Create and query a database using the Google Cloud console
This quickstart shows you how to perform basic operations in Spanner by using theGoogle Cloud console. In the quickstart, you will:
- Create a Spanner instance.
- Create a database.
- Create a schema.
- Insert and modify data.
- Run a query.
For information on the cost of using Spanner, seePricing.
Note: To explore Spanner using a 90-day free trial instance,seeCreate a Spanner free trial instance.Before you begin
- Sign in to your Google Cloud account. If you're new to Google Cloud, create an account to evaluate how our products perform in real-world scenarios. New customers also get $300 in free credits to run, test, and deploy workloads.
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Note: If you don't plan to keep the resources that you create in this procedure, create a project instead of selecting an existing project. After you finish these steps, you can delete the project, removing all resources associated with the project.Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
In the Google Cloud console, on the project selector page, select or create a Google Cloud project.
Note: If you don't plan to keep the resources that you create in this procedure, create a project instead of selecting an existing project. After you finish these steps, you can delete the project, removing all resources associated with the project.Make sure that billing is enabled for your Google Cloud project.
- Optional: The Spanner API should be auto-enabled. If not, enable it manually:Enable Spanner API
To get the permissions that you need to create instances and databases, ask your administrator to grant you the Cloud Spanner Admin (roles/spanner.admin) IAM role on your project.
Create an instance
When you first use Spanner, you must create an instance, which is anallocation of resources that are used by Spanner databases in thatinstance.
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSpanner page.
Select or create a Google Cloud project if you haven't done so already.
On theSpanner page, clickCreate a provisioned instance.
If you've used Spanner before, you'll see theSpannerInstances page instead of the product page. ClickCreate instance.
In theName your instance page, enter an instance name, such asTest Instance.
The instance ID is automatically entered based on the instance name, for example, astest-instance. Change it, if required. ClickContinue.
In theConfigure your instance page, retain the default optionRegional and select a configuration from the drop-down menu.
Your instance configuration determines the geographic location where yourinstances are stored and replicated.
ClickContinue.
In theAllocate compute capacity page, selectProcessing units (PUs)and retain the default value of 1000 processing units.
ClickCreate.
The Google Cloud console displays theOverview page for the instanceyou created.
Create a database
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSpanner Instances page.
Click the instance you created, for exampleTest Instance.
In the instance Overview page that opens, clickCreate database.
For the database name, enter a name, such asexample-db.
Select a database dialect.
For information about support for PostgreSQL and for guidance for choosing a dialect, seePostgreSQL interface.If you selected GoogleSQL, you'll define the schema in theDefine your schema text field in the next section of this quickstart.
Your database creation page now looks like this:
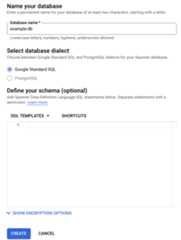
ClickCreate.
The Google Cloud console displays theOverview page for the databaseyou created.
Create a schema for your database
Note: Spanner Studio (formerly labeledQuery in the Google Cloud console)supports SQL, DML, and DDL operations in a single editor. For more information,seeManage your data using the Google Cloud console.In the navigation menu, clickSpanner Studio.
In theSpanner Studio page, clickNew tab or use the empty editor tab.
Enter:
GoogleSQL
CREATETABLESingers(SingerIdINT64NOTNULL,FirstNameSTRING(1024),LastNameSTRING(1024),SingerInfoBYTES(MAX),BirthDateDATE)PRIMARYKEY(SingerId);PostgreSQL
CREATETABLESingers(BirthDateTIMESTAMPTZ,SingerIdBIGINTPRIMARYKEY,FirstNameVARCHAR(1024),LastNameVARCHAR(1024),SingerInfoBYTEA);ClickRun.
The Google Cloud console returns to the databaseOverview page andshows thatSchema updates are underway. When the update is complete, thepage looks like this:
GoogleSQL

