CSS features reference
Discover new workflows in this comprehensive reference of Chrome DevTools features related toviewing and changing CSS.
SeeView and change CSS to learn the basics.
Select an element
TheElements panel of DevTools lets you view or change the CSS of one element at a time.

On the screenshot, theh1 element that's highlighted blue in theDOM Tree is the selected element.To the right, the element's styles are shown in theStyles tab. To the left, the element ishighlighted in the viewport, but only because the mouse is hovering over it in theDOMTree.
SeeView an element's CSS for a tutorial.
There are many ways to select an element:
- In your viewport, right-click the element and selectInspect.
- In DevTools, clickSelect an element
 or pressCommand+Shift+C (Mac) orControl+Shift+C (Windows, Linux), and then click the element inthe viewport.
or pressCommand+Shift+C (Mac) orControl+Shift+C (Windows, Linux), and then click the element inthe viewport. - In DevTools, click the element in theDOM Tree.
- In DevTools, run a query like
document.querySelector('p')in theConsole, right-click theresult, and then selectReveal in Elements panel.
View CSS
Use theElements >Styles andComputed tabs to view CSS rules anddiagnose CSS issues.
Navigate with links
TheStyles tab displays links in various places to various other places, including but not limited to:
- Next to CSS rules, to style sheets and CSS sources. Such links open theSources panel. If the style sheet is minified, seeMake a minified file readable.
- In theInherited from ... sections, to parent elements.
- In
var()calls, tocustom property declarations. - In
animationshorthand properties, to@keyframes. - Learn more links in documentation tooltips.
- And more.
Here are some of them highlighted:

Links may be styled differently. If you're not sure if something is a link, try clicking it to find out.
View tooltips with CSS documentation, specificity, and custom property values
Elements >Styles shows tooltips with useful information when you hover over specific elements.
View CSS documentation
To see a tooltip with a short CSS description, hover over the property name in theStyles tab.
Note: DevTools pulls the descriptions for tooltips fromVS Code Custom Data.
ClickLearn more to go to anMDN CSS Reference on this property.
To turn the tooltips off, checkDon't show.
To turn them back on, checkSettings >Preferences >Elements >
Show CSS documentation tooltip.
View selector specificity
Hover over a selector to see a tooltip with itsspecificity weight.

View the values of custom properties
Hover over a--custom-property to see its value in a tooltip.

View invalid, overridden, inactive, and other CSS
TheStyles tab recognizes many kinds of CSS issues and highlights them in different ways.
SeeUnderstand CSS in the Styles tab.
View only the CSS that's actually applied to an element
TheStyles tab shows you all of the rules that apply to an element, including declarations thathave been overridden. When you're not interested in overridden declarations, use theComputedtab to view only the CSS that's actually being applied to an element.
- Select an element.
- Go to theComputed tab in theElements panel.
Check theShow All checkbox to see all properties.
SeeUnderstand CSS in the Computed tab.
View CSS properties in alphabetical order
Use theComputed tab. SeeView only the CSS that's actually applied to an element.
View inherited CSS properties
Check theShow All checkbox in theComputed tab. SeeView only the CSS that's actuallyapplied to an element.
Alternatively, scroll theStyles tab and find sections namedInherited from <element_name>.

View CSS at-rules
At-rules are CSS statements that let you control CSS behavior.Elements >Styles shows the following at-rules in dedicated sections:
View@property at-rules
The@property CSS at-rule lets you defineCSS custom properties explicitly and register them in a style sheet without running any JavaScript.
Hover over the name of such property in theStyles tab, to see a tooltip with the property's value, descriptors, and a link to its registration in the collapsible@property section at the bottom of theStyles tab.
To edit an@property rule,double-click its name or value.
View@supports at-rules
TheStyles tab shows you the@supports CSS at-rules if they are applied to an element. For example, inspect the following element:

If your browser supports thelab() function, the element is green, otherwise it's purple.
View@scope at-rules
TheStyles tab shows youCSS@scope at-rules if they are applied to an element.
The new@scope at-rules are a part of theCSS Cascading and Inheritance Level 6 specification. These rules allow you to scope CSS styles, in other words, explicitly apply styles to specific elements.
@scope at-rule feature is experimental. To test it, enable theExperimental Web Platform features flag inchrome://flags/#enable-experimental-web-platform-features. Otherwise, the next preview doesn't work.View the@scope rule in the following preview:
- Inspect the text on the card in the preview.
- On theStyles tab, find the
@scoperule.

