Cloud Logging for Winston: Node.js Client
This module provides a higher-level layer for working withCloud Logging, compatible withWinston. Simply attach this as atransport to your existing Winston loggers.
A comprehensive list of changes in each version may be found inthe CHANGELOG.
- Cloud Logging for Winston Node.js Client API Reference
- Cloud Logging for Winston Documentation
- github.com/googleapis/nodejs-logging-winston
Read more about the client libraries for Cloud APIs, including the olderGoogle APIs Client Libraries, inClient Libraries Explained.
Table of contents:
Quickstart
Before you begin
- Select or create a Cloud Platform project.
- Enable the Cloud Logging for Winston API.
- Set up authentication with a service account so you can access theAPI from your local workstation.
Installing the client library
npm install @google-cloud/logging-winstonUsing the client library
const winston = require('winston');// Imports the Google Cloud client library for Winstonconst {LoggingWinston} = require('@google-cloud/logging-winston');const loggingWinston = newLoggingWinston();// Create a Winston logger that streams to Cloud Logging// Logs will be written to: "projects/YOUR_PROJECT_ID/logs/winston_log"const logger = winston.createLogger({ level: 'info', transports: [ new winston.transports.Console(), // Add Cloud Logging loggingWinston, ],});// Writes some log entrieslogger.error('warp nacelles offline');logger.info('shields at 99%');For a more detailed Cloud Logging setup guide, seehttps://cloud.google.com/logging/docs/setup/nodejs.
Creates a Winston logger that streams to Cloud Logging
Logs will be written to: "projects/YOUR_PROJECT_ID/logs/winston_log"
Using as an express middleware
NOTE: this feature is experimental. The API may change in a backwardsincompatible way until this is deemed stable. Please provide us feedback sothat we can better refine this express integration.
We provide a middleware that can be used in an express application. Apart frombeing easy to use, this enables some more powerful features of CloudLogging: request bundling. Any application logs emitted on behalf of a specificrequest will be shown nested inside the request log as you see in thisscreenshot:

This middleware adds awinston-style log function to therequest object.You can use this wherever you have access to therequest object (req in thesample below). All log entries that are made on behalf of a specific request areshown bundled together in the Cloud Logging UI.
const lw = require('@google-cloud/logging-winston');const winston = require('winston');// Import express module and create an http server.const express = require('express');const logger = winston.createLogger();async function main() { // Create a middleware that will use the provided logger. // A Cloud Logging transport will be created automatically // and added onto the provided logger. const mw = await lw.express.makeMiddleware(logger); // Alternatively, you can construct a LoggingWinston transport // yourself and pass it int. // const transport = new LoggingWinston({...}); // const mw = await lw.express.makeMiddleware(logger, transport); const app = express(); // Install the logging middleware. This ensures that a Winston-style `log` // function is available on the `request` object. Attach this as one of the // earliest middleware to make sure that the log function is available in all // subsequent middleware and routes. app.use(mw); // Setup an http route and a route handler. app.get('/', (req, res) => { // `req.log` can be used as a winston stylelog method. Alllogs generated // using `req.log` use the current request context. That is, alllogs // corresponding to a specific request will be bundled in the Cloud Logging // UI. req.log.info('this is an info log message'); res.send('hello world'); }); // `logger` can be used as a global logger, one not correlated to any specific // request. logger.info('bonjour'); // Start listening on the http server. app.listen(8080, () => { logger.info('http server listening on port 8080'); });}main();Error Reporting
AnyError objects you log at severityerror or higher can automatically be picked up byError Reporting if you have specified aserviceContext.service when instantiating aLoggingWinston instance:
const loggingWinston = new LoggingWinston({serviceContext: { service: 'my-service', // required to report logged errors // to the Error Reporting // console version: 'my-version'}});It is an error to specify aserviceContext but not specifyserviceContext.service.
Make sure to add logs to your [uncaught exception][uncaught] and [unhandled rejection][unhandled] handlers if you want to see those errors too.
You may also want to see the@google-cloud/error-reporting module which provides direct access to the Error Reporting API.
Error handling with a default callback
TheLoggingWinston class creates an instance ofLoggingCommon which by default uses theLog class from@google-cloud/logging package to write log entries. TheLog class writes logs asynchronously and there are cases when log entries cannot be written and an error is thrown - if error is not handled properly, it could crash the application. One possible way to handle the error is to provide a default callbackto theLoggingWinston constructor which will be used to initializeLog object with that callback like in example below:
// Imports the Google Cloud client library for Winstonconst {LoggingWinston} = require('@google-cloud/logging-winston');// Creates a clientconst loggingWinston = newLoggingWinston({projectId: 'your-project-id',keyFilename: '/path/to/key.json',defaultCallback: err => { if (err) { console.log('Error occured: ' + err); }},});Formatting Request Logs
NOTE: The express middleware provided by this library handles this automatically for you. These instructions are for there case where you may want to handle this manually.
To format your request logs you can provide ahttpRequest property as part of the log metadata you provide to winston. We will treat this as theHttpRequest message and Cloud Logging will show this as a request log. Example:

winston.info(`${req.url} endpoint hit`, {httpRequest: { status: res.statusCode, requestUrl: req.url, requestMethod: req.method, remoteIp: req.connection.remoteAddress, // etc.}});ThehttpRequest property must be a properly formattedHttpRequest message.
**NOTE: Due to a bug inlogform some built in Winston formatters might not work properly withLoggingWinston. For more information about the problem and possible workaround please see540. In addition,Cloud Logging for Bunyan could be considered as alternative.
Correlating Logs with Traces
NOTE: The express middleware provided by this library handles this automatically for you. These instructions are for there case where you may want to handle this manually.
If you use [@google-cloud/trace-agent][trace-agent] module, then this module will set the Cloud Logging [LogEntry][LogEntry]trace property based on the current trace context when available. That correlation allows you to [view log entries][trace-viewing-log-entries] inline with trace spans in the Cloud Trace Viewer. Example:

