Deployment Options for Redis on Google Cloud
This document provides an overview ofRedis deploymentsand migrations to Google Cloud, including the options and tradeoffs fordeploying Redis on different services, based on your requirements.
Redis is an in-memory data structure store that you can use as a database,cache, message broker, and more. Google Cloud fully supports Redis,including the following:
Fully managed options provided by Memorystore and Redis Ltd.
Self managed options using the following products:
The best way to deploy Redis on Google Cloud depends on your specificneeds and requirements. The recommendations provided in this guide are based ongeneral best practices and considerations. It's important to thoroughly analyzeyour Redis workload and consult official documentation or seek professionaladvice for specific use cases or requirements.
Architectures
You can deploy Redis using one of the following architectures:
| Architecture | Description | Use case | Deployment options | High availability | Read throughput | Write throughput |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard (standalone) | A single Redis node, with no read replicas and no high availability. | Cases where all data fits on one node, write and read throughput can be served by one node, and high availability is not required. | Supported on Memorystore (fully managed) and Redis open source software (OSS) (self-managed). Self-managing requires a more complex setup. Memorystore is a good option to get started quickly. | No | Single node | Single node |
| HA and/or read replicas | A single Redis node for write operations, with additional nodes to provide high availability and optionally share the read load, for example, using Sentinel. | Cases where write throughput can still be served by one node, but either read throughput cannot be served by one node, or high availability is required. | Supported on Memorystore (fully managed) and Redis OSS (self managed). Redis Cluster architectures offer automated scaling, high availability, and data sharding, which are ideal for large-scale, distributed applications. To understand the tradeoffs and required maintenance efforts in manual scaling, clustering and sharding, review Zero-downtime scaling in Memorystore for Redis Cluster. Self-managing requires a more complex setup. Memorystore is a good option to get started quickly. | Multi-AZ | Multi node | Single node |
| Cluster (without proxies) | Several nodes split the data write operations with separate data shards. High availability and read replicas can be optionally added. | Cases where write throughput cannot be served by one node, and high availability or read replication is optionally required. | Multi-AZ | Multi node | Multi node | |
| Cluster (with proxies) | Several nodes split the data write operations with separate data shards. High availability and read replicas can be optionally added. Proxies are deployed on each primary node. | Cases where write throughput cannot be served by one node, and high availability or read replication is optionally required, and where it is too costly or inconvenient for client applications to be refactored to use the Redis Cluster API, or the use of proxies has other benefits. | Supported by Redis Enterprise Cloud (fully managed) or Redis Enterprise Software (self-managed). Self-managing with Redis OSS requires a more complex setup. Redis Enterprise Cloud is a good option to get started quickly. | Multi-AZ or multi-region (Redis Enterprise only) | Multi node | Single node |
Deployment options
Google Cloud offers the following Redis deployment options:
- Fully-managed Memorystore for Redis by Google Cloud: A fullymanaged, highly available, and durable Redis service managed by Google that iscost effective and fast to set up, operate, and scale. Memorystoresupports bothRedis Clusterandstandalone Rediswith optional high availability.
- Self or fully-managed Redis Enterprise by Redis Ltd.: A highly availableand durable Redis cluster licensed by Redis Ltd. and with two managementoptions: managed by Redis Ltd. ("Redis Enterprise Cloud"), or self-managed("Redis Enterprise Software") with Redis Ltd.'s support. You can procure RedisEnterprise directly fromRedis Ltd., or throughGoogle Cloud Marketplace.Redis Ltd. supports deployments on Compute Engine , Google Kubernetes Engine andOpenShift.
- Self-managed Redis Open source software (OSS): A self-managed Rediscluster or standalone Redis with optional high availability, deployable onCompute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, or OpenShift.
Choose a Redis deployment option
This section describes how to choose a Redis deployment option that is bestsuited for your workload. Figure 1 provides a visual overview of the decisionpoints:
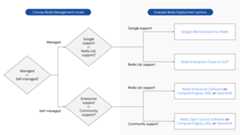
Choose a Redis management model
You can choose between one of the following management models:
Fully managed deployment. You offload deployment and management operationsto the service provider. Choose this model when you need to focus on buildingyour app and offload management tasks.
Self managed deployment. You are responsible for deployment and managementoperations. Choose this model if any of the following are true:
You have an existing operational economy of scale, and taking on managing andoperating Redis makes economic sense in your organization.
You have a strategic preference for IaaS-only dependency.
You require advanced optimizations.
Evaluate deployment options
After you choose your management model, evaluate the deployment options thatare available to you.
Fully Managed Options
For fully managed deployments, you can use Memorystore or Redis EnterpriseCloud.
Memorystore
Choose Memorystore if any of the following are true:
- You have a preference for consolidating support of managed software withGoogle Cloud.
- You have a preference for optimizing for integration with Google Cloudconstructs such as Identity and Access Management, APIs, org policies, quota, or Cloud Asset Inventory.
- You require specific features only available in Memorystore(e.g, scale back in).
For more information about Memorystore, see theMemorystore product documentation.
Deployment options
- Memorystore for Redis (Standalone, HA)
- Memorystore for Redis Cluster (Cluster, HA)
Redis Enterprise Cloud
Choose Redis Enterprise Cloud if any of the following are true:
- You require specific features only available in Redis Enterprise Cloud(for example, cross-region active-active multi-primary writes with its99.999% SLA, RedisSearch use case).
- You require cluster scaling for an application that does not support theRedis Cluster API.
For more information about Redis Enterprise Cloud, see theRedis Cloud documentation.
Procurement and billing options
Self managed options
For self-managed deployments, you can choose between Redis Enterprise and RedisOpen Source Software.
Redis Enterprise
Choose self-managed Redis Enterprise if any of the following are true:
- Your application requires its unique features, such as automatic re-shardingfor scaling out, Redis on flash, or Redis Enterprise Operator for Kubernetes.
- Your operations team does not have the required skill set to handle complexRedis issues internally without qualified third party support.
- You prefer the enterprise support provided by Redis Ltd., and the associatedlicensing costs are manageable by your organization.
For more information about Redis Enterprise Software, see theRedis Enterprise Software documentation.
Deployment options
- Self-managed Redis Enterprise Software on GKEor OpenShift, with optional use of the Redis Enterprise Operator for Kubernetes
- Self-managed Redis Enterprise Software on Compute Engine
Procurement and billing options
- License andsupport billed by Redis Inc., while the infrastructure is billed by Google.
- License and support is procured throughGoogle Cloud Marketplace, while the infrastructure is billed by Google.
Redis Open Source Software
Choose self-managed Redis Open Source Software if any of the following are true:
- You require or have a preference for full customization not otherwise possible.
- Your operations team has the required skill set to handle complex Redis issuesinternally without qualified third party support.
- You want to avoid licensing costs.
- You have extensive in house Redis and Linux kernel tuning resources, or youruse case does not require tuning.
When deploying self-managed Redis Open Source Software, choose a deploymenttarget based on your platform strategy choice. Redis Open Source Software isdeployable on Compute Engine, Google Kubernetes Engine, or OpenShift. GKEAutopilot can reduce deployment and management efforts, but may be morelimited in ways such as being harder to scale in.
For more information about Redis Open Source Software, seeRedis.io.
Additional resources
Feature comparison
The following table summarizes the key differences between all deploymentoptions:
| Deployment characteristics | Deployment options | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Memorystore for Redis andRedis Cluster | Redis Enterprise Cloud | Redis Enterprise software | Redis open source software | |
| Managed by | Fully managed by Google | Fully managed by Redis Ltd. | Self managed | Self managed |
| Supported by | Redis Ltd. | Redis Ltd. | Self supported | |
| Billed by | Redis Ltd. or Google | Infrastructure is billed by Google. Redis Ltd. license and support is billed by Redis Ltd. or Google. | ||
| Cost elements | All costs included. Includes: infrastructure, licensing, support, and management costs. For more information, seeMemorystore pricing. | All costs included. Includes: infrastructure, licensing, support, and management costs. For more information, seeRedis Enterprise Cloud Pricing. | Software license and support costs are included. Infrastructure usage is billed separately by Google Cloud. Management costs, including deployment, tuning, personnel and downtime are absorbed by the customer. For more information, seeRedis Enterprise Software Pricing. | No service or licensing fees. Infrastructure usage billed by Google Cloud. Management costs, including deployment, tuning, personnel and downtime are absorbed by the customer. |
| SLA |
For more information, see theMemorystore Service Level Agreement. |
For more information, see theRedis Cloud Service Level Agreement. | Not applicable. You are responsible for uptime. | Not applicable. You are responsible for uptime. |
| Free tier | No | Yes | 30 day free trial | Not applicable |
| Data tiering | No | Auto tiering | Auto tiering | No |
| Multi cloud | No | Yes | Manually | Possible, but involves high effort |
| Multiregion active-active | No | Yes | Manually | Possible, but involves high effort |
| Modules |
|
| ||
| Compliance | Built-in support for the different compliance regimes. See Compliance offerings for more information. | Built-in support for the different compliance regimes. SeeRedis Trust Center for more information. | Built-in support for the different compliance regimes. SeeRedis Trust Center for more information. | Manual compliance management is required. See Compliance offerings for more information. |
| Scaling cluster writes | Scales in and out | Scales in and out | Scales out. Scaling in requires manual effort. | Self managed, requires manual effort. |
| Auto rebalancing | Yes | Yes | Self managed, requires manual effort | Self managed, requires manual effort |
| Adding high availability | Seamless, no redeployment required | Seamless, no redeployment required | No redeployment is required, but requires manual effort | Requires substantial manual effort - redeployment may be required depending on your original architecture |
| Adding read replicas | Seamless, no redeployment required | Seamless, no redeployment required | Requires substantial manual effort - redeployment may be required depending on your original architecture | Self managed, requires manual effort |
| Moving to a data-sharded Redis Cluster when outgrowing write throughput | Requires redeployment, but tooling is provided to ease effort. Clients need to be refactored to support the Redis Cluster API. | Seamless, no redeployment required | Seamless, no redeployment required | Self managed, requires manual effort |
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under theCreative Commons Attribution 4.0 License, and code samples are licensed under theApache 2.0 License. For details, see theGoogle Developers Site Policies. Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2026-02-19 UTC.