In this example, the@scope rule overrides the global CSSbackground-color declaration for all<p> elements inside elements with acard class.
To edit the@scope rule, double-click it.
View@font-palette-values at-rules
The@font-palette-values CSS at-rule lets you customize the default values of thefont-palette property.Elements >Styles shows this at-rule in a dedicated section.
View the@font-palette-values section in the next preview:
- Inspect the second line of text in the preview.
- InStyles, find the
@font-palette-valuessection.

In this example, the--New font palette values override the default ones of the colored font.
To edit your custom values, double-click them.
View@position-try at-rules
The@position-try CSS rule along with theposition-try-options property lets you define alternative anchor positions for elements. To learn more, seeIntroducing the CSS anchor positioning API.
Elements >Styles resolves and links the following:
position-try-optionsproperty values to a dedicated@position-try--namesection.position-anchorproperty values andanchor()arguments to the corresponding elements withpopovertargetattributes.
Inspect theposition-try-options values and@position-try sections in the next preview:
popover- In the preview, open the submenu, that is, clickYOUR ACCOUNT thenSTOREFRONT.
- Inspect the element with
id="submenu"in the preview. - InStyles, find the
position-try-optionsproperty and click its--bottomvalue. TheStyles tab takes you to the corresponding@position-trysection. - Click the
position-anchorvalue link or the sameanchor()arguments. TheElements panel selects the element with the correspondingpopovertargetattribute and theStyles tab shows the element's CSS.

To edit values, double-click them.
View an element's box model
To viewthe box model of an element, go to theStyles tab and click the Show sidebar button in the action bar.
Show sidebar button in the action bar.

To change a value, double-click on it.
Search and filter an element's CSS
Use theFilter box on theStyles andComputed tabs to search for specific CSSproperties or values.

To also search inherited properties in theComputed tab, check theShow All checkbox.

To navigate theComputed tab, group the filtered properties in collapsible categories by checkingGroup.

Emulate a focused page
If you switch focus from the page to DevTools, some overlay elements automatically hide if they are triggered by focus. For example, drop-down lists, menus, or date pickers. TheEmulate a focused page option lets you debug such an element as if it is in focus.
Caution: With this option turned on, thedocument.visibilityState is set tovisible and thevisibilitychange event doesn't fire. For more information, seePage Visibility API.Try emulating a focused page on thisdemo page:
- Focus the input element. Another element appears under it.
- Open DevTools. The DevTools window is now in focus instead of the page, so the element disappears again.
- InElements >Styles, click:hov, checkEmulate a focused page, and make sure the inputelement is selected. You can now inspect the element under it.

You can also findthe same option on theRendering panel.
To discover more ways to freeze an element, seeFreeze screen and inspect disappearing elements.
Toggle a pseudo-class
To toggle a pseudo-class:
- Select an element.
- On theElements panel, go to theStyles tab.
- Click:hov.
- Check the pseudo-class that you want to turn on.

In this example, you can see that DevTools applies thebackground-color declaration to the element, even though the element is not actually hovered over.
TheStyles tab shows the following pseudo-classes for all elements:
Additionally, some elements may have their own pseudo-classes. When you select such an element, theStyles tab shows aForce specific element state section that you can expand and turn on pseudo-classes specific to the element.

SeeAdd a pseudostate to a class for an interactive tutorial.
View inherited highlight pseudo-elements
Pseudo-elements let you style specific parts of elements. Highlight pseudo-elements are document portions with a "selected" status and they are styled as "highlighted" to indicate this status to the user. For example, such pseudo-elements are::selection,::spelling-error,::grammar-error, and::highlight.
As mentioned in thespecification, when multiple styles conflict, cascade determines the winning style.
Note: To enable this feature, run Chrome with the--enable-blink-features=HighlightInheritance flag.To better understand the inheritance and priority of the rules, you can view the inherited highlight pseudo-elements:
- I inherited the style of my parent's highlight pseudo-element. Select me!
Select a portion of the text above.
In theStyles tab, scroll down to find the
Inherited from ::selection pseudo of...section.

