- Introduction
- Install
- Upgrade
- Configure
- Administer
- Overview
- Admin Tools
- Manage security
- Backup and migrate
- Query Accelerator
- High availability features
- Licenses
- File and folder templates
- File metadata extraction
- Workflows
- Transformations
- Content stores
- Database table cleanup
- JMX reference
- Troubleshooting
- Using
- Develop
- Getting started
- Software architecture
- Software Development Kits (SDK)
- Extension packaging (modules)
- Extension Inspector
- Extension points overview
- Out-of-Process extension points
- In-Process platform extension points
- Overview
- Content model
- Actions
- Web scripts
- JavaScript Root Objects
- Behavior policies
- Scheduled jobs
- Metadata Extractors and Embedders
- Mimetypes
- Content Transformers and Renditions
- Permissions and roles
- Data lists
- Ratings
- Bootstrapping content
- Patches
- Module components
- Subsystems
- Authentication
- Content Stores
- Audit Log
- Admin Console Components
- Share UI extension points
- Overview
- Share configuration
- Document Library
- Share Themes
- Site Presets
- Web Scripts
- Surf Pages
- Surf Dashlets
- Surf Widgets
- Surf Extension Modules
- Aikau Menus
- Aikau Pages
- Aikau Dashlets
- Aikau Widgets
- Evaluators
- JavaScript Root Objects
- Form Controls
- Form Processor
- Form Processor Filters
- Form Field Validation Handlers
- Modifying out-of-the-box code
- Useful tools
- ReST API guide
- Reference
Alfresco Query Accelerator
The Query Accelerator is a mechanism for optimising selected queries in very large content repositories. We wouldsuggest using this feature to support large transactional deployments with hundreds of millions of nodes, wheredocuments are automatically imported from other systems, rather than traditional collaborative content managementsystem where humans are creating documents. In transactional deployments there typically is a case id and one or twoother properties, which identify a related collection of documents.
An administrator may define a combination of properties and aspects as aquery set, to support a faster alternative toTransactional Metadata Query (TMDQ) or Solr. Properties may be from multiple types or aspects. A single query set canspeed up more than one query if the queries share common search properties or aspects. A number of different query setsmay be created to support queries with different search properties or aspects.
This performance comes at the cost of additional space for denormalized databases tables and indexes as well as a minimal increased time on ingestion and update. This will however allow customers to make that decision. Having many properties in a query set or having lots of query sets should be avoided, as the cost will be high and generally indicates thatthere is something wrong with the data model design.
Operational overview
Query sets may be applied to an existing Alfresco repository. For example a query set could be applied to a systemwhich has been upgraded to 7.0.0 that already contains hundreds of millions of documents.
Multiple (zero or more but typically not more than 10) query sets may be defined. Each will have its own name. It willbe possible to replace a query set with a new version or to remove it completely. The definition can include theproperties or aspects applied to nodes and if necessary (for selected databases) the order of columnsin compound indexes. Query sets are defined using JSON files.
Administrators perform a query set refresh in the Admin Console. The addition of new query sets, the replacement of an existing query set or complete removal does not require a restart, an outage or have a major impact on normal operations. The
alfresco.logwill contain messages to reflect progress. When a new query set is identified, the system will start populating a denormalized table in the background. It will also abandon the table population before it is complete, if a new version of the query set is created. The implementation will also need to identify a query set or if a previous version is no longer needed and issue a message to thealfresco.logto advise that the query set can be deleted.Once a denormalized table has been created and fully populated, it will automatically start being used.
The Query Accelerator will provide ATOMIC (transactionally consistent) results.
The Query Accelerator is only an enterprise edition feature.
Install properties
- Enable the Query Accelerator by setting the property
queryAccelerator.enabledtotrue. - Define the location of the Query Accelerator config files by setting the property
queryAccelerator.config.dir. - The size of each population batch.