PostgreSQL

Notice that PostgreSQL converts the table name to lowercase.
Insert and modify data
The Google Cloud console provides an interface for inserting, editing, anddeleting data.
Insert data
In the list of tables on the databaseOverview page, click the Singers table.
The Google Cloud console displays the Singers table'sSchema page.
In the navigation menu, clickData to display the Singers table'sData page.
ClickInsert.
The Google Cloud console displays the Singers table's Spanner Studiopage with a new query tab that contains
INSERTandSELECTstatements thatyou edit to insert a row in the Singers table and view the result of thatinsertion:GoogleSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOSingers(SingerId,BirthDate,FirstName,LastName,SingerInfo)VALUES(<SingerId>,-- type: INT64<BirthDate>,-- type: DATE<FirstName>,-- type: STRING(1024)<LastName>,-- type: STRING(1024)<SingerInfo>-- type: BYTES(MAX));-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=<SingerId>;PostgreSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOsingers(singerid,birthdate,firstname,lastname,singerinfo)VALUES(<singerid>,-- type: bigint<birthdate>,-- type: timestamp with time zone<firstname>,-- type: character varying<lastname>,-- type: character varying<singerinfo>-- type: bytea);-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid=<singerid>;Notice that PostgreSQL converts the column names to all lower case.
Edit the
INSERTstatement'sVALUESclause and theSELECTstatement'sWHEREclause:GoogleSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOSingers(SingerId,BirthDate,FirstName,LastName,SingerInfo)VALUES(1,-- type: INT64NULL,-- type: DATE'Marc',-- type: STRING(1024)'Richards',-- type: STRING(1024)NULL-- type: BYTES(MAX));-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=1;PostgreSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOsingers(singerid,birthdate,firstname,lastname,singerinfo)VALUES(1,-- type: bigintNULL,-- type: timestamp with time zone'Marc',-- type: character varying'Richards',-- type: character varyingNULL-- type: bytea);-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid=1;ClickRun.
Spanner runs the statements. When finished, theResultstab indicates that the first statement inserted one row, and provides a linkto view the table's data.
In theResults tab, click thetable link. The Singers table now has one row:
GoogleSQL
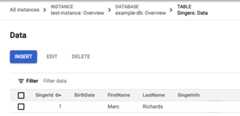
PostgreSQL
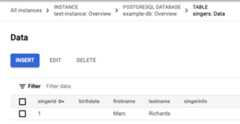
ClickInsert to add another row.
The Google Cloud console again displays the Singers table'sSpanner Studiopage with a new query tab that contains the same
INSERTandSELECTstatements.Edit the
INSERTstatement'sVALUESclause and theSELECTstatement'sWHEREclause:GoogleSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOSingers(SingerId,BirthDate,FirstName,LastName,SingerInfo)VALUES(2,-- type: INT64NULL,-- type: DATE'Catalina',-- type: STRING(1024)'Smith',-- type: STRING(1024)NULL-- type: BYTES(MAX));-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=2;PostgreSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOsingers(singerid,birthdate,firstname,lastname,singerinfo)VALUES(2,-- type: bigintNULL,-- type: timestamp with time zone'Catalina',-- type: character varying'Smith',-- type: character varyingNULL-- type: bytea);-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid=2;ClickRun.
After Spanner runs the statements, theResults tab againindicates that the first statement inserted one row.
Click thetable link. The Singers table now has two rows:
GoogleSQL
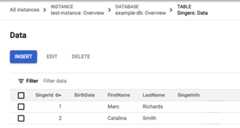
PostgreSQL
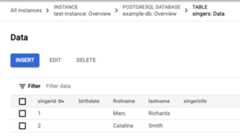
You can also insert empty string values when you enter data.
ClickInsert to add a row.
Spanner again displays the Singers table'sSpanner Studiopage with a new query tab that contains the same
INSERTandSELECTstatements.Edit the template
INSERTstatement'sVALUESclause andSELECTstatement'sWHEREclause:GoogleSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOSingers(SingerId,BirthDate,FirstName,LastName,SingerInfo)VALUES(3,-- type: INT64NULL,-- type: DATE'Kena',-- type: STRING(1024)'',-- type: STRING(1024)NULL-- type: BYTES(MAX));-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=3;PostgreSQL
-- Add new values in the VALUES clause in order of the column list.-- Each value must be type compatible with its associated column.INSERTINTOsingers(singerid,birthdate,firstname,lastname,singerinfo)VALUES(3,-- type: bigintNULL,-- type: timestamp with time zone'Kena',-- type: character varying'',-- type: character varyingNULL-- type: bytea);-- Change values in the WHERE condition to match the inserted row.SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid=3;Notice that the value provided for the last name column is an empty string,
'', not aNULLvalue.ClickRun.
After Spanner runs the statements, theResults tabindicates that the first statement inserted one row.
Click thetable link. The
Singerstable now has three rows, and the row with the primary key value of3has an empty string in theLastNamecolumn:GoogleSQL

PostgreSQL
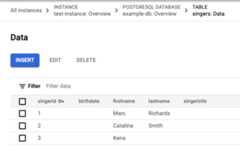
Edit data
On the Singers table'sData page, select the checkbox on the row with the primary key value of
3, and then clickEdit.The Spanner displays theSpanner Studio page with anew tab containing template
UPDATEandSETstatements that you can edit. Notethat theWHEREclauses of both statements indicate that the row to update isthe one with the primary key value of3.GoogleSQL
-- Change values in the SET clause to update the row where the WHERE condition is true.UPDATESingersSETBirthDate='',FirstName='Kena',LastName='',SingerInfo=''WHERESingerId=3;SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=3;PostgreSQL
-- Change values in the SET clause to update the row where the WHERE condition is true.UPDATEsingersSETbirthdate=NULL,firstname='Kena',lastname='',singerinfo=NULLWHEREsingerid='3';SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid='3';Edit the
UPDATEstatement'sSETclause to update only the birth date:GoogleSQL
-- Change values in the SET clause to update the row where the WHERE condition is true.UPDATESingersSETBirthDate='1961-04-01'WHERESingerId=3;SELECT*FROMSingersWHERESingerId=3;PostgreSQL
-- Change values in the SET clause to update the row where the WHERE condition is true.UPDATEsingersSETbirthdate='1961-04-01 00:00:00 -8:00'WHEREsingerid='3';SELECT*FROMsingersWHEREsingerid='3';ClickRun.
Spanner runs the statements. When finished, theResultstab indicates that the first statement updated one row, and provides a linkto view the table's data.
In theResults tab, click thetable link.
The updated row now has a value for the birth date.
GoogleSQL

PostgreSQL
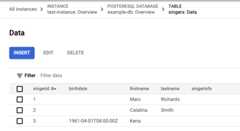
Delete data
- On the Singers table'sData page, select the checkbox on the row with
2in the first column, and then clickDelete. In the dialog that appears, clickConfirm.
The Singers table now has two rows:
GoogleSQL

PostgreSQL
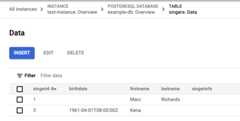
Run a query
On the databaseOverview page, clickSpanner Studio in thenavigation menu.
ClickNew tab to create a new query tab. Then, enter the following queryin the query editor:
GoogleSQL
SELECT*FROMSingers;PostgreSQL
SELECT*FROMsingers;ClickRun.
Spanner runs the query. When finished, theResultstab displays the result of your query:
GoogleSQL

PostgreSQL

Congratulations! You've successfully created a Spanner databaseand executed a SQL statement by using the query editor!
Clean up
To avoid additional charges to your Cloud Billing account, delete the databaseand the instance that you created. Deleting an instance automatically deletesall databases created in the instance.
Delete the database
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSpanner Instances page.
Click the name of the instance that has the database that you want to delete, for example,Test Instance.
Click the name of the database that you want to delete, for example,example-db.
In theDatabase details page, clickdeleteDelete database.
Confirm that you want to delete the database by entering the database name and clickingDelete.
Delete the instance
In the Google Cloud console, go to theSpanner Instances page.
Click the name of the instance that you want to delete, for example,Test Instance.
ClickdeleteDelete instance.
Confirm that you want to delete the instance by entering the instance name and clickingDelete.
What's next
- Learn aboutInstances.
- Understand the SpannerSchema and Data Model.
- Learn more aboutGoogleSQL Data Definition Language (DDL).
- Learn more aboutQuery Execution Plans.
- Learn how to use Spanner withC++,C#,Go,Java,Node.js,PHP,Python,Ruby,REST, orgcloud.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-07-11 UTC.