View cascade layers
Cascade layers enable more explicit control of your CSS files to prevent style-specificity conflicts. This is useful for large codebases, design systems, and when managing third-party styles in applications.
To view cascade layers,inspect the next element and openElements >Styles.
In theStyles tab, view the 3 cascade layers and their styles:page,component andbase.

To view the layer order, click the layer name or theToggle CSS layers view button.
Thepage layer has the highest specificity, therefore the element's background is green.
View a page in print mode
To view a page in print mode:
- Open theCommand Menu.
- Start typing
Renderingand selectShow Rendering. - For theEmulate CSS Media drop-down, selectprint.
View used and unused CSS with the Coverage tab
The Coverage tab shows you what CSS a page actually uses.
- PressCommand+Shift+P (Mac) orControl+Shift+P (Windows, Linux, ChromeOS) while DevTools isin focus to open the Command Menu.
Start typing
coverage.
SelectShow Coverage. The Coverage tab appears.

Click
Reload.The page reloads and theCoverage tab provides an overview of how much CSS (and JavaScript) isused from each file that the browser loads.

Green represents used CSS. Red represents unused CSS.
Click a CSS file to see a line-by-line breakdown of what CSS it uses in the preview above.

On the screenshot, lines 55 to 57 and 65 to 67 of
devsite-google-blue.cssare unused, whereas lines 59 to 63 are used.
Force print preview mode
SeeForce DevTools Into Print Preview Mode.
Copy CSS
From a single drop-down menu in theStyles tab, you can copy separateCSS rules, declarations, properties, values
Additionally, you can copy CSS properties in JavaScript syntax. This option is handy if you're usingCSS-in-JS libraries.
To copy CSS:
- Select an element.
- In theElements >Styles tab, right-click a CSS property.

Select one of the following options from the drop-down menu:
- Copy declaration. Copies the property and its value in CSS syntax:
cssproperty: value; - Copy property. Copies only the
propertyname. - Copy value. Copies only the
value. - Copy rule. Copies the entire CSS rule:
cssselector[, selector] { property: value; property: value; ...} - Copy declaration as JS. Copies the property and its value in JavaScript syntax:
jspropertyInCamelCase: 'value' - Copy all declarations. Copies all properties and their values in the CSS rule:
cssproperty: value;property: value;... Copy all declarations as JS. Copies all properties and their values in JavaScript syntax:```jspropertyInCamelCase: 'value',propertyInCamelCase: 'value',...
Copy all CSS changes.Copies the changes you make in theStyles tab across all declarations.
View computed value. Takes you to theComputed tab.
- Copy declaration. Copies the property and its value in CSS syntax:
Change CSS
This section lists all the ways you can change CSS inElements >Styles.
Additionally, you can:
Add a CSS declaration to an element
Since the order of declarations affects how an element is styled, you can add declarations indifferent ways:
- Add a inline declaration. Equivalent to adding a
styleattribute to the element's HTML. - Add a declaration to a style rule.
What workflow should you use? For most scenarios, you probably want to use the inlinedeclaration workflow. Inline declarations have higher specificity than external ones, so the inlineworkflow ensures that the changes take effect in the element as you'd expect. SeeSelectorTypes for more on specificity.
If you're debugging an element's styles and you need to specifically test what happens when adeclaration is defined in different places, use the other workflow.
Add an inline declaration
To add an inline declaration:
- Select an element.
- In theStyles tab, click between the brackets of theelement.style section. The cursorfocuses, allowing you to enter text.
- Enter a property name and pressEnter.
Enter a valid value for that property and pressEnter. In theDOM Tree, you cansee that a
styleattribute has been added to the element.
On the screenshot, the
margin-topandbackground-colorproperties have been applied to the selected element. In theDOM Tree you can see the declarations reflected in the element'sstyleattribute.
Add a declaration to a style rule
To add a declaration to an existing style rule:
- Select an element.
- In theStyles tab, click between the brackets of the style rule to which you want to addthe declaration. The cursor focuses, allowing you to enter text.
- Enter a property name and pressEnter.
- Enter a valid value for that property and pressEnter.