Properties example
queryAccelerator.enabled=truequeryAccelerator.config.dir=shared/classes/alfresco/extension/querysetsqueryAccelerator.populator.workerBatchSize=5000If you are using Docker Compose in development, you will need to copyyour query set definition into your running ACS repository container.One way is to use the following command:
docker cp custom_queryset.json <alfresco container>:/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/extension/querysets/In a Kubernetes environment,ConfigMapscan be used to add query set definitions. You will need to createa ConfigMap from the JSON file and mount the ConfigMap through a volumeto the ACS repository pods.
kubectl create configmap custom-queryset-config --from-file=name_of_a_file.jsonThe necessary volumes are already provided out of the box and the filesin ConfigMapcustom-queryset-config will be mounted to/usr/local/tomcat/shared/classes/alfresco/extension/querysets/.
Caution: From Kubernetes documentation: If there are some files in the mountPath location, they will be deleted.
Configuration
Use the following information to configure Query Accelerator. The query set configurations define the denormalized tables that will be created to support faster queries.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The version of the query set. |
| name | The table name. The actual database table name will have a prefix of ‘alf_qs_’ and a suffix of ‘_v’ plus the version. So for a query set called of ‘test1’ and a version of 1 that actual database table name would be ‘alf_qs_test1_v1’. |
| properties | A collection of properties to appear on the denormalized table. A property consists of a name attribute which is the name of a property and an isIndex attribute which indicates that the related column on the table should be indexed. |
| aspects | A collection of aspects to appear on the denormalized table. The table will have a boolean column for each of the aspects to indicate if the node has those aspects applied. An aspect consists of a name attribute which is the name of an aspect and an isIndex attribute which indicates that the related column on the table should be indexed. |
| compositeIndexes | A collection of composite indexes to be created for the table. A composite index consists of an attribute where the attribute name is the index name and the attribute value is a collection of names of properties and/or aspects of the query set. |
- The maximum length of the query set name and the version is the maximum table name length of the database system being used,minus 9. So for Postgres, which has a maximum table name length of 63 bytes, the maximum name and version length inthe query set is 54 bytes.
- Queries that include negations on aspects should not be accelerated.
- Properties of type MLTEXT are NOT supported. If included a WARN message will be logged,the properties will be ignored, and the corresponding denormalized table will be created without them.
- The denormalized table will have an alf_type column, holding the name of the content type.
- When aspects are used, the denormalized table will contain only the nodes that have at least one of the aspect.It is for this reason that a query checking for the absence of an aspect will not use the query acceleratorand will be performed by the standard engine.
- Auditable properties (namely: cm:creator, cm:created, cm:modifier, cm:modified and cm:accessed) defined in the configurationwill be ignored. Data of this nature is always available and there is no need to store it on the corresponding denormalisedtable.
- Properties of the following types defined in the configuration will be ignored. If included a WARN message will be logged, as the properties are already included in the denormalized table:
- cm:owner
- cm:noderef
- sys:node-dbid
- sys:node-uuid
- When files are read from the
queryAccelerator.config.dirdirectory they are read inalphanumeric order. So0101-coyote.json would be read before0102-coyote.json and it isread before0201-acme.json.
Query set configuration examples
Example 1
This first example is intentionally simple but should work on any system, providing a basic understanding of how the system works.
{ "version": 1, "name": "Test01", "properties": [ { "name": "cm:name", "isIndex": true }, { "name": "cm:author", "isIndex": true } ], "aspects": [ { "name": "cm:titled", "isIndex": true } ], "compositeIndexes": { "index_1": ["cm:name", "cm:author"], "index_2": ["cm:name", "cm:titled"] }}ACS node properties: Table entry:
Table entry:
| node_id | owner_id | alf_type | cm_name | cm_author | cm_titled |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 887 | 3 | 24 | demo1.txt | Joe Bloggs | true |
Example 2
The following example requires that at least one node in the system has the DublinCore aspect applied. This aspect ispart of the system by default. If there are no nodes, an unknown property error is reported.
