Julia in Visual Studio Code
TheJulia programming language is a high level and dynamic language built for speed and simplicity. Julia is commonly used in areas such as data science, machine learning, scientific computing, but is still a general purpose language that can handle most programming use cases.
TheJulia extension for Visual Studio Code includes built-in dynamic autocompletion, inline results, plot pane, integrated REPL, variable view, code navigation, and many other advanced language features.
Most of these features work out of the box, while some may require basic configuration to get the best experience. This page summarizes the Julia features included in the Julia VS Code extension. For a more in-depth guide on how these features work and can be configured, see theJulia in VS Code documentation.
Getting started
- Install Julia for your platform:https://julialang.org/install.
- Install VS Code for your platform:https://code.visualstudio.com/download.
- Open the Julia extension on theVS Code Marketplace and pressInstall; or manually install by doing the following steps:
- Start VS Code.
- Inside VS Code, go to the Extensions view by clickingView on the top menu bar and then selectingExtensions.
- In the Extensions view, search for the term "julia" in the Marketplace search box, then select the Julia extension (julialang.language-julia) and select theInstall button.
- Restart VS Code.
If you run into any issues installing the Julia VS Code extension, check outinstall an extension, which should help clarify any issues.

Running code
There are several ways to run Julia code within VS Code. You can run a Julia file (via⌃F5 (Windows, LinuxCtrl+F5), which will run whatever Julia file you have open and active), execute Julia commands via the REPL, or even execute a specific block of code from a file you have open. To learn more about these options, head toJulia in VS Code - Running Code.
Debugging
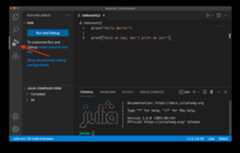
You can start debugging by opening the Julia file that you would like to debug. Then, select theRun and Debug view on the Activity bar (as shown below):
Next, you can add a breakpoint by clicking to the left of the line number:
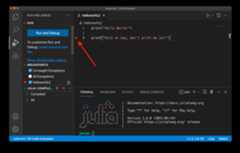
The red dot will not show up until after you have selected the area next to a line number.
After you have a breakpoint added (or any other type of debug configuration), select theRun and Debug button on the left. It may take a few seconds for the initial run to begin. You should then see the output of running the code with the debug configuration. In this example, since we added a breakpoint, you will see the following:
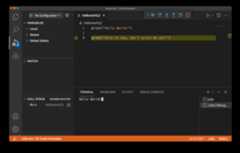
Notice that the second print command has yet to execute and there is only text from the first print command in the terminal. You can finish the execution of the program by selecting theContinue button:
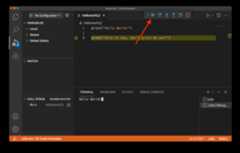
To find out more about debugging Julia code with VS Code, you can readJulia in VS Code - Debugging.
Code completion (IntelliSense)
The Julia VS Code extension comes with code completion thanks to IntelliSense. This feature works out of the box and is useful for experienced and beginner Julia developers alike.

You can learn more in theVS Code IntelliSense topic.
Julia view
By default, on the left side of the window in the Activity bar, you will see the Julia three dots logo as shown below:

If you select the Julia icon, the Julia view will open that displays sections forWorkspace,Documentation, and thePlot Navigator. TheWorkspace section displays a collection of source code that is loaded into your active Julia session. By default, it will be blank since you have not yet run any code, but after you run something, you will be able to see the state of the workspace.

TheDocumentation section lets you review details about specific Julia functions without needing to open a separate browser window. You can search the documentation of any Julia package you have loaded into your active session (by doingusing some_package), but by default, the search bar will only display results from the core Julia documentation.

There is also a built-inPlot Navigator, which can be very helpful when you are working on projects with visualization components. You can set the plots to render by default in VS Code and then conveniently navigate back and forth through them.
Next steps
This has been a brief overview showing the Julia extension features within VS Code. For more information, see the details provided in the Julia extensionREADME.
To stay up to date on the latest features/bug fixes for the Julia extension, see theCHANGELOG.
If you have any issues or feature requests, feel free to log them in the Julia extensionGitHub repo.
If you'd like to learn more about VS Code, try these topics:
- Basic Editing - A quick introduction to the basics of the VS Code editor.
- Install an Extension - Learn about other extensions are available in theMarketplace.
- Code Navigation - Move quickly through your source code.