On the screenshot, a style rule gets the newborder-bottom-style:groove declaration.
Change a declaration name or value
Double-click a declaration's name or value to change it. SeeChange enumerable values withkeyboard shortcuts for shortcuts for quickly incrementing or decrementing a value by 0.1, 1,10, or 100 units.
Change enumerable values with keyboard shortcuts
While editing an enumerable value of a declaration, for example,font-size, you can use the following keyboard shortcuts to increment the value by a fixed amount:
- Option+Up (Mac) orAlt+Up (Windows, Linux) toincrement by 0.1.
- Up to change the value by 1, or by 0.1 if the current value is between -1 and 1.
- Shift+Up to increment by 10.
- Shift+Command+Up (Mac) orControl+Shift+Page Up(Windows, Linux) to increment the value by 100.
Decrementing also works. Just replace each instance ofUp mentioned earlier withDown.
Change length values
Deprecated: This feature is deprecated in Chrome 123. To temporarily turn it back on again, clear theSettings >Experiments >Deprecate CSS <length> authoring tool in the Styles tab. Feel free to leave feedback incrbug/1522657.You can use your pointer to change any property with length, such as width, height, padding, margin, or border.
To change the length unit:
- Hover over the unit name and notice that it's underlined.
Click the unit name to select a unit from the drop-down.
To change the length value:
- Hover over the unit value and notice that your pointer changes to a horizontal double-headed arrow.
Drag horizontally to increase or decrease the value.
To adjust the value by 10, holdShift when dragging.
Add a class to an element
To add a class to an element:
- Select the element in theDOM Tree.
- Click.cls.
- Enter the name of the class in theAdd New Class box.
- PressEnter.
Emulate light and dark theme preferences and enable automatic dark mode
To toggleautomatic dark mode or emulate the user's preference oflight or dark themes:
- On theElements >Styles tab, click
Toggle common rendering emulations.

Select one of the following from the drop-down list:
- prefers-color-scheme: light. Indicates that the user prefers the light theme.
- prefers-color-scheme: dark. Indicates that the user prefers the dark theme.
- Automatic dark mode. Displays your page in dark mode even if you didn't implement it. Additionally, sets
prefers-color-schemetodarkautomatically.
This drop-down is a shortcut forEmulate CSS media featureprefers-color-scheme andEnable automatic dark mode options of theRendering tab.
Toggle a class
To enable or disable a class on an element:
- Select the element in theDOM Tree.
- Open theElement Classes section. SeeAdd a class to an element. Below theAdd NewClass box are all of the classes that are being applied to this element.
- Toggle the checkbox next to the class that you want to enable or disable.
Add a style rule
To add a new style rule:
- Select an element.
- ClickNew Style Rule
. DevTools inserts anew rule beneath theelement.style rule.

On the screenshot, DevTools adds theh1.devsite-page-title style rule after clickingNew Style Rule.
Choose which style sheet to add a rule to
Whenadding a new style rule, click and holdNew Style Rule to choose which style sheetto add the style rule to.

Toggle a declaration
To toggle a single declaration on or off:
- Select an element.
- In theStyles tab, hover over the rule that defines the declaration. Checkboxes appear nextto each declaration.
- Check or clear the checkbox next to the declaration. When you clear a declaration, DevToolscrosses it out to indicate that it's no longer active.

On the screenshot, thecolor property for the currently-selected element is toggled off.
Edit the::view-transition pseudo-elements during an animation
See the corresponding section inAnimations.
For more information, seeSmooth and simple transitions with the View Transitions API.
Align grid items and their content with the Grid Editor
See the correspondingsection in Inspect CSS grid.
Change colors with the Color Picker
SeeInspect and debug HD and non-HD colors with the Color Picker.
Change angle value with the Angle Clock
TheAngle Clock provides a GUI for changing<angle>s in CSS property values.
To open theAngle Clock:
- Select an element with angle declaration.
In theStyles tab, find the
transformorbackgrounddeclaration that you want to change.Click theAngle Preview box next to the angle value.
The small clocks to the left of
-5degand0.25turnare the angle previews.Click the preview to open theAngle Clock.