{ "version": 6, "name": "ac", "properties": [ { "name": "cm:name", "isIndex": true }, { "name": "cm:publisher", "isIndex": true } ], "aspects": [ { "name": "cm:titled", "isIndex": true }, { "name": "cm:dublincore", "isIndex": true } ], "compositeIndexes": { "index_1": ["cm:name", "cm:publisher"], "index_2": ["cm:name", "cm:titled"] }}ACS node properties and aspects: Table entry:
Table entry:
| node_id | owner_id | alf_type | cm_name | cm_publisher | cm_titled | cm_dublincore |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 918 | 3 | 24 | demo2 | Egmont | true | true |
Query sets and TMDQ queries
Here we give an example of how to create a query set to replace a TMDQ.
The following TMDQ selects all documents (cm:content) which have a dublincore aspect (cm:dublincore), apublisher (cm:publisher) equal to ‘Hachette Livre’ and a type (cm:type) equal to ‘Action’.
{ "query":{ "query":"select * from cmis:document as d join cm:dublincore as dc on d.cmis:objectId = dc.cmis:objectId where dc.cm:publisher = 'Hachette Livre' and dc.cm:type='Action'", "language":"cmis" }}The following Query Set would be able to support the above TMDQ. It also requires that at least one node in the systemhas the DublinCore aspect applied.
{ "version": "1", "name": "doc_dublincore", "properties": [ { "name": "cm:publisher", "isIndex": true }, { "name": "cm:type", "isIndex": true } ], "aspects": [ { "name": "cm:dublincore", "isIndex": true } ]}Query set status and caching
Denormalized tables have a status. For example:
| Name | Version | State | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| tableA | 1 | OBSOLETE | Should be removed |
| tableA | 2 | RETIRED | Can be removed |
| tableA | 3 | LIVE | Currently being used |
| tableA | 4 | INPROGRESS | Created but not fully populated yet, so cannot be used |
| tableA | 5 | NEW | Seen but population of denormalized data has not started |
The transition from NEW to INPROGRESS will normally happen almost immediately.
Logging
The Admin Console currently only indicates if updates were detected. For a more complete picture of the query sets configuration DEBUG logging must be used:
log4j.logger.org.alfresco.enterprise.repo.queryaccelerator=debugLogs when a Query Set Refresh was performed but there are no updates:
2021-01-14 17:12:33,020 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Refreshing query sets - checking for updates...2021-01-14 17:12:33,022 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigFileFinder] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] file /Users/p3700509/Documents/build/queryaccelerator/test01-qs.json config read2021-01-14 17:12:33,029 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] QuerySet: 'test01' with version: '2' already exists.2021-01-14 17:12:33,030 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query set configuration - no new tables detected2021-01-14 17:12:33,031 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query set configuration - no deleted tables detected2021-01-14 17:12:33,033 DEBUG [queryaccelerator.population.PopulateRqaServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Number of PopulateRqaTableWorkers found: 0Logs when a Query Set Refresh has started:
2021-01-14 17:14:15,906 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Refreshing query sets - checking for updates...2021-01-14 17:14:15,907 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigFileFinder] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] file /Users/p3700509/Documents/build/queryaccelerator/test01-qs.json config read2021-01-14 17:14:15,911 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query set configuration - detected new version: test01 version: 32021-01-14 17:14:15,915 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query sets - creating table script for : test01 version: 32021-01-14 17:14:15,916 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetRegistryImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Registering table: test01, version: 3, status: INPROGRESS2021-01-14 17:14:15,929 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query sets - adding to cache: alf_qs_test01_v32021-01-14 17:14:15,930 INFO [schema.script.ScriptExecutorImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Executing database script /var/folders/r7/mybxmf_d2sb2sw6g8ksg3h0x0ylsgp/T/Alfresco/AlfrescoSchema-PostgreSQLDialect-Update-562184015453156440.sql (Copied from file:/var/folders/r7/mybxmf_d2sb2sw6g8ksg3h0x0ylsgp/T/Alfresco/test01-11276349223693844289.sql).2021-01-14 17:14:15,954 DEBUG [repo.queryaccelerator.QuerySetConfigServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Query set configuration - no deleted tables detected2021-01-14 17:14:15,957 DEBUG [queryaccelerator.population.PopulateRqaServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] Number of PopulateRqaTableWorkers found: 12021-01-14 17:14:15,959 DEBUG [queryaccelerator.population.PopulateRqaServiceImpl] [http-bio-8080-exec-6] PopulateRqaTableWorker(s) will be started at Thu Jan 14 17:17:15 EET 2021 on process 46672@L3700101035.ness.com (just in case you want to kill this JVM as we do not use daemon executors here)It is also possible to obtain detailed logs for the query engine. The logs provide information about the process of selecting the query set, based on the query, by activating the DEBUG level, as in this example:
log4j.logger.org.alfresco.repo.search.impl.querymodel.impl.db=debugLogs when a query is accepted by the engine:
15:02:26,097 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] Query request received15:02:26,098 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - query is being prepared15:02:26,099 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - query sent to the database15:02:37,722 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - query predicates list:15:03:15,823 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - aspect: qname={http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}titled15:06:43,325 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - Examining 1 queryset(s)...15:06:43,326 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - queryset table alf_qs_testbb01_v41 accepted for this query!15:06:43,328 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-10] - using denormalised table for the queryLogs when a query is refused by the engine:
15:26:54,753 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] Query request received15:26:54,753 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - query is being prepared15:26:54,755 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - query sent to the database15:26:58,389 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - query predicates list:15:26:58,389 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - aspect: qname={http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}dublincore15:26:58,389 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - column: qname={http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}publisher15:27:00,108 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - Examining 1 queryset(s)...15:27:00,108 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - queryset table alf_qs_testbb01_v41 excluded as qname not found: {http://www.alfresco.org/model/content/1.0}dublincore15:27:00,108 DEBUG [impl.db.DBQueryEngine] [http-bio-8080-exec-3] - using standard table for the queryRemoving a query set
You can remove a query set by performing its removal in the Admin Console. There is no need to perform a refresh after the query set removal, however the JSON config file should be manually removed from the config directory.
During the refresh the JSON config files will be compared against the internal registry of query sets. If a query set inthe registry does not have a corresponding JSON config file with the same tableName then a warning will be logged.The denormalized database table will NOT be dropped.
Updating a query set
You can update/replace a query set by changing the properties, aspects and compositeIndexes in the query set JSON config.
You then need to update the version in the query set JSON config and then perform a query set refresh in the Admin Console.
This will start a process that will replace the previous version of the query set.
- A new version of the query set will be added to the internal query set registry.
- A new version of the denormalized table will be created.
- The denormalized table for the previous version will continue in-use until it has been replaced by the new version.
- The new version of the denormalized table will be populated. This could take a considerable time depending on the scale of the Alfresco installation.
- When the population is completed
- the query set will be flagged as live
- the previous version of the query set will be flagged as retired
- the denormalized table for the previous version can now be dropped manually via the Remove Query Set button in the Admin Console
Important: If you edit a query set config and change the name and request a query set refresh, the system will see this as the retirement of the original query set and the creation of a new one.
Query Set Refresh in Admin Console
The query sets can be refreshed in the Admin Console.
SelectQuery Accelerator in the left hand menu.

Press theRefresh Query Set button.

If there are updates to the query sets in the folder defined byqueryAccelerator.config.dir (normallyshared/classes/alfresco/extension/querysets) you will see:

If there are no updates to the query sets you will see:

Query Set Remove in Admin Console
The query sets can be removed in the Admin Console.
On theQuery Accelerator page, complete the query set name and version text fields.
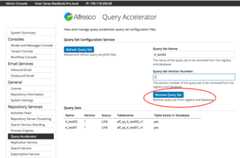
Press theRemove Query Set button.
If the query set is successfully removed you will see:

If no matching query set was found you will see:
