Manage Jupyter Kernels in VS Code
The Visual Studio Code notebooks' kernel picker helps you to pick specific kernels for your notebooks. You can open the kernel picker by clicking onSelect Kernel on the upper right-hand corner of your notebook or through the Command Palette with theNotebook: Select Notebook Kernel command.
Once you open the Kernel Picker, VS Code shows the most recently used (MRU) kernel(s):

Note: In the previous versions of VS Code (version <1.76), VS Code used to show all available kernels by default.
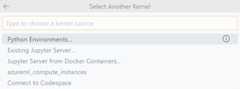
To see other kernels, you can clickSelect Another Kernel.... All existing kernels are categorized into kernel source options, with these sources supported by the Jupyter extension out of the box:

By default, VS Code will recommend the one you've previously used with your notebook, but you can choose to connect to any other Jupyter kernels as shown below. VS Code will also remember the last selected kernel for your notebooks, and will automatically select them the next time you open your notebook.
Jupyter Kernels
TheJupyter Kernels category lists all Jupyter kernels that VS Code detects in the context of the compute system it's operating in (your desktop,GitHub Codespaces, remote server, etc.). Each Jupyter kernel has a Jupyterkernel specification, or Jupyter kernelspec, which contains a JSON file (kernel.json) with details about the kernel—name, description, and CLI information required to launch a process as a kernel.
Python Environments
ThePython Environments category lists the Python environments that VS Code detects from the compute system it's operating in (your desktop, Codespaces, remote server, etc.). It shows all Python environments grouped by type (for example, conda, venv)—whether theIPyKernel is installed or not.
Note: Youdo not need to installjupyter into the Python environment you want to use. Only the IPyKernel package is required to launch a Python process as a kernel and execute code against your notebook (
pip install ipykernel). Visit theJupyter extension wiki to learn more.
Existing Jupyter Server
TheExisting Jupyter Server category lists remote Jupyter servers previously connected. You can also use this option to connect to an existing Jupyter server running remotely or locally. Find the URL for your Jupyter server, for example,http://<ip-address>:<port>/?token=<token> and paste it in theEnter the URL of the running Jupyter server option to connect to the remote server and execute code against your notebook using that server.

When you're starting your remote server, be sure to:
- Allow all origins (for example
--NotebookApp.allow_origin='*') to allow your servers to be accessed externally. - Set the notebook to listen on all IPs (
--NotebookApp.ip='0.0.0.0').
Once connected, all active Jupyter sessions will appear on this list.
You can create a new session from the server's kernelspec by:
- Running theNotebook: Select Notebook Kernel command.
- ChooseSelect Another Kernel.
- ChooseExisting Jupyter Server.
- Select your server.
Codespaces Jupyter Server
TheConnect to Codespace category contains a special type of Jupyter server where you can use remote Jupyter servers powered byGitHub Codespaces, a cloud resource that you getup to 60 hours free each month. To use the Codespaces Jupyter server:
Install theGitHub Codespaces extension.
Note: If you're on VS Code for the Web (vscode.dev orgithub.dev), this extension is already installed for you. Also ensure that theJupyter extension is also installed.
Go to the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)), selectCodespaces: Sign In and follow the steps to sign into Codespaces.
Open the kernel picker by clicking onSelect Kernel on the upper right-hand corner of your notebook, selectConnect to Codespace.
Tip: If you don't see theConnect to Codespace option, go to the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)), selectDeveloper: Reload Window to reload the window and try again.
It is not required, but you can also manage all your Codespaces and Codespaces Jupyter servers on theGitHub Codespaces page. To learn more, you can read theGitHub Codespaces documentation.
Adding Kernel Options
If you do not have any Jupyter kernel or Python environment on your machine, VS Code can help you set up: go to the Command Palette (⇧⌘P (Windows, LinuxCtrl+Shift+P)), selectPython: Create Environment, and follow the prompts. You can also add additional ways to select kernels, by installing additional extensions likeAzure Machine Learning.
Questions or feedback
You can add afeature request orreport a problem by creating an issue in our repository, which is actively being monitored and managed by our engineering team.