PDF (A4) - 35.2Mb
Man Pages (TGZ) - 256.4Kb
Man Pages (Zip) - 361.2Kb
Info (Gzip) - 3.4Mb
Info (Zip) - 3.4Mb
MySQL Globalization
MySQL Information Schema
MySQL Installation Guide
MySQL and Linux/Unix
MySQL and macOS
MySQL Partitioning
MySQL Performance Schema
MySQL Replication
Using the MySQL Yum Repository
MySQL Restrictions and Limitations
Security in MySQL
MySQL and Solaris
Building MySQL from Source
Starting and Stopping MySQL
MySQL Tutorial
MySQL and Windows
MySQL NDB Cluster 7.5
Support for DTrace is deprecated in MySQL 5.7 and is removed in MySQL 8.0.
The DTrace probes in the MySQL server are designed to provide information about the execution of queries within MySQL and the different areas of the system being utilized during that process. The organization and triggering of the probes means that the execution of an entire query can be monitored with one level of probes (query-start andquery-done) but by monitoring other probes you can get successively more detailed information about the execution of the query in terms of the locks used, sort methods and even row-by-row and storage-engine level execution information.
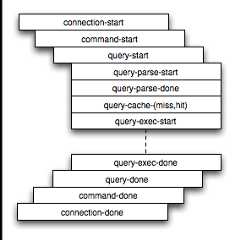
The DTrace probes are organized so that you can follow the entire query process, from the point of connection from a client, through the query execution, row-level operations, and back out again. You can think of the probes as being fired within a specific sequence during a typical client connect/execute/disconnect sequence, as shown in the following figure.
Global information is provided in the arguments to the DTrace probes at various levels. Global information, that is, the connection ID and user/host and where relevant the query string, is provided at key levels (connection-start,command-start,query-start, andquery-exec-start). As you go deeper into the probes, it is assumed either you are only interested in the individual executions (row-level probes provide information on the database and table name only), or that you intend to combine the row-level probes with the notional parent probes to provide the information about a specific query. Examples of this are given as the format and arguments of each probe are provided.
MySQL includes support for DTrace probes on these platforms:
Solaris 10 Update 5 (Solaris 5/08) on SPARC, x86 and x86_64 platforms
OS X / macOS 10.4 and higher
Oracle Linux 6 and higher with UEK kernel (as of MySQL 5.7.5)
Enabling the probes should be automatic on these platforms. To explicitly enable or disable the probes during building, use the-DENABLE_DTRACE=1 or-DENABLE_DTRACE=0 option toCMake.
If a non-Solaris platform includes DTrace support, buildingmysqld on that platform includes DTrace support.
Additional Resources
For more information on DTrace and writing DTrace scripts, read theDTrace User Guide.
For an introduction to DTrace, see the MySQL Dev Zone articleGetting started with DTracing MySQL.
PDF (A4) - 35.2Mb
Man Pages (TGZ) - 256.4Kb
Man Pages (Zip) - 361.2Kb
Info (Gzip) - 3.4Mb
Info (Zip) - 3.4Mb
MySQL Globalization
MySQL Information Schema
MySQL Installation Guide
MySQL and Linux/Unix
MySQL and macOS
MySQL Partitioning
MySQL Performance Schema
MySQL Replication
Using the MySQL Yum Repository
MySQL Restrictions and Limitations
Security in MySQL
MySQL and Solaris
Building MySQL from Source
Starting and Stopping MySQL
MySQL Tutorial
MySQL and Windows
MySQL NDB Cluster 7.5