If you wish to set the LogEntrytrace,spanId, andtraceSampled properties with custom values, then set Winston metadata properties for'logging.googleapis.com/trace','logging.googleapis.com/spanId','logging.googleapis.com/trace_sampled', which is exported by this module asLOGGING_TRACE_KEY,LOGGING_SPAN_KEY, andLOGGING_SAMPLED_KEY respectively. For example:
const winston = require('winston');const {LoggingWinston} = require('@google-cloud/logging-winston');// ...winston.info('Log entry with custom trace value', {[LoggingWinston.LOGGING_TRACE_KEY]: 'custom-trace-value'[LoggingWinston.LOGGING_SPAN_KEY]: 'custom-span-value'[LoggingWinston.LOGGING_SAMPLED_KEY]: true});Specifying default labels in the constructor
You can specifylabels when initiating the logger constructor.
// Creates a Winston Cloud Logging clientconst loggingWinston = new LoggingWinston({labels: { name: 'some-name', version: '0.1.0'}});// Writes some log entrieslogger.debug('test msg');// you can also put some `labels` when calling the logger function// the `labels` will be merge togetherlogger.debug('test msg', {labels: { module: 'some-module'}});Thelabels will be on the Log Viewer.

Add a prefix to easily identify logs
You can specify aprefix in the constructor, and thatprefix will be prepended to all logging messages. This can be helpful, for example, to quickly identify logs from different modules in a project.
// Creates a Winston Cloud Logging clientconst loggingWinston = new LoggingWinston({prefix: 'some-module'});logger.debug('test msg');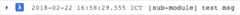
Alternative way to ingest logs in Google Cloud managed environments
If you use this library with the Cloud Logging Agent, you can configure the handler to output logs toprocess.stdout usingthestructured logging Json format.To do this, addredirectToStdout: true parameter to theLoggingWinston constructor as in sample below.You can use this parameter when running applications in Google Cloud managed environments such as AppEngine, Cloud Run,Cloud Function or GKE. The logger agent installed on these environments can captureprocess.stdout and ingest it into Cloud Logging.The agent can parse structured logs printed toprocess.stdout and capture additional log metadata beside the log payload.It is recommended to setredirectToStdout: true in serverless environments like Cloud Functions since it could decrease logging record loss upon execution termination - since all logs are written toprocess.stdout thosewould be picked up by the Cloud Logging Agent running in Google Cloud managed environment.Note that there is also auseMessageField option which controls if "message" field is used to store structured, non-text data insidejsonPayload field whenredirectToStdout is set. By defaultuseMessageField is alwaystrue.
// Imports the Google Cloud client library for Winstonconst {LoggingWinston} = require('@google-cloud/logging-winston');// Creates a client that writes logs to stdoutconst loggingWinston = newLoggingWinston({ projectId: 'your-project-id', keyFilename: '/path/to/key.json', redirectToStdout: true,});Waiting for logs to be written
Starting from v3.0, theWinston library no longer supportscallbacks in their logging API, which reduces the ability to wait for logs to be written before exit/shutdown. The issue tracking the ask to reestablish callback support in Winston is tracked by2095.One possible solution is to adopt anAlternative way to ingest logs in Google Cloud managed environments.Another possible way is to use asetTimeout with a desired interval in order to let the library to send as many logs as possible.
Samples
Samples are in thesamples/ directory. Each sample'sREADME.md has instructions for running its sample.
| Sample | Source Code | Try it |
|---|---|---|
| Quickstart | source code |  |
| Explicit Auth Setup | source code |  |
TheCloud Logging for Winston Node.js Client API Reference documentationalso contains samples.
Supported Node.js Versions
Our client libraries follow theNode.js release schedule.Libraries are compatible with all currentactive andmaintenance versions ofNode.js.If you are using an end-of-life version of Node.js, we recommend that you updateas soon as possible to an actively supported LTS version.
Google's client libraries support legacy versions of Node.js runtimes on abest-efforts basis with the following warnings:
- Legacy versions are not tested in continuous integration.
- Some security patches and features cannot be backported.
- Dependencies cannot be kept up-to-date.
Client libraries targeting some end-of-life versions of Node.js are available, andcan be installed through npmdist-tags.The dist-tags follow the naming conventionlegacy-(version).For example,npm install @google-cloud/logging-winston@legacy-8 installs client librariesfor versions compatible with Node.js 8.
Versioning
This library followsSemantic Versioning.
This library is considered to bestable. The code surface will not change in backwards-incompatible waysunless absolutely necessary (e.g. because of critical security issues) or withan extensive deprecation period. Issues and requests againststable librariesare addressed with the highest priority.
More Information:Google Cloud Platform Launch Stages
Contributing
Contributions welcome! See theContributing Guide.
Please note that thisREADME.md, thesamples/README.md,and a variety of configuration files in this repository (including.nycrc andtsconfig.json)are generated from a central template. To edit one of these files, make an editto its templates indirectory.
License
Apache Version 2.0
SeeLICENSE
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2025-10-30 UTC.