Change the angle value by clicking on theAngle Clock circle or scroll your mouse toincrease / decrease the angle value by 1.
There are more keyboard shortcuts to change the angle value. Find out more in theStyles panekeyboard shortcuts.
Change box and text shadows with the Shadow Editor
TheShadow Editor provides a GUI for changingtext-shadow andbox-shadow CSS declarations.
To change shadows with theShadow Editor:
Select an element with a shadow declaration. For example, select the next element.
In theStyles tab, find a shadow
 icon next to the
icon next to thetext-shadoworbox-shadowdeclaration.
Click the shadow icon to open theShadow editor.

Change the shadow properties:
- Type (only for
box-shadow). PickOutset orInset. - X and Y offsets. Drag the blue dot or specify values.
- Blur. Drag the slider or specify a value.
- Spread (only for
box-shadow). Drag the slider or specify a value.
- Type (only for
Observe the changes applied to theelement.
Edit animation and transition timings with the Easing Editor
TheEasing Editor provides a GUI for changing the values oftransition-timing-function andanimation-timing-function.
To open theEasing Editor:
- Select an element with a timing function declaration, like the
<body>element on this page. - In theStyles tab, find the purple
 icon next to the
icon next to thetransition-timing-function,animation-timing-functiondeclarations, or thetransitionshorthand property.
- Click the icon to open theEasing Editor:

Use presets to adjust timings
To adjust timings with a click, use the presets in theEasing Editor:
- In theEasing Editor, to set akeyword value, click one of the picker buttons:
- linear

- ease-in-out

- ease-in

- ease-out

- linear
In thePresets switcher, click
or
buttons to pick one of the following presets:
- Linear presets:
elastic,bounce, oremphasized. - Cubic Bezier presets:
- Linear presets:
| Timing keyword | Preset | Cubic Bezier |
|---|---|---|
| ease-in-out | In Out, Sine | cubic-bezier(0.45, 0.05, 0.55, 0.95) |
| In Out, Quadratic | cubic-bezier(0.46, 0.03, 0.52, 0.96) | |
| In Out, Cubic | cubic-bezier(0.65, 0.05, 0.36, 1) | |
| Fast Out, Slow In | cubic-bezier(0.4, 0, 0.2, 1) | |
| In Out, Back | cubic-bezier(0.68, -0.55, 0.27, 1.55) | |
| ease-in | In, Sine | cubic-bezier(0.47, 0, 0.75, 0.72) |
| In, Quadratic | cubic-bezier(0.55, 0.09, 0.68, 0.53) | |
| In, Cubic | cubic-bezier(0.55, 0.06, 0.68, 0.19) | |
| In, Back | cubic-bezier(0.6, -0.28, 0.74, 0.05) | |
| Fast Out, Linear In | cubic-bezier(0.4, 0, 1, 1) | |
| ease-out | Out, Sine | cubic-bezier(0.39, 0.58, 0.57, 1) |
| Out, Quadratic | cubic-bezier(0.25, 0.46, 0.45, 0.94) | |
| Out, Cubic | cubic-bezier(0.22, 0.61, 0.36, 1) | |
| Linear Out, Slow In | cubic-bezier(0, 0, 0.2, 1) | |
| Out, Back | cubic-bezier(0.18, 0.89, 0.32, 1.28) |
Configure custom timings
To set custom values for timing functions, use the control points on the lines:
For linear functions, click anywhere on the line to add a control point and drag it. Double-click to remove the point.
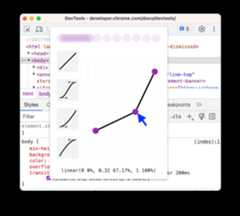
For Cubic Bezier functions, drag one of the control points.

Any change triggers a ball animation in thePreview at the top of editor.
(Experimental) Copy CSS changes
Note: To enable this experimental feature, checkSync CSS changes in the Styles tab underWith this experiment enabled, theStyles tab highlights your CSS changes in green.
To copy a single CSS declaration change, hover over the highlighted declaration and click theCopy button.

To copy all CSS changes across declarations at once, right-click on any declaration and selectCopy all CSS changes.

Additionally, you cantrack changes you make with theChanges tab.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2024-03-12 UTC.


