && response.status.code <=420# Requests/responses: request.verb == "GET" request.header.A == 'B' || request.queryparam.X == 'Y'# Query parameters: request.queryparam.myparam == 'fish' (request.queryparam.param1 == 'X' || request.queryparam.param2 == 'Y') && request.queryparam.param3 == 'Z'# Faults: fault.code != 'messaging.runtime.RouteFailed' fault.name == 'IPDeniedAccess'
For information about using custom variables, seeHow to use custom attributes in Apigee in theApigee Community.
Predefined UI filters
The Apigee UI provides a set of common filters so that you don't have to write your own custom filters. The predefined filters are as summarized in the following table.
| Filter Name | Description |
|---|---|
Response Time Greater Than | Checks for latency issues where:
For example: target.duration > 420 && client.duration > 1000 For more information, see |
Response Code | Checks if the HTTP response code matches the specified value; for example: response.status.code <= 599 message.status.code instead ofresponse.status.code. |
Header | Checks if the specified request header is equal to the specified value; for example: request.header.cache-control.1 == "16544" |
Path | Checks if the request matches the specified path. You can use wildcard matching in your value; for example: request.path == /myproxy/customer/4* |
Query Param | Checks if the specified request query parameter is equal to the specified value; for example: request.queryparam.lang == "language:en-us" |
Custom | Lets you insert your own expressions. You can use any objects in theFlow variables reference and the syntax inConditions reference. In addition, you can use custom variables. For more information about creating custom filters, seeFilter syntax. |
Viewing debug sessions
Apigee saves debug session data for24 hours. You cannot configure this value; after 24 hours,the data will no longer be available. Before that time, you can view the debug sessions.
Note: If you want to save debug session data for future reference, Apigee recommends that youdownload the debug session.To view downloaded debug session data, use theOffline Debug tool.
View recent debug sessions using the Apigee UI or API, as described in the following sections.
Apigee UI
Debug v2 (new)
To view debug sessions using the Google Cloud console
In the Google Cloud console, go to theProxy development> API Proxies page.
- Click the proxy that you want to debug.
- Click theDebug tab.
- TheRecent debug sessions displays a list of debug sessions that are available.
Click the link for the session you want to view.
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To view debug sessions using the New Proxy Editor:
- Sign in to theGoogle Cloud console.
SelectProxy development > API Proxies.
- Select the proxy that you want to debug.
- Click theDebug tab.
- TheRecent debug sessions displays a list of debug sessions that are available.
Click the link for the session you want to view.
API
Using the API, you can:
- View all debug sessions
- View all transactions for a debug session
- View transaction data for a debug session
View all debug sessions using the API
To view all recent debug sessions defined for an API proxy revision in an environment, issue a GET request to the following resource:
https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/org/environments/env/apis/api/revisions/rev/debugsessions
Optionally, you can specify one of the following query parameters to control the amount of datareturned:
- pageSize: Maximum number of debug sessions to list. The page size defaults to 25.
- pageToken: Page token, returned from a previous call, that you can use to retrieve the next page.
The following example demonstrates how to view the debug sessions for revision 1 of thehelloworld API proxy in thetest environment.
curl "https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/myorg/environments/test/apis/helloworld/revisions/1/debugsessions" \-X GET \-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where$TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token, as described inObtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token. For information about thecurl options used in this example, seeUsing curl. For a description of environment variables you can use, seeSettingenvironment variables for Apigee API requests.
The response includes asessions object that contains a list of currentlyactive debug sessions, as shown in the following example:
{"sessions": [{"id": "a423ac73-0902-4cfa-4242-87a353a84d87","timestamp_ms": 1566330186000},{"id": "f1eccbbe-1fa6-2424-83e4-3d063b47728a","timestamp_ms": 1566330286000}]}Only debug sessions that contain at least one transaction are included in the response; debugsessions that do not have any transactions are not included in this list.
For more information, seeList Debug sessions API.
View all transactions for a debug session using the API
To view a list of transactions for a debug session, issue a GET request to the following resource:
https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/org/environments/env/apis/api/revisions/rev/debugsessions/debugsession/data
Wheredebugsession is the ID of a debug session returned when youview debug sessions.
The following example demonstrates how to view the transactions for a debug session for revision 1 of thehelloworld API in thetest environment.
curl "https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/myorg/environments/test/apis/helloworld/revisions/1/debugsessions/a423ac73-0902-4cfa-4242-87a353a84d87/data" \-X GET \-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where$TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token, as described inObtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token. For information about thecurl options used in this example, seeUsing curl. For a description of environment variables you can use, seeSettingenvironment variables for Apigee API requests.
The response includes an array of transaction IDs, as shown in the following example:
["myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-64","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-65","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-66","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-67","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-68","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-69","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-70","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-71","myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-72"]
For more information, seeList debug session data API.
Viewing transaction data for a debug session using the API
To view transaction data for a debug session, issue a GET request to the following resource:
https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/{org}/environments/{env}/apis/{api}/revisions/{rev}/debugsessions/{debugsession}/data/{transactionId}Wheredebugsession is the ID of a debug session returned when youview debug sessions andtransactionId is thetransaction ID returned when youView a list of transactions for a debug session.
You cannot use this API to view an entire sessions' data at one time; to do that, you must use theUI, as described inDownloading debug data.The transaction data saved during a debug session is formatted in JSON. You can load this data intheOffline Debug tool.
The following example demonstrates how to download the transaction data for a debug session for revision 1 of thehelloworld API in thetest environment.
curl "https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/myorg/environments/test/apis/helloworld/revisions/1/debugsessions/a423ac73-0902-4cfa-4242-87a353a84d87/data/myorg-test-ver-5qxdb-64" \-X GET \-H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where$TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token, as described inObtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token. For information about thecurl options used in this example, seeUsing curl. For a description of environment variables you can use, seeSettingenvironment variables for Apigee API requests.
The response consists of a JSON payload that contains the data for the specifiedtransaction, as described inDownload data structure.
Debug data contains all information about the request and response for eachpart of the flow in a proprietary JSON format. You can save this data and later use it intheOffline Debug tool.
If no requests were added to the session before it ended, then the response will look likethe following:
[]
For more information, seeGet debug session data API.
Selecting view options in the UI
This section describes how to select view options to filter what is shown in the UI.
To choose the view options for the debug session, select or clear options from theView options pane. These view options are persisted across debug session for each user.


| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Show disabled policies | Show any disabled policies. A policy can be disabled with the public API. SeeAPI proxy configuration reference. |
| Show skipped policies | Show any policies that were skipped. A skipped policy occurs when policy was not executed because the step condition evaluated to false. SeeConditions with flow variables for more information. |
| Show all FlowInfos | Represent transitions within a flow segment. |
| Show all flow conditions | Represent the conditions that were evaluated for each flow. |
Share a debug session
You can share a debug session with other users who have access to your organization and the necessary permissions. To do so, just send them the URL displayed in your browser when you are viewing the debug session. The link is only valid for 24 hours after the debug session is created.
Downloading debug session data
You can download a file of raw debug results for offline viewing. The downloadedfile shows the complete details of the debug session including the contents of all headers,variables, and policies.
Debug session data is available to download or view in the UI for 24 hours only. After thatpoint, Apigee deletes the session data.
To view downloaded debug session data, use theOffline Debug tool.
Note:- You cannot use the Apigee API to view an entire sessions' data at one time; you can only use the API to view individual transaction data, as described inViewing debug sessions.
- Metadata is NOT included when downloading transactions via the Apigee API. It is necessary to manually add metadata in order to upload and view the transaction using Offline Debug.
Apigee UI
Debug v2 (new)
To download the current debug session in the Google Cloud console, clickDownload in the Debug view.
Note: A debug session is deleted within 24 hours of the time it is completed, so if you want to view the debug session after that time, you need to download it before then.Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To download the current debug session, clickDownload Session in the left-hand pane of the Debug view.
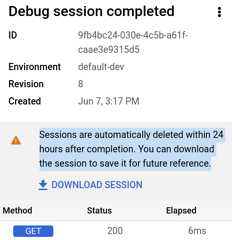
Note that a debug session is deleted within 24 hours of the time it is completed, so if you want to view the debug session after that time, you need to download it before then.
API
To view the IDs of all transactions for the current debug session using the Apigee API, enter the following command:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/ORG/environments/ENV/apis/PROXY/revisions/REV/debugsessions/SESSION_ID/data
whereSESSION_ID is the ID for the debug session you want to download.
See List the transaction IDs from a debug session.
To get the debug data for a transaction using the Apigee API, enter the following command:
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer $(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/ORG/environments/ENV/apis/PROXY/revisions/REV/debugsessions/SESSION_ID/data/TRANSACTION_ID
Download data structure
The download structure of the debug session data is different for the Apigee UI and Apigee API.
Apigee UI
When you download data using the Apigee UI, the data structure:
- Includes all transactions in the entire session
- Stores transactions in a
Messagesarray - Includes metadata about the session (as a
DebugSessionobject)
API
You cannot use the Apigee API to view an entire sessions' data at one time; you can only use the API to view individual transaction data, as described inViewing debug sessions.
For example:
{"completed": true,"point": [ ......}Download data examples
Note: Metadata is NOT included when downloading transactions via the Apigee API. It is necessary to manually add metadata in order to upload and view the transaction using Offline Debug.The following example highlights aDebugSession metadata object in the downloadeddata. This object is following by theMessages array that contains the transactionsin the session.
{ "DebugSession": { "Retrieved": "2019-06-08T13:08:13.395Z", "Organization": "myorg", "Environment": "prod", "API": "myproxy", "Revision": "1", "SessionId": "a2a271aa-4242-4ac6-97cb-aec8dcb115a9" }, "Messages": [ { "completed": true, "point": [ { "id": "Paused" }, { "id": "Resumed" }, { "id": "StateChange", "results": [ { "ActionResult": "DebugInfo", "properties": { "property": [ { "name": "To", "value": "REQ_HEADERS_PARSED" }, { "name": "From", "value": "REQ_START" } ] }, "timestamp": "8-6-19 13:08:37:718" }, { "ActionResult": "RequestMessage", "headers": [ { "name": "accept", "value": "*/*" }, { "name": "accept-encoding", "value": "gzip,gzip,deflate,br" }, { "name": "content-length", "value": "0" }, { "name": "host", "value": "myorg.example.domain.net" }, { "name": "user-agent", "value": "Google-Apigee" }, { "name": "x-b3-sampled", "value": "0" }, { "name": "x-b3-spanid", "value": "d4ee579206759662" }, { "name": "x-b3-traceid", "value": "adc1e171777c237dd4ee579206759662" }, { "name": "x-forwarded-for", "value": "66.102.8.98" }, { "name": "x-forwarded-proto", "value": "https" }, { "name": "x-request-id", "value": "54e05cba-4242-4490-4242-60c45c156f90" } ], "uRI": "/myproxy", "verb": "GET" } ] }, { "id": "FlowInfo", "results": [ { "ActionResult": "DebugInfo", "properties": { "property": [ { "name": "environment.name", "value": "prod" }, { "name": "environment.qualifiedname", "value": "myorg__prod" }, { "name": "environment.orgname", "value": "myorg" } ] }, "timestamp": "8-6-19 13:08:37:718" } ] }, { "id": "FlowInfo", "results": [ { "ActionResult": "DebugInfo", "properties": { "property": [ { "name": "organization.name", "value": "myorg" } ] }, "timestamp": "8-6-19 13:08:37:718" } ] }, { "id": "FlowInfo", "results": [ { "ActionResult": "DebugInfo", "properties": { "property": [ { "name": "apiproxy.qualifiedname", "value": "myproxy__1" }, { "name": "apiproxy.basepath", "value": "/" }, { "name": "apiproxy.revision", "value": "1" }, { "name": "apiproxy.name", "value": "myproxy" } ] }, "timestamp": "8-6-19 13:08:37:718" } ] }, ... ... } ]}If the debug session did not include any requests, then theMessage array is empty,as the following example shows:
{ "DebugSession": { "Retrieved": "2019-06-08T13:08:13.395Z", "Organization": "myorg", "Environment": "prod", "API": "myproxy", "Revision": "1", "SessionId": "a2a271aa-4242-4ac6-97cb-aec8dcb115a9" },"Messages": []}Deleting data for a debug session
Delete data for a debug session using the Apigee UI or API, as described in the following sections.
Apigee UI
Debug v2 (new)
To delete a debug session in the Google Cloud console:
- On theDebug tab, click the row for the session you want to delete.
- In theDebug session pane, clickDelete.
Debug v1
Important: Debug v1 will be shutdown on January 15, 2026. Use Debug v2 instead of Debug v1.To delete a debug session:
- Select the row for the session you want to delete.
- Click the three-dot menu at the end of the row and selectDelete.
API
Caution: You cannot delete individual transactions or specific debug sessions from the stored debug data. If you issue a deletion request, you delete all debug sessions and all the data associated with those sessions.To delete all debug session data using the API, issue a DELETE request to the following resource:
https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/org/environments/env/apis/api/revisions/rev/debugsessions/debugsession/data
Wheredebugsession is the ID of a debug session returned when youview debug sessions.
The following example demonstrates how to delete debug session data for revision 1 of thehelloworld API in thetest environment.
curl "https://apigee.googleapis.com/v1/organizations/myorg/environments/test/apis/helloworld/revisions/1/debugsessions/a423ac73-0902-4cfa-4242-87a353a84d87/data" \ -X DELETE \ -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where$TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token, as described inObtaining an OAuth 2.0 access token. For information about thecurl options used in this example, seeUsing curl. For a description of environment variables you can use, seeSettingenvironment variables for Apigee API requests.
If successful, the response body will be empty.
Debug session data is persisted for 24 hours only. If you do not explicitly delete it before that time, then Apigee deletes it for you.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-12-17 UTC.
